Abstract
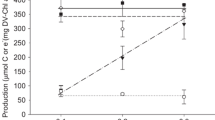
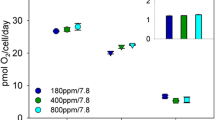
Blooms of the marine prymnesiophyte genus Phaeocystis link the oceanic and atmospheric compartments of the carbon and sulfur cycles. Modeling the fluxes of dimethylsulfide from the ocean to the atmosphere has been limited due to a lack of information on functional responses to environmental variables. In this study, the light-dependence of extracellular carbon production and dimethyl sulfide (DMS) production by non-axenic polar clones of Phaeocystis spp. was examined at different growth stages. Comparative experiments were run with non-axenic arctic clones of the diatoms Thalassiossira nordenskioeldii and Skeletonema costatum. A large portion of carbon incorporated by the colonial stage of Phaeocystis spp. is released extracellularly, in particular in stationary colonies. This extracellular production can be modeled as a function of irradiance, as for carbon incorporation. In Phaeocystis spp., cellular and extracellular carbon incorporation represent different uptake rates, indicating the formation of two distinct carbon pools. The release of extracellular carbon by polar Phaeocystis spp. was not a constant fraction of total production over the irradiance range used. We observed little extracellular carbon production by cells at high irradiance, and maximal rates were observed at intermediate irradiance. Newly incorporated carbon that accumulates in the mucilage of the colonial stage of antarctic Phaeocystis sp. during photosynthesis was not reutilized for cellular growth during the dark period, as observed for temperate clones. In contrast, only a minor fraction of the radiocarbon incorporated by the diatoms was released extracellularly for all growth stages. The production of DMS was an order of magnitude higher for Phaeocystis spp. than for diatoms. The chlorophyll-specific production of DMS and DMSP (dimethylsulphoniopropionate, the precursor to DMS) by Phaeocystis spp. showed a hyperbolic response to irradiance, while arctic diatoms (weak or non-producers of DMS), on the other hand, did not show any light-dependency of DMS production. An inverse relationship between DMS and DMSP production in stationary clones of arctic P. pouchetii was observed, but not for the exponentially growing antarctic clone. Stationary colonies also had higher DMS and dissolved DMSP production rates than exponentially growing ones. These relationships can be extrapolated to the field in areas where Phaeocystis spp. dominates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae MO (1990) Ocean-atmosphere interactions in the global biogeochemical sulfur cycle. Mar Chem 30: 1–29
Ayers GP, Ivery JP, Gillett RW (1990) Coherence between seasonal cycles of dimethyl sulphide, methane sulphonate, and sulphate in marine air. Nature, Lond 349: 404–406
Barnard WR, Andreae MO, Iverson RL (1984) Dimethylsulfide and Phaeocystis pouchetii in the Southeastern Bering Sea. Contin Shelf Res 3: 103–113
Bates TS, Cline JD, Gammon RH, Kelly-Hansen SR (1987) Regional and seasonal variations in the flux of oceanic dimethylsulfide to the atmosphere. J geophys Res 92: 2930–2938
Baumann MEM, Lancelot C, Brandini FP, Sakshaug E, John DM (1994) The taxonomic identity of the cosmopolitan prymnesiophyte Phaeocystis. J mar Syst 5: 5–22
Berresheim H (1987) Biogenic sulfur emissions from the subAntarctic and Antarctic oceans. J geophys Res 92: 13245–13262
Cadee GC, Hegeman J (1991) Historical phytoplankton data of the Mardsiep. Hydrobiol J 24: 111–118
Charlson RJ, Lovelock JE, Andreae MO, Warren SG (1987) Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulphur, cloud albedo and climate. Nature, Lond 326: 655–661
