Abstract
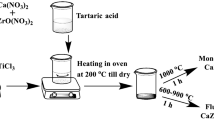
Polycrystalline zirconia fibres, doped with 2–8 mol% of oxides of trivalent lanthanum, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, gadolinium, and dysprosium (in decreasing cation size), were prepared by spinning of acetate-derived sols and baking the gel fibres thus obtained at 900–1300 °C for 1 h. The larger sized dopants lanthanum, praseodymium and neodymium (Group A) gave rise to tetragonal zirconia, with or without cubic zirconia, at 900 °C which converted partly or fully to monoclinic zirconia, in certain cases accompanied by a cubic zirconate phase at higher temperatures. The smaller sized dopants samarium, gadolinium and dysprosium (Group B) generated only tetragonal or cubic, or both polymorphs of zirconia, depending on the cation type, concentration and temperature. This “stabilization” of higher symmetry polymorphs with Group B dopants was associated with relatively large crystallite size (especially when calcined at 1300 °C). The maximum tensile strength values of usable fibres calcined at 1300 °C were found to decrease with increasing size in dopant dysprosium > gadolinium > samarium > neodymium, praseodymium, lanthanum=0). Although all the dopant cations were larger in size than Zr4+ (in the same oxygen coordination), the relative closeness in size of Group B cations with Zr4+ was considered to be the reason behind the obtained differences in properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Hayase, H. Asami, H. Asakura and T. Saeki, Shinagawa Tech. Rep. 31 (1988) 129.
K. Hattori and T. Kurushima, Ceram. Trans. 31 (1993) 147.
E. Leroy, C. Robin-Brosse and J. P. Torre, in “Ceramics in Advanced Energy Technologies”, edited by H. Krockel, M. Merz and O. Van der Biest (Reidel, Dordrecht, Holland, 1984) pp. 501–17.
K. Kamiya, T. Yoko, K. Tanaka and H. Itoh, Yogyo Kyokai-Shi 95 (1987) 1157.
D. B. Marshall, F. F. Lange and P. D. Morgan, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 70 (1987) c-187.
K. Kamiya, K. Takahashi, T. Maeda, H. Nasu and T. Yoko, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 7 (1991) 295.
M. Chatterjee, A. Chatterjee and D. Ganguli, Ceram. Int. 18 (1992) 43.
W. Pyda, K. Haberko and Z. Zurek, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 10 (1992) 453.
T. Log, R. A. Cutler, J. F. Jue and A. V. Virkar, J. Mater. Sci. 28 (1993) 4503.
H. P. Klug and L. E. Alexander, “X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials” (Wiley, New York, 1954) p. 491.
W. H. Hall, Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 62 (1949) 741.
I. H. Cowdrey and R. G. Adams, “Materials Testing: Theory and Practice” (Wiley, New York, 1949) p. 17.
J. L. McCall and W. M. Mueller, “Microstructural Analysis: Tools and Techniques” (Plenum Press, London. 1973) pp. 42–8.
A. K. Bhattacharya, A. Hartridge, K. K. Mallick and J. L. Woodhead, J. Mater. Sci. 29 (1994) 6076.
R. A. McCauley, J. Appl. Phys. 51 (1980) 290.
J. L. Shi, Z. X. Lin and T. S. Yen, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 8 (1991) 117.
R. C. Garvie, J. Phys. Chem. 69 (1965) 1238.
R. Dal Maschio, M. Filipponi, G. D. Soraju, G. Carturan and G. M. Del Felice, Bull Amer. Ceram. Soc. 71 (1992) 204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naskar, M.K., Ganguli, D. Rare-earth doped zirconia fibres by sol-gel processing. JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 31, 6263–6267 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354448
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354448