Summary
A grassland primary producer model for simulating intraseasonal biomass dynamics as a function of temperature, moisture, light, and nitrogen was developed for Bouteloua gracilis (H.B.K.) Lag., the dominant C4 grass of the North American shortgrass prairie. Plant state variables included young and mature leaves, crowns, and roots from three depth categories while simulated processes included spring regrowth, photosynthesis, respiration, photosynthate allocation, death, and litterfall. Sensitivity analyses revealed the model was most sensitive to changes in photosynthesis and photosynthate allocation and least sensitive to changes in initial values of state variables, leaf dark respiration rates, and rate of spring regrowth.
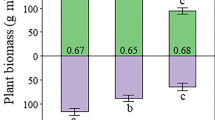
An abiotic submodel driven by observed weather data was used in conjunction with the primary producer model to simulate plant biomass dynamics under a variety of conditions including untreated controls (C), nitrogen fertilization (F), irrigation (I), and irrigation plus fertilization (IF). Model predictions of life shoot biomass (B s) and annual aboveground net primary production (NPP A) followed the same trends as field measurements with B sand NPP Aof IF>I>F>C. Failure of the model to accurately predict measured declines in peak B sand NPP Aafter several years of irrigation may have been caused by failure to account for growth lags following water stress, inadequate simulation of interspecific competition, or failure to simulate response to some mineral nutrients which had become limiting after several years of this treatment. A simulated annual carbon budget for plants in the four treatments suggests that from 61% (IF) to 80% (C) of the net carbon fixed above ground is ultimately translocated and utilized below ground.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ares, J.: Dynamics of the root system of blue grama. J. Range Manage. 29, 208–213 (1976)
Barlow, E.W.R., Boersma, L., Young, J.L.: Photosynthesis, transpiration and leaf elongation in corn seedlings at suboptimal soil temperature. Agron. J. 69, 95–100 (1977)
Bartos, D.L., Jameson, D.A.: A dynamic root model. Am. Midl. Nat. 91, 499–504 (1974)
Benedict, H.M., Brown, G.B.: The growth and carbohydrate responses of Agropyron smithii and Bouteloua gracilis to changes in nitrogen supply. Plant Physiol. 19, 481–494 (1944)
Black, C.A.: Soil plant relationship, 792 pp. New York: Wiley 1968
Boyer, J.S.: Leaf enlargement and metabolic rates in corn, soybean, and sunflower at various leaf water potentials. Plant Physiol. 46, 233–235 (1970)
Bray, J.R.: Root production and the estimation of net productivity. Can. J. Bot. 41, 65–72 (1963)
Brown, L.F., Trlica, M.J.: Interacting effects of soil water, temperature and irradiance on CO2 exchange rates of two dominant grasses of the shortgrass prairie. J. Appl. Ecol. 14, 197–204 (1977a)
Brown, L.F., Trlica, M.J.: Carbon dioxide exchange of blue grama swards as influenced by several ecological variables in the field. J. Appl. Ecol. 14, 205–213 (1977b)
Caldwell, M.M., White, R.S., Moore, R.T., Camp, L.B.: Carbon balance, productivity and water use of cold-winter desert shrub communities dominanted by C3 and C4 species. Oecologia (Berl.) 29, 275–300 (1977)
Catský, J., Tichá, I., Sólarová, J.: Ontogenetic changes in the internal limitations to bean leaf photosynthesis. I. Carbon dioxide exchanges and conductance for carbon dioxide transfer. Photosynthetica 10, 394–402 (1976)
Chollet, R., Ogren, W.L.: Regulation of photorespiration in C3 and C4 species. Bot. Rev. 41, 137–179 (1975)
Christie, E.K.: Physiological response of semiarid grasses. IV. Photosynthetic rates of Thyridolepis mitchelliana and Chenchrus ciliaris leaves. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 26, 459–466 (1975)
Chu, A.C.P., McPherson, H.G.: Sensitivity to desiccation of leaf extension in prairie grass. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 4, 381–387 (1977)
