Summary
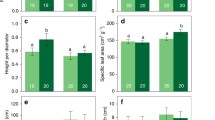
Changes in plant growth and competitive balance between pairs of competing species were documented as a result of supplementary ultraviolet-B radiation (principally in the 290–315 nm waveband) under field conditions. This component of the terrestrial solar spectrum would be intensified if the atmospheric ozone layer were reduced. A method for calculating and statistically analyzing relative crowding coefficients was developed and used to evaluate the competitive status of the species pairs sown in a modified replacement series. The effect of the supplementary UV-B irradiance was generally detrimental to plant growth, and was reflected in decreased leaf area, biomass, height and density as well as changes in competitive balance for various species. For some species, interspecific competition apparently accentuated the effect of the UV-B radiation, while more intense intraspecific competition may have had the same effect for other species. A few species when grown in a situation of more severe mutual interspecific competition exhibited enhanced growth under the UV-B radiation treatment. This, however, was usually associated with a detrimental effect of the radiation on its competitor and thus was likely the result of its improved competitive circumstance rather than a beneficial physiological effect of the radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, J.P., Runeckles, V.C.: Effects of low levels of ozone on plant competition. J. Appl. Ecol. 14, 877–880 (1977)
Brandle, J.R., Campbell, W.F., Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Net photosynthesis, electron transport capacity, and ultrastructure of Pisum sativum L. exposed to ultraviolet-B radiation. Plant Physiol. 60, 165–169 (1977)
Caldwell, M.M.: Solar UV irradiation and the growth and development of higher plants. In: Photophysiology (A.C. Giese, ed.), pp. 131–177. New York: Academic Press 1971
Caldwell, M.M.: The effects of solar UV-B radiation (280–315 nm) on higher plants: implications of stratospheric ozone reduction. In: Research in photobiology (A. Castellani, ed.), pp. 597–607. London: Plenum 1977
Cline, M.G., Salisbury, F.B.: Effects of ultraviolet radiation on the leaves of higher plants. Radiat. Bot. 6, 151–163 (1965)
Dewit, C.T.: On competition. Versl. Landbowk. Onderzoek. The Hague 66, 1–82 (1960)
Hering, W.S., Borden, T.R.: Ozonesonde observations over North America. U.S. Air Force, Environ, Res. Pap. No. 279, Vol. IV. Bedford, Mass. U.S. Air Force Cambridge Research Lab. 1967
Hudson, R.D. (ed.): Chlorofluoromethanes and the stratosphere. NASA Ref. Pub. 1010, 266 pp. Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office 1977
Molina, J.M., Rowland, F.S.: Stratospheric sink for chlorofluoromethanes: chlorine atom-catalysed destruction of ozone. Nature 249, 810–812 (1974)
Palmblad, I.G.: Competition in experimental populations of weeds with emphasis on the regulation of population size. Ecology 49, 26–34 (1968)
Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Lamp/filter systems for simulation of solar UV irradiance under reduced atmospheric ozone. Photochem. Photobio. 21, 453–456 (1975)
Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Photosynthesis, dark respiration, and growth of Rumex patientia L. exposed to ultraviolet irradiance (288 to 315 nanometers) simulating a reduced atmospheric ozone column. Plant Physiol. 58, 563–568 (1976)
Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Atmospheric ozone depletion: reduction of photosynthesis and growth of a sensitive higher plant exposed to enhanced UV-B radiation. J. Exptl. Bot. 28, 691–705 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fox, F.M., Caldwell, M.M. Competitive interaction in plant populations exposed to supplementary ultraviolet-B radiation. Oecologia 36, 173–190 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349807
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349807