Cole JJ, Likens GE, Hobbie JE (1984) Decomposition of planktonic algae in an oligotrophic lake. Oikos 42: 257–266
Cota GF, Smith WO, Jr, Mitchell BG (1994) Photosynthesis of Phaeocystis in the Greenland Sea. Limnol Oceanogr 39:948–953
Dacey JWH, Wakeham SG (1986) Oceanic dimethylsulfide: production during zooplankton grazing on phytoplankton. Science, NY 233: 1314–1316
Davidson AT, Marchant HJ (1987) Binding of manganese by Antarctic Phaeocystis pouchetii and the role of bacteria in its release. Mar Biol 95: 481–487
Davidson AT, Marchant HJ (1992) Protist abundance and carbon concentration during a Phaeocystis-dominated bloom at an Antarctic coastal site. Polar Biol 12: 387–395
Diaz MR, Taylor BF (1994) Comparison of dimethylsulfonio-propionate lyase activity in a prokaryote and an eukaryote. A Mtg microbiol Soc Am Abstr 94: p. 48
Erickson DJ III, Ghan SJ, Penner JE (1990) Global ocean-toatmosphere dimethyl sulfide flux. J geophys Res 95: 7543–7552
Estep KW, Nejstgaard JC, Skjoldal H-R, Rey F (1990) Predation by copepods upon natural populations of Phaeocystis pouchetii as a function of the physiological state of the prey. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 67: 235–249
Falkowski PG, Kim Y, Kolber Z, Wilson C, Wirick C, Cess R (1992) Natural versus anthropogenic factors affecting low-level cloud albedo over the North Atlantic. Science, NY 256: 1311–1313
Fisher NS, Fabris JG (1982) Complexation of Cu, Zn, and Cd by metabolites excreted from marine diatoms, Mar Chem 11: 245–255
Fogelqvist E (1991) Dimethylsulphide (DMS) in the Weddell Sea surface and bottom water. Mar Chem 35: 169–177
Fryxell GA (1989) Marine phytoplankton at the Weddell Sea ice edge: seasonal changes at the specific level. Polar Biol 10: 1–18
Gibson JAE, Garrick RC, Buton HR, McTaggart AR (1988) Dimethylsulfide concentrations in the ocean close to the Antarctic continent. Geomicrobiol J 6: 179–184
Gibson JAE, Garrick RC, Buton HR, McTaggart AR (1990) Dimethylsulfide and the alga Phaeocystis pouchetii in antarctic coastal waters. Mar Biol 104: 339–346
Gieskes WWC, van Bennekom AJ (1973) Unreliability of the 14C method for estimating primary productivity in eutrophic Dutch coastal waters. Limnol Oceanogr 18: 494–495
Gilstad M, Sakshaug E (1990) Growth rates of ten diatom species from the Barents Sea at different irradiances and day lengths. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 64: 169–173
Guillard RRL, Hellebust JA (1971) Growth and the production of extracellular substances by two strains of Phaeocystis pouchetii. J Phycol 7: 330–338
Holligan PM, Balch WM (1991) From the ocean to cells: coccolithophore optics and biogeochemistry. In: Demers S (ed) Particle analysis in oceanography. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 301–324
Holligan PM, Turner SM, Liss PS (1987) Measurements of dimethylsulphide in frontal regions. Contin Shelf Res 7: 213–224
Holm-Hansen O, Lorenzen CJ, Holmes RW, Strickland JDH (1965) Fluorometric determination of chlorophyll. J Cons perm int Explor Mer 30: 3–15
Huntley ME, Tande K, Eilertsen H-C (1987) On the trophic fate of Phaeocystis pouchetii. II. Grazing rates of Calanus hyperboreus on diatoms and different size categories of P. pouchetii. J exp mar Biol Ecol 110: 197–212
Jonsson GS (1986) Algal blooms in Iceland. Hafrannsóknir. (Mar Res Inst, Reykjavík) 35: 69–75
Karsten U, Wiencke C, Kirst GO (1990a) β-dimethylsulphonio-propionate (DMSP) content of macroalgae from Antarctica and Southern Chile. Botanica mar 33: 143–146
Karsten U, Wiencke C, Kirst GO (1990b) The effect of light intensity and daylength on the β-dimethylsulphoniopropionate (DMSP) content of marine green macroalgae from Antarctica. Pl, Cell Envir 13: 989–993
