Abstract
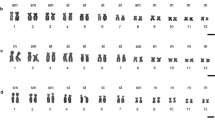
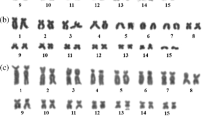
Late replication banding and C-banding analyses were performed on the metaphase chromosomes of six species and one subspecies of Palearctic water frogs, genus Rana. Although C-banding patterns showed interspecific or intersubspecific variation, late replication banding patterns of all 13 chromosome pairs of these species were homologous. Minor differences of banding patterns were observed only in chromosomes 2, 7 and 13. Close comparison of the late replication banding patterns with those of three non-water frog species of Rana, and one each of Hyla and Bufo, provided important information on interspecific and intergeneric variability. In the Rana species, the banding patterns of all 13 pairs were homologous except for those some regions of 8 pairs. In one species each of Hyla and Bufo that was examined, the six large chromosome pairs (Nos. 1-6) showed banding homologies. Furthermore, among the Rana, Hyla and Bufo species the four large chromosome pairs (Nos. 1-3, 5 of Rana and Hyla, and Nos. 1, 3–5 of Bufo) shared banding homologies. These results show that the large chromosomes have been highly conserved in the evolutionary history of the three genera.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger L (1967) Embryonal and larval development of F1 generation of green frogs different combination. Acta Zool Cracov 12:123–160
Berger L (1968) Morphology of the F1 generation of various crosses within Rana esculenta-complex. Acta Zool Cravov 13:301–324
Bogart JP (1973) Evolution of anuran karyotypes. In: Vial JL (ed) Evolutionary biology of the anurans. Contemporary research on major problems. Univ Missouri Press, Columbia, Missouri, pp 337–349
Bogart JP (1991) The influence of life history on karyotypic evolution in frogs. In: Green DM, Sessions SK (ed) Amphibian cytogenetics and evolution. Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 233–258
Dubois A (1983) Classification et nomenclature supragénérique des amphibiens anoures. Bull Men Soc Linnéenne Lyon 52:270–276
Dubois A (1992) Notes sur la classification des Ranidae (Amphibiens Anoures). Bull Mens Soc Linn Lyon 61:305–352
Duellman WE (1975) On the classification of frogs. Occasional Papers Mus Nat Hist Univ Kansas 42:1–14
Duellman WE (1993) Amphibian species of the world: additions and corrections. Univ Kansas Mus Nat Hist Special Publication 21:1–372
Heppich S (1978) Hybridogenesis in Rana esculenta: C-band karyotypes of Rana ridibunda, Rana lessonae and Rana esculenta. Z Zool Syst Evol Forsch 16:27–39
Heppich S, Tunner HG, Greilhuber J (1982) Premeiotic chromosome doubling after genome elimination during spermatogenesis of the species hybrid Rana esculenta. Theor Appl Genet 61:101–104
Kawamura T, Nishioka M (1979) Isolating mechanisms among the water frog species distributed in the Palearctic region. Mitt Zool Mus Berlin 55:171–185
Koref-Santibañez S (1979) The karyotypes of Rana lessonae Camerano, Rana ridibunda Pallas and of the hybrid form Rana “esculenta” Linné (Anura). Mitt Zool Mus Berlin 55:115–124
Kuramoto M (1990) A list of chromosome numbers of anuran amphibians. Bull Fukuoka Univ Educ PartIII 39:83–127
Kuro-o M, Ikebe C, Kohno S (1987) Cytogenetic studies of Hynobiidae (Urodela) VI. R-banding patterns in five pond-type Hynobius from Korea and Japan. Cytogenet Cell Genet 44:69–75
Laurent RF (1979) Esquisse d'une phylogénèse des anoures. Bull Soc Zool France 104:397–422
Miura I, Nishioka M, Borkin LJ, Wu Z (1995) The origin of the brown frogs with 2n=24 chromosomes. Experientia, in press
Morescalchi A (1968) Hypotheses on the phylogeny of the Salientia, based on karyological data. Experientia 24:964–966
Morescalchi A (1973) Amphibia. In: Chiarelli AB, Capanna E (eds) Cytotaxanomy and vertebrate evolution. Academic Press, London and New York, pp 233–348
Moriya K (1960) Studies on the five races of the Japanese pond frog, Rana nigromaculata Hallowell III. Sterility in interracial hybrids. J Sci Hiroshima Univ SerB Div 1 18:125–156
Nishioka M, Sumida M (1992) Biochemical differentiation of pond frogs distributed in the Palearctic region. Sci Rep Lab Amphibian Biol Hiroshima Univ 11:71–108
Nishioka M, Okumoto H, Ryuzaki M (1987) A comparative study on the karyotypes of pond frogs distributed in Japan, Korea, Taiwan, Europe and North America. Sci Rep Lab Amphibian Biol Hiroshima Univ 9:135–163
Nishioka M, Miura I, Saitoh K (1993) Sex chromosomes of Rana rugosa with special reference to local differences in sex-determining mechanism. Sci Rep Lab Amphibian Biol Hiroshima Univ 12:55–81
Schempp W, Schmid M (1981) Chromosome banding in Amphibia VI. BrdU-replication patterns in Anura and demonstration of XX/XY sex chromosomes in Rana esculenta. Chromosoma 83:697–710
Schmid M, Klett R (1994) Chromosome banding in Amphibia XX. DNA replication patterns in Gastrotheca riobambae (Anura, Hylidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 65:122–126
Schmid M, Steinlein C (1991) Chromosome banding in Amphibia XVI. High-resolution replication banding patterns in Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma 101:123–132
Schmid M, Vitelli L, Batistoni R (1987) Chromosome banding in Amphibia XI. Constitutive heterochromatin, nucleolus organizers, 18S+28S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in Ascaphidae, Pipidae, Discoglossidae and Pelobatidae. Chromosoma 95:271–284
Seto T (1965) Cytogenetic studies in lower vertebrates. II. Karyological studies of several species of frogs (Ranidae). Cytologia 30:437–446
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306
Takayama S, Taniguchi T, Iwashita Y (1981) Application of the 4Na-EDTA Giemsa staining method for analysis of DNA replication patern. CIS 31:36–38
Tunner HG (1973) Das Albumin und andere bluteiweisse bei Rana ridibunda Pallas, Rana lessonae Camerano, Rana esculenta Linné und deren Hybriden. Z Zool Syst Evol Forsch 11:219–233
Tunner HG (1974) Die klonale Struktur einer Wasserfroschpopulation. Z Zool Syst Evol Forsch 12:309–314
Uzzell T (1979) Immunological distances between the serum albumins of Rana ridibunda and Rana lessonae. Proc Acad Nat Sci Philadelphia 130:1–10
Uzzell T (1982) Immunological relationships of western Palearctic water frogs (Salientia: Ranidae). Amphibia-Reptilia 3:135–143
Uzzell T, Berger L (1975) Electrophoretic phenotypes of Rana ridibunda, Rana lessonae, and their hybridogenetic associate, Rana esculenta. Proc Acad Nat Sci Philadelphia 127:13–24
Yang S-Y, Yu C-H, Park B-S (1988) Natural hybridization and reproductive isolating mechanisms between two species of Rana nigromaculata and Rana plancyi (Anura). Korean J Zool 31:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, I. The late replication banding patterns of chromosomes are highly conserved in the genera Rana, Hyla, and Bufo (Amphibia: Anura). Chromosoma 103, 567–574 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355322
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355322