Clark, F.E., Coleman, D.C.: Secondary productivity below ground in Pawnee Grassland, 1971, 23 pp. US/IBP Grassland Biome Tech. Rep. No. 169, Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, Colorado (1972)
Coleman, D.C.: Compartmental analysis of “total soil respiration”: an exploratory study. Oikos 24, 361–366 (1973)
Coleman, D.C., Andrews, R., Ellis, J.S.: Energy flow and partitioning in selected man-managed and natural ecosystems. Agro-Ecosystems 3, 45–54 (1976)
Davidson, R.L.: Effects of soil nutrients and moisture on root/shoot ratios in Lolium perenne L. and Trifolium repens L. Ann. Bot. 33, 571–577 (1969)
Detling, J.K., Parton, W.J., Hunt, H.W.: An empirical model for estimating CO2 exchange of Bouteloua gracilis (H.B.K.) Lag. in the shortgrass prairie. Oecologia (Berl.) 33, 137–147 (1978)
Dickinson, C.E., Dodd, J.L.: Phenological pattern in the shortgrass prairie. Am. Midl. Nat. 96, 367–378 (1976)
Dickman, D.I.: Photosynthesis and respiration by developing leaves of cottonwood (Populus deltoides Bartr.). Bot. Gaz. 132, 253–259 (1971)
Dodd, J.L., Lauenroth, W.K.: Analysis of the response of a grassland ecosystem to stress. In: Perspectives in grassland ecology (N.R. French, ed.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978 (in press)
Duncan, W.G., Loomis, R.W., Williams, W.A., Hannu, R.: A model for simulating photosynthesis in plant communities. Hilgardia 38, 181–205 (1967)
Fick, C.W., Loomis, R.W., Williams, W.A.: Sugar beet. In: Crop physiology: Some case studies (L.T. Evans, ed.), pp. 259–295. London: Cambridge Univ. Press 1974
Gifford, R.M.: A comparison of potential phototsynthesis, productivity and yield of plant species with differing photosynthetic metabolism. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1, 107–117 (1974)
Gilmanov, T.G.: Plant submodel in the holistic model of a grassland ecosystem (with special attention to the belowground part). Ecol. Model. 3, 149–163 (1977)
Herman, R.P.: Root contribution to “total soil respiration” in a tallgrass prairie. Am. Midl. Nat. 98, 227–232 (1977)
Herman, R.P., Kucera, C.L.: Vegetation management and microbial function in a tallgrass prairie. Iowa State J. Res. 50, 255–260 (1975)
Holt, D.A., Bula, R.J., Miles, G.E., Schreiber, M.M., Peart, R.M.: Environmental physiology, modeling and simulation of alfalfa growth: I. Conceptural development of SIMED, 26 pp. Purdue Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Bull. 907, Purdue Univ., Lafayette, Indiana (1975)
Hsiao, T.C.: Plant responses to water stress. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 24, 519–570 (1970)
Hughes, A.P.: A comparison of the effects of light intensity and duration on Chrysanthemum morifolium cv. Bright Golden Anne in controlled environments. Ann. Bot. 37, 267–274 (1973)
Hunt, R.: Further observations on root/shoot equilibrium in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Ann. Bot. 39, 745–755 (1975)
Hylton, L.O., Ulrich, A., Cornelius, D.R.: Comparison of nitrogen constituents as indicators of the nitrogen status of Italian ryegrass, and relation to top to root growth. Crop Sci. 5, 21–22 (1965)
Innis, G.S. (ed.): Ecological studies, Vol. 26, Grassland simulation model, 298 pp. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978a
Innis, G.S.: Objectives and structure for a grassland simulation model. In: Ecological studies, Vol. 26, Grassland simulation model (G.S. Innis, ed.), pp. 1–21. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978b
Jewiss, O.R., Woledge, J.: The effect of age on the rate of apparent photosynthesis in leaves of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.). Ann. Bot. 31, 661–671 (1967)
Kemp, P.R.: Niche divergence between Agropyron smithii, C3, and Bouteloua gracilis, C4: A study of the role of differing photosynthetic pathways in the shortgrass prairie ecosystem. Ph.D. Diss., Washington State Univ., Pullman, Washington (1977)
Knight, D.H.: Leaf area dynamics of a shortgrass prairie in Colorado. Ecology 54, 891–896 (1973)
Lauenroth, W.K., Dodd, J.L., Sims, P.L.: The effects of water-and nitrogen-induced stresses on plant community structure in a semiarid grassland. Oecologia (Berl.) 36, 211–222 (1978)