Keller MD (1991) Dimethyl sulfide production and marine phytoplankton: the importance of species composition and cell size. Biol Oceanogr 6: 375–382
Keller MD, Bellows WK, Guillard RRL (1989) Dimethyl sulfide production in marine phytoplankton. In: Saltzman ES, Cooper WJ (eds) Biogenic sulfur in the environment. Vol. 393. American Chemical Society. Washington, DC, pp 167–182
Kiene RP (1990) Dimethyl sulfide production from dimethylsulfoniopropionate in coastal seawater samples and bacterial cultures. Appl envirl Microbiol 56: 3292–3297
Kiene RP (1992) Dynamics of dimethyl sulfide and dimethylsul-foniopropionate in oceanic water samples. Mar Chem 37: 29–52
Kiene RP, Service SK (1991) Decomposition of dissolved DMSP and DMS in estuarine waters: dependence on temperature and substrate concentration. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 76: 1–11
Lancelot C, Mathot S (1985) Biochemical fractionation of primary production by phytoplankton in Belgian coastal waters during short- and long-term incubations with 14C-bicarbonate. II. Phaeocystis pouchetii colonial population. Mar Biol 86: 227–232
Lancelot C, Mathot S, Owens N (1986) Modeling protein synthesis, a step to an accurate estimate of net primary production: the case of Phaeocystis pouchetii colonies in Belgian coastal water. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 32: 193–202
Lee BG, Fisher NS (1992) Degradation and elemental release rates from phytoplankton debris and their geochemical implications. Limnol Oceanogr 37: 1345–1360
Lewis MR, Smith JC (1983) A small volume, short-incubation-time method for the measurement of photosynthesis as a function of incident irradiance. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 13: 99–102
Matrai PA, Balch WM, Cooper DJ, Saltzman ES (1993) Ocean color and atmospheric DMS: on their mesoscale variability. J geophys Res 98: 23469–23476
Matrai PA, Keller MD (1993) Dimethyl sulphide in a large scale coccolithophorid bloom in the Gulf of Maine. Contin Shelf Res 13: 831–843
Matrai PA, Keller MD (1994) Total organic sulfur and dimethylsul-foniopropionate in marine phytoplankton: intracellular variations. Mar Biol 119: 61–68
Noji TT, Estep KW, MacIntyre F, Norrbin F (1990) Image analysis of faecal material grazed upon by three species of copepods: evidence for coprorhexy, coprophagy, and coprochaly. J mar biol Ass UK 71: 465–480
Palmisano AC, SooHoo JB, SooHoo SL, Kottmeier ST, Graft LL, Sullivan CW (1986) Photoadaptation in Phaeocystis pouchetii advected beneath annual sea ice in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. J Plankton Res 8: 891–906
Passow U, Wassmann P (1994) On the trophic fate of Phaeocystis pouchetii (Hariot). IV. The formation of marine snow by P. pouchetii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 104: 153–161
Platt T, Harrison WG, Irwin B, Horne EP, Gallegos CL (1982) Photosynthesis and photoadaptation of marine phytoplankton in the Arctic. Deep-Sea Res 29: 1159–1170
Pomeroy LR, Deibel D (1986) Temperature regulation of bacterial activity during the spring bloom in Newfoundland coastal waters. Science, NY 233: 359–361
Pomeroy LR, Wiebe WJ (1993) Energy sources for microbial food webs. Mar microb Fd Webs 7: 101–118
Putaud JP, Mihalopoulos N, Nguyen BC, Campin JM, Belviso S (1992) Seasonal variations of atmospheric sulfur dioxide and dimethylsulfide concentrations at Amsterdam Island in the Southern Indian Ocean. J atmos Chem 15: 117–132
Rousseau V, Vaulot D, Casotti R, Cariou V, Lenz J, Gunkel J, Baumann M (1994) The life cycle of Phaeocystis (Prymnesiophyceae): evidence and hypothesis. J mar Syst 5: 23–40
Riemann B, Jensen LM (1991) Measurements of phytoplankton primary production by means of the acidification and bubbling method. J Plankton Res 13: 853–862
