Summary
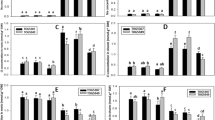
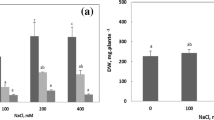
This paper reports the effects of NaCl on the in vivo activity of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) and on the in vitro activity of GDH, both enzymes having been isolated from plants differing in salt tolerance. The plants investigated were Vicia faba (salt-sensitive), Atriplex nitens and Atriplex calotheca (more or less salt-tolerant), and Atriplex halimus (halophyte) grown at various NaCl concentrations. GDH and GOT isolated from various salt-tolerant plants grown at low NaCl concentrations were inhibited in a similar way. At high NaCl concentrations, the enzyme activities remain at constant values only in the Atriplex species. GOT was more impaired by NaCl than GDH. In the case of GOT, the double reciprocal plot indicated the type of a noncompetitive inhibition. The in vitro effect of NaCl on the activity of GDH from the differentially salt-tolerant plants was of a different kind, i.e. GDH isolated from V. faba was clearly inhibited by NaCl, whereas NaCl stimulated the activity of GDH from all Atriplex species investigated. Kinetic analysis showed that substrate inhibition of GDH from A. nitens and A. calotheca grown at non-saline conditions could be removed by NaCl. Inhibition by high NaCl concentrations at low substrate concentrations was removable by increasing substrate concentrations. Moreover, the inhibition at low substrate concentrations was shown to be competitive. GDH lost this regulatory property when the plants were pretreated with 500 mM NaCl. GDH from A. halimus also possessed this control, but in contrast to A. nitens and A. calotheca, activity and control of GDH isolated from A. halimus were stimulated by pretreating the plants with 500 mM NaCl. The results showed that DDH isolated from the salt-tolerant Atriplex species was adapted to high NaCl concentrations of the tissue. Possible mechanisms of the interactions between GDH from salt-tolerant Atriplex species and NaCl are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, R., Kinzel, H.: Unterscheidung von Physiotypen bei Halophyten des Neusiedlerseegebietes (Österreich). Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 70, 138–157 (1973)
Ashby, B., Wootton, J.C., Fincham, J.R.S.: Slow conformational changes of a Neurospora glutamate dehydrogenase studied by protein fluorescence. Biochem. J. 143, 317–329 (1974)
Austenfeld, F.-A.: Der Einfluß des NaCl und anderer Alkalisalze auf die Nitratreduktaseaktivität von Salicornia europaea L. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 71, 288–296 (1974)
Bergmeyer, H.-U.: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1974
Brownell, P.F.: Sodium as an essential micronutrient element for a higher plant (Atriplex vesicaria). Plant Physiol 40, 460–468 (1965)
Brownell, P.F., Crossland, C.J.: Requirement for sodium as a micronutrient by species having the C4-dicarboxylic photosynthetic pathway. Plant Physiol. 49, 794–797 (1972)
Flowers, T.J.: The effects of sodium chloride on enzyme activities from four halophyte species of Chenopodiaceae. Phytochem. 11, 1881–1886 (1972)
Flowers, T.J.: Salt tolerance in Suaeda maritima (L.) Dum. J. Exptl. Bot. 25, 101–110 (1973)
Flowers, T.J., Troke, P.F., Yeo, A.R.: The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28, 89–121 (1977)
Greenway, H., Osmond, C.B.: Salt responses of enzymes from species differing in salt tolerance. Plant Physiol. 49, 256–259 (1972)
Greenway, H., Setter, T.: Effects of chloride salts at high concentrations on glycolysis in vitro. J. Exptl. Bot. 28, 545–558 (1977)
Greenway, H., Sims, A.P.: Effects of high concentrations of KCl and NaCl on response of malate dehyrogenase (decarboxylating) to malate and various inhibitors. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1, 15–29 (1974)
Holmes, P.K., Halvorsan, H.O.: The inactivation and reactivation of salt-requiring enzymes from an extreme obligate halophile. Can. J. Microbiol. 9, 904–906 (1963)
