Abstract
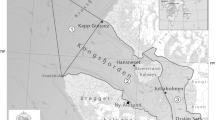
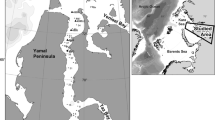
Monthly trawl surveys were performed in 1989 in North Bay and South Bay of St Vincent (New Caledonia) with both a shrimp trawl and fish trawl to produce a reference standard of the natural variability of an unexploited tropical soft-bottom fish assemblage. A total of 230 species belonging to 62 families were recorded. The mean density and biomass were 0.18 fishes m-2 and 4.31 g m-2, respectively. The major variations were explained by spatial factors. Species richness, density and biomass were greater in South Bay (204 species, 0.26 fishes m-2 and 5.90 g m-2) than in North Bay (105 species, 0.10 fishes m-2 and 2.71 g m-2), 34% of the species being present in both areas. The North Bay assemblage was characterized by four abundant benthic species (Saurida undosquamis, Gerres ovatus, Secutor ruconius and Upeneus moluccensis) and by numerous pelagic species (Carangidae, Sphyraenidae and Scombridae). The South Bay assemblage was characterized by several Mullidae, Bothidae and Balistidae, and by some rare species usually found on coral reefs (Pomacentridae and Chaetodontidae). These differences were induced by the physical and benthic characteristics of the two bays. North Bay was an homogeneous, confined, deposit area with few benthic organisms, whereas the substrate was more heterogeneous and the benthic organisms more diversified and abundant in South Bay, which was connected to the adjacent reef lagoon. Species richness remained stable in time, except in January when a hurricane disturbed the environment. Seasonal tendencies in species composition were evidenced in North Bay, with an autumn-winter structure opposed to a spring-summer structure, and characterized by the relative importance of the major species. No seasonal tendencies were observed in the organization of the South Bay assemblage. Nevertheless, mean density and biomass were at a minimum in summer in both bays; maxima occurred in winter. Biomass was negatively correlated to both temperature and rainfall, and reflected the population variations of the main species, particularly their reproductive migrations. Thus, the soft-bottom fish assemblages were strongly organized spatially in New Caledonia, but remained relatively stable over time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama T (1973) The demersal fish stocks and fisheries of the South China Sea. FAO, Rome (SCS/DEV/73/3)
Cannon IRG, Goeden GB, Campbell P (1987) Community patterns revealed by trawling in the inter-reef regions of the Great Barrier Reef. Mem Qd Mus 25:45–70
Carpenter KE, Allen GR (1989) FAO species catalogue. Vol. 9. Emperor and large-eye breams of the world (family Lethrinidae). FAO, Rome (FIR/S124 Vol. 9)
Chardy P, Chevillon C, Clavier J (1988) Major benthic communities of the south-west lagoon of New Caledonia. Coral Reefs 7:69–75
Chardy P, Clavier J (1988) Biomass and trophic structure of macrobenthos in the south-west lagoon of New Caledonia. Mar Biol 99:195–202
Chong VC (1984) Prawn resource management in the west coast of peninsular Malaysia. Wallaceana (Univ Malaya) 37:3–6
Conand F (1988) Biologie et écologie des poissons pélagiques du lagon de Nouvelle-Calédonie utilisables comme appât thonier. Etudes et thèses, ORSTOM, Paris
Doherty PJ (1991) Spatial and temporal patterns in recruitment. In: Sale PF (ed). The ecology of fishes on coral reefs. Academic Press, London, pp 261–293
Dredge MCL (1988) By-catch from the central Queensland prawn fisheries. Part I. The trawl fisheries, species composition and site associations from the by-catch. Fisheries Research Station, Burnett Heads Department of Primary Industries, Burnett Heads, Qd (Fish Res Brch tech Rep FRB 88/04)
Federizon RR (1992) Description of the subareas of Ragay Gulf, Philippines, and their fish assemblages by exploratory data analysis. Aust J mar Freshwat Res. 43:379–391
Gulland JA (1975) Manual of methods for fisheries resource survey. Part 5. Objectives and basic methods. FAO Fish tech Pap 145: 1–29
