Abstract
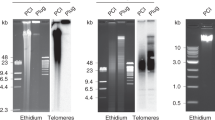
Pulsed electrophoresis was used to study the organization of the human centromeric region. Genomic DNA was digested with rare-cutting enzymes. DNA fragments from 0.2 to greater than 5.7 Mb were separated by electrophoresis and hybridized with alphoid and simple DNA repeats. Rare-cutting enzymes (Mlu I, Nar I, Not I, Nru I, Sal I, Sfi I, Sst II) demonstrated fewer restriction sites at centromeric regions than elsewhere in the genome. The enzyme Not I had the fewest restriction sites at centromeric regions. As much as 70% of these sequences from the centromeric region are present in Not I DNA fragments greater than 5.7 and estimated to be as large as 10 Mb in size. Other repetitive sequences such as short interspersed repeated segments (SINEs), long interspersed repeated segments (LINEs), ribosomal DNA, and minisatellite DNA that are not enriched at the centromeric region, are not enriched in Not I fragments of greater than 5.7 Mb in size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J.W., Kaufman, R.E., Kretschmer, P.J., Harrison, M., and Neinhuis, A.W.: A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human β globin gene. Nucl Acids Res 8: 6113–6128, 1980.
Arn, P.H., Ketabgian, A.A., Smith, C., Schwartz, D.C., and Jabs, E.W.: The macromolecular organization of human centromeric regions. In M. Resnick and B. Vig (eds), Mechanisms of Chromosome Distribution and Aneuploidy, pp. 1–8, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York, 1989.
Benbow, R.M., Krauss, M.R., and Reeder, R.H.: DNA synthesis in a multi-enzyme system from Xenopus laevis eggs. Cell 13: 307–318, 1978.
Bird, A., Taggart, M., Frommer, M., Miller, O.J., and Macleod, D.: A fraction of the mouse genome that is derived from islands of nonmethylated CpG-rich DNA. Cell 40: 91–99, 1985.
Chen, T.L., and Manuelidis, L.: SINEs and LINEs cluster in distinct DNA fragments of Giemsa band size. Chromosoma 98: 309–316, 1989.
Clarke, L. and Baum, M.P.: Functional analysis of a centromere from fission yeast: A role for centromere-specific repeated DNA sequences. Mol Cell Bio 10: 1863–1872, 1990.
Cutting, G.R., Kazazian, H.H., Antonarakis, S.E., Killen, P.D., Yamada, Y., and Francomano, C.A.: Macrorestriction mapping of COL4A1 and COL4A2 collagen genes on human chromosome 13q34. Genomics 3: 256–263, 1988.
Deininger, P.L., Jolly, D.J., Rubin, C.M., Friedmann, T., and Schmid, C.W.: Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol 151: 17–33, 1981.
Higgins, M.J., Wang, H., Shtromas, I., Haliotis, T., Roder, J.C., Holden, J., and White, B.N.: Organization of repetitive human 1.8 Kpn I sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma 93: 77–86, 1985.
Jabs, E.W., Wolf, S.F., and Migeon, B.R.: Characterization of a cloned DNA sequence which is present at centromeres of all human chromosomes and the X chromosome and shows polymorphic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 4884–4888, 1984.
Jabs, E.W. and Persico, M.G.: Characterization of human centromeric regions of specific chromosomes by means of alphoid DNA sequences. Am J Hum Genet 41: 374–390, 1987.
Jabs, E.W., and Carpenter, N.: Molecular cytogenetic evidence for amplification of chromosome-specific alphoid sequences at enlarged C-bands on Chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet 43: 69–74, 1988.
Jabs, E.W., Goble, C.A., and Cutting, G.R.: Macromolecular organization of human centromeric regions reveals high-frequency, polymorphic macro DNA repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 202–206, 1989.
Jabs, E.W., Tuck-Muller, C.M., Cusano, R., and Rattner, J.B.: Studies of mitotic and centromeric abnormalities in Roberts syndrome: Implications for a defect in the mitotic mechanism. Chromosoma 100: 251–261, 1991.
Jeffreys, A.J., Wilson, V., Thein, S.L.: Hypervariable “minisatellite” regions in human DNA. Nature 314: 67–73, 1985.
