Abstract
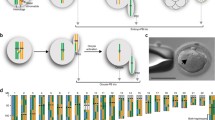
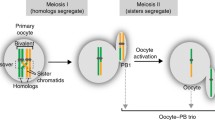
The X chromosome pair was identified in diakinesis/metaphase I stage mouse oocytes using a repeat sequence DNA probe and fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Chiasma positions along the X bivalent were measured in 57 oocytes from 4 females. Overall, our observations showed that while there were no obvious “hotspots” for chiasma formation along the X chromosome, there was a tendency to favour the distal end. Minimum inter-chiasma distances were substantial indicating the occurrence of strong genetic interference. Estimates of both genetic distances and recombination fractions for any interval along the chromosome can be calculated from the chiasma data. The average chiasma frequency for the X bivalent was 1.37 giving an estimated total genetic map length of 68.5 cM. In general, the pattern of chiasma distribution along the X chromosome resembled that anticipated from recombination distances in published consensus linkage maps. There were, however, some intriguing differences between the two approaches. The reason for these discrepancies are unknown but may be related to lack of precision in cytogenetic mapping of loci, inter-strain and/or interspecies differences in the genetic controls over the distribution of crossover events. One advantage of the chiasma analysis approach is its suitability for investigating these problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley T, Cacheiro NL, Russell LB, Ward DC (1993) Molecular characterisation of a pericentric inversion in mouse chromosome 8 implicates telomeres as promoters of meiotic recombination. Chromosoma 102:112–120
Coates DJ, Shaw DD (1982) The chromosomal component of reproductive isolation in the grasshopper Caledia captiva. I. Meiotic analysis of chiasma distribution patterns in two chromosomal taxa and their F1 hybrids. Chromosoma 86:509–531
Disteche CM, McConnell GK, Grant SG, Stephenson DA, Chapman VM, Gandy S, Adler DA (1989) Comparison of the physical and recombination maps of the mouse X chromosome. Genomics 5:177–184
Fox DP (1973) The control of chiasma distribution in the locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Chromosoma 43:289–328
Gorlov IP, Zhelezova AI, Gorlova OU (1994) Sex differences in chiasma distribution along two marked mouse chromosomes: differences in chiasma distribution as a reason for sex differences in recombination frequency. Genet Res 64:161–166
Henderson SA (1963) Chiasma distribution at diplotene in a locust. Heredity 18:173–190
Henderson SA, Edwards RC (1968) Chiasma frequency and maternal age in mammals. Nature 218:22–28
Herman GE, Boyd Y, Chapman V, Chatterjee A, Brown SDM (1994) The mouse X chromosome. Mammalian Genome 5: S276–288
Hultén M (1974) Chiasma distribution at diakinesis in the normal human male. Hereditas 76:55–78
Hultén MA, Palmer RW, Laurie DA (1982) Chiasma derived genetic maps and recombination fractions: Chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet 46:167–175
Hultén M, Lawrie NM, Laurie D (1990) Chiasma-based genetic maps of chromosome 21. Am J Med Genet 7:148–154
Hultén M (1990) The topology of meiotic chiasmata prevents terminalization. Ann Hum Genet 54:307–314
Hultén M, Goldman ASH, Saadallah N, Wallace BMN, Creasey MR (1992) Meiotic studies in man. In: Rooney DE, Czepuldouski BH (eds) Human cytogenetics. A practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford Washington DC, pp 193–221
Jones GH (1984) The control of chiasma distribution. In: Evans CW, Dickinson HG (eds) Controlling events in meiosis. The Company of Biologists, Cambridge, pp 293–320
Jones GH (1987) Chiasmata. In: Moens PB (ed) Meiosis. Academic Press, London, pp 213–244
Laird CD (1971) Chromatid structure: relationship between DNA control and nucleotide sequence diversity. Chromosoma 32:378–406
Laurie DA, Palmer RW, Hultén MA (1982) Chiasma derived genetic lengths and recombination fractions: Chromosomes 2 and 9. Ann Hum Genet 46:233–244
Laurie DA, Hultén MA (1985) Further studies on chiasma distribution and interference in the human male. Ann Hum Genet 49:203–214
Laurie DA, Jones GH (1981) Inter-individual variation in chiasma distribution in Chorthippus brunneus (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Heredity 47:409–416
Laurie DA, Palmer RW, Hultén MA (1984) Studies on chiasma frequency and distribution in two fertile men carrying reciprocal translocations; one with a t(9;10) karyotype and one with a t(Y;10) karyotype. Hum Genet 68:235–247
Laurie DA, Palmer RW, Hultén MA (1985) Chiasma derived genetic lengths and recombination fractions; a 46;XY,t(9;10) (p22;q24) reciprocal translocation. Ann Hum Genet 49: 135–146
Lawrie NM, Tease C, Hultén MA (1995) Chiasma frequency, distribution and interference maps of mouse autosomes. Chromosoma. In Press
Lyon MF, Kirby MC (1994) Mouse chromosome atlas. Mouse Genome 92:19–61
Lyon MF, Zenthon J, Burtenshaw MD, Evans EP (1987) Localisation of the Hprt locus by in situ hybridisation and distribution of loci on the mouse X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 44, 163–166
Mather K (1936) The determination of position in crossing-over. I. Drosophila melanogaster. J Genet 33:207–235
Quinn P, Barros C, Whittingham DG (1982) Preservation of hamster oocytes to assay the fertilizing capacity of human spermatozoa. J Reprod Fertil 66:161–168
Rabbitts P, Impey H, Heppell-Parton A, Langford C, Tease C, Lowe N, Bailey D, Ferguson-Smith M, Carter N (1995) Chromosome specific paints from a high resolution flow karyotype of the mouse. Nature Genet 9:369–375
Saadallah N, Hultén M (1983) chiasma distribution, genetic lengths, and recombination fractions: A comparison between chromosome 15 and 16. J Med Genet 20:290–299
Shaw DD, Knowles GR (1976) Comparative chiasma analysis using a computerised optical digitiser. Chromosoma 59:103–127
Tarkowski AK (1966) An air-drying method for chromosome preparations from mouse oocytes. Cytogenetics 5:394–400
Vergnaud G (1994) No increase in female recombination frequency in the distal part of the pseudoautosomal region. Genomics 24, 610–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hultén, M.A., Tease, C. & Lawrie, N.M. Chiasma-based genetic map of the mouse X chromosome. Chromosoma 104, 223–227 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352187
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352187