Hallier JP, Kulbicki M (1985) Analyse des résultats de la pêcherie à la canne de Nouvelle-Calédonie (août 1981 avril 1983). Rapp scient tech ORSTOM Nouméa 36:1–141
Harris AN, Poiner IR (1991) Changes in species composition of demersal fish fauna of Southeast Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia, after 20 years of fishing. Mar Biol 111:503–519
Hutchings P (1990) Review of the effects of trawling on macrobenthic epifaunal communities. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 41: 111–120
Kailola PJ, Wilson MA (1978) The trawl fishes of the Gulf of Papua. Res Bull Dep Prim Industry Pt Moresby (Papua New Guinea) 20:1–85
Kulbicki M, Mou-Tham G, Bargibant G, Menou JL, Tirard P (1987) Résultats préliminaires des pêches expérimentales à la palangre dans de lagon Sud-Ouest de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Rapp scient tech ORSTOM Nouméa 49:1–104
Kulbicki M, Wantiez L (1990) Variations in the fish catch composition in the Bay of St Vincent, New Caledonia, as determined by experimental trawling. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 41:121–144
Legendre L, Legendre P (1984) Ecologie numérique. 2. La structure des données écologiques: seconde édition. Collection d'écologie. Masson, Paris
Liu HC (1976) The demersal fish stocks of the waters of North and Northwest Australia. Acta oceanogr taiwan 6:128–134
Loneragan NR, Potter IC (1990) Factors influencing community structure and distribution of different life-cycle categories of fishes in shallow waters of a large Australian estuary. Mar Biol 106:25–37
May JL, Blaber SJM (1989) Benthic and pelagic fish biomass of the upper continental slope off eastern Tasmania. Mar Biol 101: 11–25
Merrett NR, Gordon JDM, Stehmann M, Haedrich RL (1991) Deep demersal fish assemblage structure in the Porcupine Seabight (Eastern North Atlantic): slope sampling by three different trawls compared. J mar biol Ass UK 71:329–358
Mines AN (1984) Biological study of predominant fish species caught by bottom trawl in Ragay Gulf, Buria Pass, Ticao Pass and waters north of Samar Sea. In: Mines AN (eds) Assessment of trawlable areas in Philippines II: Ragay Gulf, Buria Pass, Ticao Pass and waters north of Samar Sea. University of the Philippines, Quezon City, pp 9–25 (Tech Rep Dep mar Fish No. 5)
Mohsin AKM, Said MZBM, Ambak MAB, Hayase MNBASS, Sekioka M (1988) Marine catch by experimental trawling in the south western portion of the South China Sea. Ekspedisi Matahari 86: 113–120 (Occ Publ Fac Fish mar Sci, Univ Pertanian, Selangor, Malaysia)
Nelson JS (1984) Fishes of the world. 2nd edn. Wiley Interscience, New York
Okera W, Gunn JS (1986) Exploratory trawl surveys by FRV Solea in the Australian fishing zone sector of the Timor-Arafura seas and in the Gulf of Carpentaria. Rep mar Lab CSIRO 150:1–104
Pauly D (1979) Theory and management of tropical multispecies stocks: a review, with emphasis on the Southeast Asian demersal fisheries. ICLARM Stud Rev 1:1–37
Pauly D (1987) Theory and practice of overfishing: a Southeast Asian perspective. ICLARM Contr (Manilla) 356:146–163
Poiner JR, Harris A (1986) The effect of commercial prawn trawling on the demersal fish communities of the South Eastern Gulf of Carpentaria. In: Haines AK, Williams GC, Choats D (eds) Torres Strait Fisheries Seminar, Australian Government Publishing Service, Camberra, pp 239–259
Quinn NJ, Kojis BL (1987) The influence of diel cycle, tidal direction and trawl alignment on beam trawl catches in an equatorial estuary. Envir Biol Fish 19:297–308
Rainer SF (1984) Temporal changes in a demersal fish and cephalopod community of an unexploited coastal area in Northern Australia. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 35:747–768
Rainer SF, Munro ISR (1982) Demersal fish and cephalopod communities of an unexploited coastal environment in Northern Australia. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 33:1039–1055
Ramm DC, Pender PJ, Willing RS, Buckworth RC (1990) Largescale spatial patterns of abundance within the assemblage of fish caught by prawn trawlers in Northern Australian waters. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 41:79–95
