Abstract
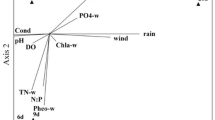
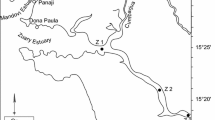
A range of physical and chemical parameters were measured through the water column at two previously unstudied shallow-water sites in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland, in the spring of 1991. Sediment traps were also deployed at one of the sites. The results of this survey are presented and discussed. A bloom of Skeletonema costatum was observed at one site through March and into April, when it collapsed completely, the phytoplanktonic cells sedimenting out of the water column. No significant bloom or sedimentation was observed at the second study site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes H, Goodley EFW (1961) The general hydrography of the Clyde Sea area, Scotland. Part I. Description of the area; drift bottle and surface salinity data. Bull mar Ecol 5:112–150
Bienfang PK, Harrison PJ, Quarmby LM (1982) Sinking rate response to depletion of nitrate, phosphate and silicate in four marine diatoms. Mar Biol 67:295–302
Bodungen BV, von Broeckel KV, Smetacek V, Zeitschel B (1981) Growth and sedimentation of the phytoplankton spring bloom in the Bornholm Sea (Baltic Sea). Kieler Meeresforsch (Sndhft) 5: 49–60
Boney AD (1986) Seasonal studies on the phytoplankton and primary production in the inner Firth of Clyde. Proc R Soc Edinb (Sect B) 90:203–222
Davies RM, Payne R (1984) Supply of organic matter to the sediment in the northern North Sea during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Mar Biol 78:315–324
Edwards A, Baxter MS, Ellett DJ, Martin JHA, Meldrum DT, Griffiths CR (1986) Clyde sea hydrography. Proc R Sco Edinb (Sect B) 90:67–83
Grantham B, Tett P (1993) The nutrient status of the Clyde Sea in winter. Estuar cstl, Shelf Sci 36:449–462
Hannah FJ, Boney AD (1983) Nanophytoplankton in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland: seasonal abundance, carbon fixation and species composition. J exp mar Biol Ecol 67:105–147
Johnston R, Adams JA, Dooley HD (1974) Some observations on the hydrography, chemistry and plankton of the Firth of Clyde in relation to nitrate-rich effluents. Publs nat Envir Res Coun, Swindon (Ser C) 11:16–21
Mackay DW, Halcrow W (1976) The distribution of nutrients in relation to water movements in the Firth of Clyde. In: Skreslet S, Leinebo R, Matthews JBL, Sakshaug E (eds) Freshwater on the sea. Association of Norwegian Oceanographers, Oslo, pp 109–118
Margalef R, Estrada M, Blasco D (1979) Functional mortality of organisms involved in red tides, as adapted to decaying turbulence. In: Taylor DL, Seliger HH (eds) Toxic dinoflagellate blooms. Elsevier North Holland Inc. New York, pp 89–94
Marshall SM, Orr AP (1927) The relation of the plankton to some chemical and physical factors in the Clyde Sea area. J mar Biol Ass UK 14:837–868
Marshall SM, Orr AP (1930) A study of the spring diatom increase in Loch Striven. J mar biol Ass UK 17:853–878
Morrison JA, Napier IR, Gamble JC (1991) Mass mortality of herring eggs associated with a sedimenting diatom bloom. ICES J mar Sci 48:237–245
Napier IR (1993a) A study of herring spawning grounds on gravel and maerl in the Firth of Clyde. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis University of London
Napier IR (1993b) The organic carbon content of gravel bed herring spawning grounds and the impact of herring spawn deposition. J mar biol Ass UK 73:863–870
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Smetacek VS (1980) Annual cylce of sedimentation in relation to plankton ecology in western Kiel Bight. Ophelia (Suppl) 1: 65–76
Solórzano L (1969) Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol Oceanogr 14:800–801
Stainton MP (1974) Simple, efficient reduction column for use in the automated determination of nitrate in water. Analyt Chem 46: 1616
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis 2nd edn. Fish Bull Res Bd Can 167:1–310
Taylor FJR (1987) Ecology of dinoflagellates: A General and marine ecosystems. In: Taylor FJR (ed) The biology of dinoflagellates, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 399–501
Tett P (1987) Plankton. In: Baker JM, Wolff WJ (eds) Biological surveys of estuaries and coasts. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 280–341
Tett P, Gowen R, Grantham B, Jones K (1986) The phytoplankton ecology of the Firth of Clyde sea-lochs Striven and Fyne. Proc R Soc Edinb (Sect B) 90:223–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Napier, I.R. Growth and collapse of a spring phytoplankton bloom in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland. Marine Biology 123, 189–195 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350339
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350339