Ludlow, M.M.: Effect of water stress on the decline of leaf net photosynthesis with age. In: Environmental and biological control of photosynthesis (R. Marcelle, ed.), pp. 123–134. The Hague: Junk 1975
Ludlow, M.M.: Ecophysiology of C4 grasses. In: Ecological studies, Vol. 19, Water and plant life (O.L. Lange, L. Kappen, E.D. Schulze, eds.), pp. 364–386. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Ludlow, M.M., Ng, T.T.: Water stress suspends leaf aging. Plant Sci. Lett. 3, 235–240 (1974)
Ludlow, M.M., Ng, T.T.: Leaf elongation rate in Panicum maximum var. Trichoglume following removal of water stress. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 4, 263–272 (1977)
Ludlow, M.M., Wilson, G.L.: Studies on the productivity of tropical pasture plants. I. Growth analysis, photosynthesis, and respiration on Hamil grass and Siratro in a controlled environment. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 19, 35–45 (1968)
Majerus, M.E.: Response of root and shoot growth of three grass species to decrease in soil water potential. J. Range Manage. 28, 473–476 (1975)
McCree, K.J., Troughton, J.M.: Nonexistence of an optimum leaf area index for the production rate of white clover under constant conditions. Plant Physiol. 41, 1615–1622 (1966)
McNaughton, S.J.: Developmental control of net productivity in Typha latifolia ecotypes. Ecology 55, 864–869 (1974)
Menke, J.W.: Effects of defoliation on carbohydrate reserves, vigor and herbage yield for several important Colorado range species. Ph.D. Diss., Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, 283 pp. (1973)
Mooney, H.A.: The carbon balance of plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 3, 315–346 (1972)
Ng, T.T., Wilson, J.R., Ludlow, M.M.: Influence of water stress on water relations and growth of a tropical (C4) grass, Panicum maximum var. Trichoglume. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 2, 581–595 (1975)
Parton, W.J.: Abiotic section of ELM. In: Ecological studies, Vol. 26, Grassland simulation model (G.S. Innis, ed.), pp. 31–53. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978
Parton, W.J., Singh, J.S., Coleman, D.C.: A model of production and turnover of roots in shortgrass prairie. J. Appl. Ecol. 47 (in press)
Potter, J.R., Jones, J.W.: Leaf area partitioning as an important factor in growth. Plant Physiol. 59, 10–14 (1977)
Promnitz, L.C.: A photosynthate allocation model for tree growth. Photosynthetica 9, 1–15 (1975)
Redmann, R.E.: Carbon dioxide exchange by native Great Plains grasses. Can. J. Bot. 49, 1341–1345 (1971)
Reed, K.L., Hammerly, E.R., Dinger, B.E., Jarvis, P.G.: An analytical model for field measurement of photosynthesis. J. Appl. Ecol. 13, 925–942 (1976)
Regehr, D.L., Bazzaz, F.A., Boggess, W.R.: Photosynthesis, transpiration, and leaf conductance of Populus deltoides in relation to flooding and drought. Photosynthetica 9, 52–61 (1975)
Risser, P.G., Johnson, F.L.: Carbon dioxide exchange characteristics of some prairie seedlings. Southwest. Nat. 18, 85–91 (1973)
Running, S.W., Waring, R.H., Rydell, R.A.: Physiological control of water flux in conifers: A computer simulation model. Oecologia (Berl.) 18, 1–16 (1975)
Sauer, R.H.: A simulation model for grassland primary producer phenology and biomass dynamics. In: Ecological studies, Vol. 26, Grassland simulation model (G.S. Innis, ed.), pp. 55–87. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978
Schulze, E.D., Lange, O.L., Evenari, M., Kappen, L., Vuschbom, V.: An empirical model of net photosynthesis for the desert plant Hammada scorparia (Pomel) Iljim. I. Description and test of the model. Oecologia (Berl.) 22, 355–372 (1976)
Scott, J.R., French, N.R., Leetham, J.W.: Patterns of consumption in grasslands. In: Perspectives in grassland ecology (N.R. French, ed.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978 (in press)
Seligman, N.G., Van Keulen, H., Goudriaan, J.: An elementary model of nitrogen uptake and redistribution by annual plant species. Oecologia (Berl.) 21, 243–261 (1975)