Killen, P.D., Francomano, C.A., Yamada, Y., Modi, W.S., and O'Brien, S.J.: Partial structure of the human α 2(IV) collagen chain and chromosomal localization of the gene (COL4A2). Hum Genet 77: 318–324, 1987.
Korenberg, J.R. and Rykowski, M.C.: Human genome organization; Alu, LINES, and the molecular structure of metaphase chromosome bands. Cell, 53: 391–400, 1988.
Manuelidis, L. and Ward, D.C.: Chromosomal and nuclear distribution of the Hind III 1.9 kb human DNA repeat-segment. Chromosoma 91: 28–38, 1984.
McCutchan, T., Hsu, H., Thayer, R.E., and Singer, M.F.: Organization of African Green monkey DNA at junctions between α-satellite and other DNA sequences. J Mol Biol 157: 195–211, 1982.
Moyzis, R.K., Albright, K.L., Bartholdi, M.F., Cram, L.S., Deaven, L.L., Hildebrand, C.E., Joste, N.E., Longmire, J.L., Meyne, J., Schwarzacher-Robinson, T.: Human-specific repetitive DNA sequences: Novel markers for genetic analysis. Chromosoma 95: 375–386, 1987.
Moyzis, R.K., Torney, D.C., Meyne, J., Buckingham, J.M., Wu, J.-R., Burks, C., Sirotkin, K.M., and Goad, W.B.: The distribution of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the human genome. Genomics 4: 273–289, 1989.
Nelson, M., and McClelland, M.: Effect of site-specific methylation on DNA modification methyltransferases and restriction endonucleases. Nucl Acids Res 177 (Suppl): r389-r415, 1989.
Oakley, R. and Tyler-Smith, C.: Y chromosome DNA haplotyping suggests that most European and Asian men are descended for one of two males. Genomics 7: 325–330, 1990.
Poustka, A., Pohl, T.M., Barlow, D.P., Frischauf, A.-M., and Lehrach, H.: Construction and use of human chromosome jumping libraries from Not I-digested DNA. Nature 325: 353–355, 1987.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T.: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Second Edition, pp. 1–21, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989.
Schmickel, R.D. and Knoller, M.: Characterization and localization of the human genes for ribosomal ribonucleotide acid. Ped Res 11: 929–935, 1977.
Schwartz, D.C.: Giga-dalton DNA molecules, thesis, Columbia University, 1985.
Schwartz, D.C. and Cantor, C.R.: Separation of yeast chromosomesized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell 37: 67–75, 1984.
Schwartz, D.C., and Koval, M.: Conformational dynamics of individual DNA molecules during gel electrophoresis. Nature 338: 520–522, 1989.
Schwartz, D.C., Smith, L.C., Baker M., and Hsu, M.: ED: Pulsed electrophoresis instrument. Nature 342: 575, 1989.
Singer, M.F.: Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol 76: 67–193, 1982.
Smith, C.L., Matsumoto, G., Niwa, O., Klco, S., Fan, J.B., Yanagida, M., and Cantor, C.R.: An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucl Acids Res 15: 4481–4488, 1987.
Waye, J.S. and Willard, H.F.: Human β satellite DNA: Genomic organization and sequence definition of a class of highly repetitive tandem DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 6250–6254, 1989.
Wells, R.A., Green, P., and Reeders, S.T.: Simultaneous genetic mapping of multiple human minisatellite sequence using DNA fingerprinting. Genomics 5: 761–772, 1989.
Wevrick, R. and Willard, H.F.: Long-range organization of tandem arrays of α satellite DNA at the centromeres of human chromosomes: High0frequency array-length polymorphism and meiotic stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9394–9398, 1989.
Wu, J.C. and Manuelidis, L.: Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol 142: 363–386, 1980.
Yunis, J.J.: Mid-prophase human chromosomes: The attainment of 2000 bands. Hum Genet 56: 293–298, 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arn, P.H., Li, X., Smith, C. et al. Analysis of DNA restriction fragments greater than 5.7 Mb in size from the centromeric region of human chromosomes. Mammalian Genome 1, 249–254 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352332
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352332