Sakshaug E, Holm-Hansen O (1986) Photoadaptation in Antarctic phytoplankton: variations in growth rate, chemical composition and P versus I curves. J Plankton Res 8: 459–473
Smith DC, Simon M, Alldredge AL, Azam F (1992) Intense hydrolytic enzyme activity on marine aggregates and implications for rapid particle dissolution. Nature, Lond 359: 139–142
Smith WO Jr, Codispoti LA, Nelson DM, Manley T, Buskey EJ, Niebauer HJ, Cota G (1991) Importance of Phaeocystis blooms in the high-latitude ocean carbon cycle. Nature, Lond 352: 514–516
Smith WO, Sakshaug E (1990) Polar phytoplankton. In: Smith WO, Jr (ed) Polar oceanography. Part B. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 477–525
Steeman Nielsen E (1952) The use of radio-active carbon for measuring organic production in the sea. J Cons perm int Explor Mer 18: 117–140
Stefels J, van Boekel WHM (1993) Production of DMS from dissolved DMSP in axenic cultures of the marine phytoplankton species Phaeocystis sp. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 97: 11–18
Thingstad F, Billen G (1994) Microbial degradation of Phaeocystis material in the water column. J mar Syst 5: 55–66
Thingstad F, Martinussen I (1991) Are bacteria active in the cold pelagic ecosystem of the Barents Sea? Polar Res 10: 255–266
Thompson AM, Esaias WE, Iverson RL (1990) Two approaches to determining the sea-to-air flux of dimethyl sulfide: satellite ocean color and a photochemical model with atmospheric measurements. J geophys Res 95: 20551–20558
Turner SM, Malin G, Liss P (1988) The seasonal variation of dimethyl sulfide and dimethylsulfonioprionate concentrations in near-shore waters. Limnol Oceanogr 33: 364–375
Vaivaramurthy A, Andreae MO, Iverson RL (1985) Biosynthesis of dimethylsulfide and dimethyl propiothetin by Hymenomonas carterae in relation to sulfur source and salinity variations. Limnol Oceanogr 30: 59–70
Veldhuis MJW, Admiraal W (1985) Transfer of photosynthetic products in gelatinous colonies of Phaeocystis pouchetii (Haptophyceae) and its effect on the measurement of excretion rate. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 26: 301–304
Veldhuis MJW, Colijn F, Venekamp LAH (1986) The spring bloom of Phaeocystis pouchetii (Haptophyceae) in Dutch coastal waters. Neth J Sea Res 20: 37–48
Verity PG (1981) Effects of temperature, irradiance, and daylength on the marine diatom Leptocylindrus danicus Cleve. 2. Excretion. J exp mar Biol Ecol 55: 159–169
Verity PA, Smayda TJ, Sakshaug E (1990) Photosynthesis, excretion, and growth rates of Phaeocystis colonies and solitary cells. Polar Biol 10: 117–128
Verity PG, Villareal TA, Smayda TJ (1988) Ecological investigations of blooms of colonial Phaeocystis pouchetii. I. Abundance, biochemical composition, and metabolic rates. J Plankton Res 10: 219–248
Vetter YA, Sharp JH (1993) The influence of light intensity on dimethylsulfide production by a marine diatom. Limnol Oceanogr 38: 419–424
Wassmann P, Vernet M, Mitchell BG, Rey F (1990) Mass sedimentation of Phaeocystis pouchetii in the Barents Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 66: 183–195
Zlotnik I, Dubinsky Z (1989) The effect of light and temperature on DOC excretion by phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 34: 831–839
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N.H. Marcus, Tallassee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matrai, P.A., Vernet, M., Hood, R. et al. Light-dependence of carbon and sulfur production by polar clones of the genus Phaeocystis . Marine Biology 124, 157–167 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349157
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349157