Huber, W.: Über den Einfluß von NaCl- oder Abscisinsäurebehandlung auf den Proteinmetabolismus und einige weitere Enzyme des Aminosäurestoffwechsels in Keimlingen von Pennisetum typhoides. Planta (Berl.) 121, 225–235 (1974)
Huber, W., Kreutmeier, F., Sankhla, N.: Eco-physiological studies on Indian arid zone plants. VI. Effect of sodium chloride and abscisic acid on amino acid and protein metabolism in leaves of Phaseolus aconitifolius. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 81, 234–247 (1977)
Jäger, H.-J., Meyer, H.R.: Effect of water stress on growth and proline metabolism of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Oecologia (Berl.) 30, 83–96 (1977)
Jefferies, R.L.: The ionic relations of the seedlings of the halophyte Triglochin maritima L. In: Ion transport in plants (W.P. Anderson, ed.), London-New York: Academic Press 1973
Kalir, A., Poljakoff-Mayber, A.: Malic dehydrogenase from Tamarix roots. Effects of sodium chloride in vivo and in vitro. Plant Physiol. 55, 155–162 (1975)
Larsen, H.: Biochemical aspects of extreme halophilism. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1, 97–132 (1967)
Neumann, P., Markau, K., Sund, H.: Studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. Regulation of glutamate dehydrogenase from Candida utilis by a pH and temperature-dependent conformational transition. Europ. J. Biochem. 65, 465–472 (1976)
Osmond, C.B.: Acid metabolism in Atriplex. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 20, 575–587 (1967)
Osmond, C.B.: Ion absorption and carbon metabolism in cells of higher plants. In: Transport in plants, Vol. II, Part A (U. Lüttge, M.G. Pitman, eds.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York, Springer 1976
Osmond, C.B., Greenway, H.: Salt responses of carboxylation enzymes from species differing in salt tolerance. Plant Physiol. 49, 260–263 (1972)
Osmond, C.B., Lüttge, U., West, K.R., Pallaghy, H.: Ion absorption in Atriplex leaf tissues. II. Secretion of ions to epidermal bladders. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 22, 797–814 (1969)
Pahlich, E.: Allosterische Regulation der Aktivität der Glutamat-dehydrogenase aus Erbsenkeimlingen durch das Substrat α-Ketoglutarsäure. Planta (Berl.) 100, 222–227 (1971)
Pahlich, E., Gelleri, B., Kindt, R.: The effect of neutral salt anions on the oxidative deamination activity of plant glutamate dehydrogenase. Planta (Berl.) 138, 161–165 (1978)
Stewart, G.R., Lee, J.A.: The role of proline accumulation in halophytes. Planta (Berl.) 120, 279–289 (1974)
Storey, R., Wyn Jones, R.G.: Quarternary ammonium compounds in plants in relation to salt resistance. Phytochem. 16, 447–453 (1977)
Treichel, S.P., Kirst, G.O., von Willert, D.J.: Veränderung der Aktivität der Phosphoenolpyruvat-Carboxylase durch NaCl bei Halophyten verschiedener Biotope. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 71, 437–449 (1974)
Willert, D.J. von: Der Einfluß von NaCl auf die Atmung und Aktivität der Malatdehydrogenase bei einigen Halophyten und Glykophyten Oecologia (Berl.) 14, 127–137 (1974)
Willert, D.J. von: Der Einfluß von NaCl auf den Vorgang der nächtlichen Malatanhäufung in Blattstreifen des Halophyten Mesembryanthemum cristallinum. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 76, 44–50 (1975)
Wilson, R.H., Evans, H.J.: The effect of potassium and other univalent cations on the conformation of enzymes. In: The role of potassium in agriculture (V.J. Kilmer, S.E. Younts, N.C. Brady, eds.). Madison: Am. Soc. Agron. 1968
Wong, C.H., Jäger, H.-J.: Salt-induced vesiculation in mesophyll cells of Atriplex species. Plant Sci. Let. (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priebe, A., Jäger, HJ. Responses of amino acid metabolizing enzymes from plants differing in salt tolerance to NaCl. Oecologia 36, 307–315 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348056
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348056