Sheehy, J.E., Green, R.M., Robson, M.J.: The influence of water stress on the photosynthesis of a simulated sward of perennial ryegrass. Ann. Bot. 39, 387–401 (1975)
Sinclair, T.R., Murphy, Jr., C.E., Knoerr, K.R.: Development and evaluation of simplified models for simulating canopy photosynthesis and transpiration. J. Appl. Ecol. 13, 813–829 (1976)
Singh, J.S., Coleman, D.C.: Distribution of photo-assimilated 14carbon in the root system of a shortgrass prairie. J. Ecol. 62, 359–365 (1974)
Singh, J.S., Coleman, D.C.: Evaluation of functional root biomass and translocation of photoassimilated 14carbon in a shortgrass prairie ecosystem. In: The belowground ecosystem: A synthesis of plantassociated processes (J.K. Marshall, ed.), pp. 123–131. Range Sci. Dep. Sci. Ser. No. 26, Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, Colorad (1977)
Strain, B.R., Higginbotham, K.O., Mulroy, J.C.: Temperature preconditioning and photosynthetic capacity of Pinus taeda L. Photosynthetica 16, 47–53 (1976)
Struik, G.J., Bray, J.R.: Root/shoot ratios of native forest herbs and Zea mays at different soil moisture levels. Ecology 51, 892–893 (1970)
Stubbendieck, J., Burzlaff, D.F.: Effects of temperature and day length on axillary bud and tiller development in blue grama. J. Range Manage. 23, 63–66 (1970)
Thornley, J.H.M.: A model to describe the partitioning of photosynthate during vegetative plant growth. Ann. Bot. 36, 419–430 (1972a)
Thornley, J.H.M.: A balanced quantitative model for root: shoot ratios in vegetative plants. Ann. Bot. 36, 431–441 (1972b)
Thornley, J.H.M.: Mathematical models in plant physiology, 318 pp. New York: Academic Press 1976
Troughton, A.: Relationship between the root and shoot systems of grasses. In: The belowground ecosystem: A synthesis of plant-associated processes (J.K. Marshall, ed.), pp. 39–51. Range Sci. Dep. Sci. Ser. No. 26, Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, Colorado (1977)
Wardlaw, I.F.: The control and pattern of movement of carbohydrates in plants. Bot. Rev. 34, 79–105 (1968)
Wardlaw, J.F.: The effect of water stress on translocation in relation to photosynthesis and growth. II. Effect during leaf development in Lolium temulentum L. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 22, 1–16 (1969)
Waring, R.H., Running, S.W.: Water uptake, storage and transpiration by conifers: A physiological model. In: Ecological studies, Vol. 19, Water and plant life (O.L. Lange, L. Kappen, E.-D. Schulze, eds.), pp. 189–202. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Williams, G.J., III: Photosynthetic adaptation to temperature in C3 and C4 grasses. A possible ecological role in the shortgrass prairie. Plant Physiol. 54, 709–711 (1974)
Williams, G.J., III, Kemp, P.R.: Simultaneous measurement of leaf and root gas exchange of shortgrass prairie species. Bot. Gaz. 139, 150–157 (1978)
Williams, J.: Root density and water potential gradients near the plant root. J. Exp. Bot. 25, 669–674 (1974)
Williams, R.D.: Assimilation and translocation in perennial grasses. Ann. Bot. 28, 419–426 (1964)
Wilson, J.R.: Comparative response to nitrogen deficiency of a tropical and temperature grass in the interrelation between photosynthesis, growth, and the accumulation of non-structural carbohydrate. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 23, 104–112 (1975)
Woledge, J.: The effects of shading and cutting treatments on the photosynthetic rate of ryegrass leaves. Ann. Bot. 41, 1279–1286 (1977)
Woodmansee, R.G.: Critique and analyses of the grassland ecosystem model ELM. In: Ecological studies, Vol. 26, Grassland simulation model (G.S. Innis, ed.), pp. 257–281. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Detling, J.K., Parton, W.J. & Hunt, H.W. A simulation model of Bouteloua gracilis biomass dynamics on the North American shortgrass prairie. Oecologia 38, 167–191 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346562
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346562