Summary
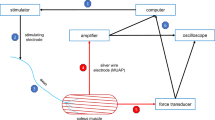
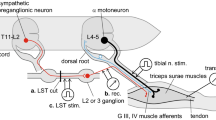
The time course of the active state curve has been studied in the tibialis anterior, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscles of the cat. The technique employed was the method of quick release described by Hill (1953), Ritchie (1954), and Ritchie and Wilkie (1955).
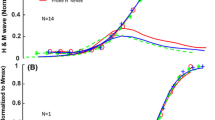
The rate of relaxation of the contractile elements was higher in the fast-contracting tibialis anterior and gastrocnemius muscles than in the slow-contracting soleus muscle. The active state of the tibialis anterior, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscle ended at about 90 msec, 100 msec, and 210 msec respectively after a single stimulus. The duration of the active state was prolonged by a stretch applied to the muscles prior to stimulation.
Adrenaline reduced the rate of relaxation of the contractile elements in the tibialis anterior muscle and increased that of the soleus muscle. This effect was diminished by stretch of the muscles. Isoprenaline exerted a similar effect on the duration of the active state as did adrenaline, whereas noradrenaline proved to be much less potent in influencing the rate of relaxation.
It is therefore concluded that the difference in fusion frequency of fast- and slow-contracting muscles of the cat is due to a different time course of relaxation of the contractile elements. The changes in tension development in the soleus and tibialis anterior muscles following administration of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and isoprenaline result from a reduced (soleus) or an increased (tibialis anterior) duration of the active state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bleckmann, I., I. Jurna u. W. Rummel: Vergleichende Untersuchungen von Methoden zur Bestimmung der Plateaudauer des aktiven Zustandes an Warmblütermuskeln. Verhalten des Soleus und Tibialis anterior der Katze unter Sympathicomimetica und Coffein. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. (im Druck).
Bowman, W. C., and E. Zaimis: A comparison between the responses of the tibialis anterior and the soleus muscle in the cat to adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 128, 14–15 p (1955).
— The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on skeletal muscle contractions in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 144, 92–107 (1958).
Hill, A. V.: The mechanics of active muscle. Proc. roy. Soc. B 141, 104–117 (1953).
Jurna, I., u. W. Rummel: Die Wirkung von Adrenalin und Noradrenalin auf die Spannungsentwicklung von Soleus und Tibialis anterior der Katze. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 275, 137–151 (1962).
Ritchie, J. M.: The effect of nitrate on the active state of muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 126, 155–168 (1954).
— and D. R. Wilkie: The effect of previous stimulation on the active state of muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 130, 488–496 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 5 Textabbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jurna, I., Rummel, W. & Schäfer, H. Die abfallende Phase des aktiven Zustandes des Tibialis anterior, Gastrocnemius und Soleus der Katze und ihre Beeinflussung durch Dehnung und Sympathicomimetica. Pflügers Archiv 277, 513–522 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363175
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363175