Abstract
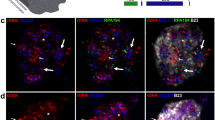
Monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) were raised against isolated Chinese hamster protein-depleted chromosomes Chromosome scaffolds) in order to probe for components involved in the higher-order structure of mammalian chromosomes. One of the Mabs detected a ring-like structure in metaphase at the centromere, which is conserved between Chinese hamster and human cells. Additionally, the Mab stained the centrioles in interphase cells in these two species. The antigen was enriched in chromosomal protein preparations by comparison with nuclear protein samples, and has an apparent Mr=170,000. The centromere antigen remained present in chromosome scaffold preparations, indicating that it was tightly associated with DNA. The antigen was distinct in its centromeric localisation from any of the centromere antigens reported to date. A possible role of the antigen in stabilising the centromere, by holding the sister chromatids together until their separation at the metaphase-anaphase transition is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph KW, Cheng SM, Paulson JR, Laemmli UK (1977) Isolation of a protein scaffold from mitotic HeLa cell chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:4937–4941
Bischoff FR, Maier G, Tilz G, Ponsting H (1990) A 47-kDa human nuclear protein recognised by antikinetochore autoimmune sera is homologous with the protein encoded by RCC1, a gene implicated in onset of chromosome condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8617–8621
Brenner S, Pepper D, Berns MW, Tan E, Brinkley BR (1981) Kinetochore structure, duplication, and distribution in mammalian cells: analysis by human autoantibodies from scleroderma patients. J Cell Biol 91:95–102
Cooke CA, Heck NMS, Earnshaw WC (1987) The inner centromere protein (INCENP) antigens: movement from inner centromere to midbody during mitosis. J Cell biol 105:2053–2067
Cooke CA, Bernat RL, Earnshaw WC (1990) CENP-B a major human centromere protein located beneath the kinetochore. J Cell Biol 110:1475–1488
Cox JV, Schenk EA, Olmsted JB (1983) Human anti-centromere antibodies: distribution, characterisation of antigens, and effect on microtubule organisation. Cell 35:331–339
Earnshaw WC, Rothfield NF (1985) Identification of a family of human centromere proteins using autoimmune sera from patients with scleroderma. Chromosoma 91:313–321
Earnshaw WC, Halligan N, Cooke C, Rothfield N (1984) The kinhetochore is part of the metaphase chromosome scaffold. J Cell Biol 98:352–357
Earnshaw WC, Sullivan KF, Machlin PS, Cooke CA, Kaiser DA, Pollard TD, Rothfield NF, Cleveland DW (1987) Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol 104:817–829
Fritzler MJ, Kinsella TD, Garbutt E (1980) The CREST syndrome: a distinct serological entity with anticentromere antibodies. Am J Med 69:520–523
Hadlaczky Gy, Sumner AT, ross A (1981) Protein depeted chromosomes. Chromosoma 81:537–555
Hadlaczky Gy, Praznovszky T, bisztray G (1982) Structure of isolated protein-depeleted chromosomes of plants. Chromosoma 86:643–659
Hadlaczky Gy, Went M, Ringertz NR (1986) Direct evidence for non-random localisation of mammalian chromosomes in the interphase nucleus. Exp Cell Res 167:1–15
Hadlaczky Gy, Praznovszky T, Sofi J, Udvardy A (1988) Intracellular forms of Drosophila topoisomerase II detected with monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10013–10023
Hadlaczky Gy, Praznovszky T, Rasko I, Kereso J (1989) Centromere proteins: I. Mitosis specific centromere antigen recognised by anti-centromere autoantibodies. Chromosoma 97:282–288
Hadlaczky Gy, Praznovszky T, Cserpan I, Kereso J, Peterfy M, Atalay E, Szeles A, Szelei J, Tubak V, Burg K (1991) Centromere formation in mouse cells cotransformed with human DNA and a dominant marker gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8106–8110
Köhler G, Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256:495–499
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laemmli UK, Cheng SM, Adolph KW, Paulson JR, Brown JA, Baumbach WR (1978) Metaphase chromosome structure: the role of non-histone proteins. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 42:351–360
Masumoto H, Msukata H, Muro Y, Nozaki N, Okazki T (1989) A human centromere antigen (CENP-B) interacts with a short specific sequence in alphoid DNA, a human centromeric satellite. J Cell Biol 109:1963–1973
Moroi Y, Peebles C, Fritzler MJ, Steigerwald J, Tan EM (1980) Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1627–1631
Oudet P, Gross-Bellard M, Chambon P (1975) Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell 4:281–300
Palmer DK, O'Day K, Trong HL, Charbonneau H, Margolis RL (1991) Purification of the centromere-specific protein CENP-A and demonstration that it is a distinctive histone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3734–3738
Pankov R, Lemieux M, Hancock R (1990) An antigen located in the kinetochore region in metaphase and on polar microtubule ends in the midbody region in anaphase, characterised using a monoclonal antibody. Chromosoma 99:95–101
Pluta AF, Saitoh N, Goldberg I, Earnshaw WC (1992) Identification of a subdomain of CENP-B that is necessary and sufficient for localisation to the human centromere. J Cell Biol 116:1081–1093
Rattner JB, Kingwell BG, Fritzler MJ (1988) Detection of distinct structural domains within the primary constriction using auto-antibodies. Chromosoma 96:360–367
Saitoh H, Tomkiel J, Cooke CA, Ratrie H, Maurer M, Rothfield NF, Earnshaw WC (1992) CENP-C, an autoantigen in Scleroderma, is a component of the human inner kinetochore plate. Cell 70:115–125
Stenman S, Rosenqvist M, Ringertz NR (1975) Preparation and spread of unfixed metaphase chromosomes for immunofluorescence staining of nuclear antigens. Exp Cell Res 90:87–94
Taagepera S, Rao PN, Drake FH, Gorbsky GJ (1993) DNA topoisomerase IIα is the major chromosome protein recognised by the mitotic phosphoprotein antibody MPM-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8407–8411
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applictions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Tyler-Smith C, Willard HF (1993) Mammalian chromosome structure. Curr Opin Genet Dev 3:390–397
Valvidia MM, Brinkley BR (1985) Fractionation and initial characterisation of the kinetochore from mammalian metaphase chromosomes. J Cell Biol 101:1124–1134
Yen TJ, Compton DA, Earnshaw WC, Cleveland DW (1991) CENP-E, a novel human centromere-associated protein required for progression from metaphase to anaphase. EMBO J 10:1245–112545
Yen TY, Schaar BT, Szilak I, Cleveland DW (1992) CENP-E is a putative kinetochore motor that accumulates just before mitosis. Nature 359:536–539
Yoda K, Kitagawa N, Masumoto H, Muro Y, Okazaki T (1992) A human centromere protein, CENP-B, has a DNA binding domain containing four potential α helices at the NH2 terminus, which is separable from dimerizing activity. J Cell Biol 119:1413–1427
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holland, K.A., Keresõ, J., Zákány, J. et al. A tightly bound chromosome antigen is detected by monoclonal antibodies in a ring-like structure on human centromeres. Chromosoma 103, 559–566 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355321
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355321