Richer de Forges B, Bargibant G, Menou JL, Guarrigue, C (1987) Le lagon sud-ouest de la Nouvelle-Calédonie. Observations préalables a la cartographic bionomique des fonds meubles. Rapp scient tech ORSTOM Nouméa 45:1–72
Rivaton J, Richer de Forges B (1990) Poissons récoltés par dragages dans le lagon de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Rapp scient tech ORSTOM Nouméa 55:1–101
Rougerie F (1986) Le lagon sud-ouest de la Nouvelle-Calédonie: spécificié hydrologique, dynamique et productivité. Etudes et thèses. ORSTOM, Paris
Russell BC, Houston W (1989) Offshore fishes of the Arafura Sea. The Beagle, Rec Nth Territory Mus Arts Sciences 6:69–84
Sainsbury KJ (1979) CSIRO defining fish stocks on NW shelf. Aust Fish March 1979:4–12
Sainsbury KJ (1987) Assessment and management of the demersal fishery on the continental shelf of Northwestern Australia. In: Povolina JJ, Ralston S (eds) Tropical snappers and groupers: biology and fishery management, Westview Press, London, pp 465–503
Sainsbury KJ, Kailola PJ, Leyland GG (1984) Continental shelf fishes of Northern and North-Western Autralia. Clouston & Hall, Canberra
Saville A (1978) Méthodes de prospection pour l'évaluation des ressources helieutiques. FAO Doc tech Pêches 171:1–81
Senta T, Tan SM (1973) Trawl fishing grounds in North Adaman Sea. (SEAFDEC/SCS.73, S-12) Southeast Asian Fisheries Research Development Center, Chagi Point, Singapore, pp 66–70
Shindo S (1973) General review of the trawl fishery and the demersal fish stocks of the South China Sea. FAO Fish tech Pap 120:1–49
Siegel S, Castellan J (1988) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioural sciences. 2nd edn. Statistics Series. McGraw-Hill International Editions, New York
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. 2nd edn. W. H. Freeman & Co., New York
Sudarsan D, John ME, Joseph A (1989) An assessment of demersal stocks in the southwest coast of India with particular reference to exloitable resources in outer continental shelf and slope. Bull cent mar Fish Res Inst (Indian Coun agric Res) Cochin 44:266–272
Villoso EP, Hermosa GV (1982) Demersal trawl fish resources of Samar Sea and Carigara Bay, Philippines. Fishery Res J Univ Phillip, Quezon City 7:59–78
Wantiez L (1994a) Les poissons des fonds meubles du lagon nord et de la baie de Saint-Vincent de Nouvelle-Calédonic. Description des peuplements, structure et fonctionnement des communautés Trav Docums ORSTOM 121:1–444 (Microfiché)
Wantiez L (1994b) Réseaux trophiques de l'ichtyofaune des founds meubles lagonaires de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Cr Rebd Séanc Acad Sci, Paris (Ser III) 317:847–856
Wantiez L (1996) Comparison of fish assemblages sampled by a shrimp trawl and a fish trawl, in St Vincent Bay, New Caledonia. J mar biol Ass UK (In press)
Wantiez L, Kulbicki M (1991) Les pêches exploratoires au chalut en baic de Saint Vincent (Nouvelle Calédonie). Rapp scient tech ORSTOM Nouméa 60:1–73
Watson RA, Dredge MLC, Mayer DG (1990) Spatial and seasonal variation in demersal trawl fauna associated with a prawn fishery on the central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 41:65–77
Watson RA, Goeden G (1989) Temporal and spatial zonation of the demersal trawl fauna of the central Great Barrier Reef. Mem Qd Mus 27:611–620
Wright JM (1989) Diel variation and seasonal consistency in the fish assemblage of the non-estuarine Sulaibikhat Bay, Kuwait. Mar Biol 102:135–142
Young PC, Wadley VA (1979) Distribution of shallow-water epibenthic macrofauna in Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Mar Biol 53:83–97
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. Rodriguez, Puerto Real
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wantiez, L., Harmelin-Vivien, M. & Kulbicki, M. Spatial and temporal variation in a soft-bottom fish assemblage in St Vincent Bay, New Caledonia. Marine Biology 125, 801–812 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349263
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349263