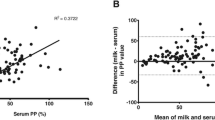
Abstract
A newly developed milk dot blot test was used to detect anti-bovine leukaemia virus (BLV) antibody in milk samples from 2079 lactating adult cows from among 61 herds. The milk dot blot test was highly repeatable; the concordance rate, compared with the agar gel immunodiffusion test performed on serum, was 83.5%. All herds contained BLV-positive cows; the prevalence rate was 36%. BLV-positive cows tended to come from larger herds and were older and more often later in lactation. Fourteen production and related variables (herd size, age, days open, days in milk, milk somatic cell count, milk, fat, and protein produced in the current lactation, projected production of milk, fat, and protein, and breed class average deviations for milk, fat, and protein) were compared between BLV-positive and BLV-negative cows. Although somatic cell count, milk produced, and projected production of milk and protein were related significantly to BLV status using simple tests of association, once the variables herd size, age and days in milk were controlled, these differences were removed. Further analyses using logistic (outcome: individual cow BLV status) and least-squares regression (outcome:herd proportion of BLV-positive cows) failed to show an association between any of the measured production or related variables and BLV-positivity. We concluded that the effect of BLV on production and related variables in dairy cows was below the sensitivity of our analytical techniques or was non-existent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABCA:
-
herd average breed class average for milk, fat, and protein production
- AVGAGE:
-
average age of the herd
- ADIM:
-
herd average for days in milk
- AGID:
-
agar gel immunodiffusion
- AVGSCC:
-
herd average milk somatic cell count
- BCA:
-
breed class average, a milk, fat and protein production index calculated by comparing a cow's actual 305-day lactation production to the corresponding BCA standard for the same breed, age, and month of calving
- BLV:
-
bovine leukaemia virus
- CALVINT:
-
calving interval
- COWAGE:
-
cow age
- DBCA:
-
breed class average deviation for milk, fat, and protein production, the difference between an individual cow's BCA and the herd average
- DIM:
-
days in milk
- HS:
-
herd size corresponding to the number of lactating cows in a herd
- LACT:
-
actual amount of milk, fat, and protein produced in a cow's lactation
- ODHIC:
-
Ontario Dairy Herd Improvement Corporation
- PCTPOS:
-
percentage of herd that is BLV-positive
- PROJ:
-
projected 305-day production for milk, fat, and protein by fitting to a standard lactation curve adjusted for days in milk and age at calving
- RHBCA:
-
rolling herd average for breed class average for milk, fat, and protein production, the average for all cows that completed a lactation (cows must have completed a 305-day lactation) during the previous 12 months
- SCC:
-
milk somatic cell count
References
Baumgartner, L.E., Olson, C., Miller, J.M. and Van derMaaten, M.J., 1975. Survey for antibodies to leukemia (C-type) virus in cattle. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 166, 249–251
Brenner, J., Meirom, B., Avraham, R., Savir, D. and Trainen, Z., 1988. Trial of two methods of the eradication of bovine leukosis virus (BLV) infection from two large dairy herds in Israel. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 22, 168–175
Brenner, J., Van-Haam, M., Savir, D. and Trainen, Z., 1989. The implication of BLV infection in the productivity, reproductive capacity and survival rate of a dairy cow. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 22, 299–305
Burny, A., Bruck, C., Chantrenne, H., Cleuter, Y., Dekegel, D., Ghysdael, J., Kettmann, R., Leclarq, M., Leunen, J., Mammerickx, M. and Portetelle, D., 1980. Bovine leukemia virus: molecular biology and epidemiology. In: G.Klein (ed.), Viral Oncology, (Raven Press, New York), 231–289
Burridge, M.J., Wilcox, C.J. and Hennemann, J.M., 1979. Influence of genetic factors on the susceptibility of cattle to bovine leukemia virus infection. European Journal of Cancer, 15, 1395–1400
Burridge, M.J., Puhr, D.M. and Hennemann, J.M., 1981. Prevalence of bovine leukemia virus infection in Florida. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 179, 704–707
Burridge, M.J., Thurmond, M.C., Miller, J.M., Schmerr, M.J.F. and Van derMaaten, M.J., 1982a. Fall in antibody titer to bovine leukemia virus in the periparturient period. Canadian Journal of Comparative Medicine, 46, 270–271
Burridge, M.J., Thurmond, M.C., Puhr, D.M., Wilcox, C.J. and Simeri, N.A., 1982b. Preliminary studies on impact of bovine leukaemia virus infection on dairy productivity. In: O.C.Straub (ed.), Fourth International Symposium on Bovine Leukosis, (Nijhoff, Boston), 599–605
Dohoo, I.R. and Meek, A.H., 1982. Somatic cell counts in bovine milk. Canadian Veterinary Journal, 23, 119–125
Everitt, B., 1989. Statistical Methods for Medical Investigators, (E. Arnold Co., New York), 20–22
Fetrow, J. and Ferrer, J.F., 1982. Bovine leukemia virus infection and mastitis. Journal of Dairy Science, 65, 881–882
Foil, L.D., French, D.D., Hoyt, P.G., Issel, C.J., Leprince, D.J., McManus, J.M. and Seger, C.L., 1989. Transmission of bovine leukemia virus by Tabanus fuscicostatus. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 50, 1771–1773
Gupta, P. and Ferrer, J.F., 1981. Comparison of various serological and direct methods for the diagnosis of BLV infection in cattle. International Journal of Cancer, 28, 179–184
Gottschau, A., Willeberg, P., Franti, C.E. and Flensburg, J.C., 1990. The effect of a control program for enzootic bovine leukosis. Changes in herd prevalence in Denmark, 1969–1978. American Journal of Epidemiology, 131, 356–364
Heeney, J.L. and Valli, V.E.O., 1989. A rapid stick test for the diagnosis of bovine leukemia virus infection from serum or milk. Canadian Veterinary Journal, 30, 9
House, C., House, J.A. and Glover, F.L., 1977. Antibodies to the glycoprotein antigen of bovine leukemia virus in the cattle population of five states. Cornell Veterinrian, 67, 510–522
Huber, N.L., DiGiacomo, R.F., Evermann, J.F. and Studer, E., 1981a. Bovine leukemia virus infection in a large Holstein herd; cohort analysis of the prevalence of antibody-positive cows. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 42, 1474–1476
Huber, N.L., DiGiacomo, R.F., Evermann, J.F. and Studer, E., 1981b. Bovine leukemia virus infection in a large Holstein herd; prospective comparison of production and reproductive performance in antibody-negative and antibody-positive cows. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 42, 1477–1481
Jacobs, R.M., 1986. Bovine lymphoma. In: R.Olsen, S.Krakowka and J.Blakeslee (eds.), Comparative Pathobiology of Viral Diseases, (CRC Reviews, Baton Rouge, FL, USA), 21–51
Langston, A., Ferdinand, G.A.A., Ruppanner, R., Theilen, G.H., Drlica, S. and Behymer D., 1978. Comparison of production variables of bovine leukemia virus antibody-negative and antibody-positive cows in two California dairy herds. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 39, 1093–1098
Lassauzet, M.-L.G., Johnson, W.O. and Thurmond, M.C., 1989. Regression models for time to seroconversion following experimental bovine leukemia virus infection. Statistics in Medicine, 8, 725–741
Lewin, H.A. and Bernoco, D., 1986. Evidence for BoLA-linked resistance and susceptibility to subclinical progression of bovine leukemia virus infection. Animal Genetics, 17, 197–207
Lewin, H.A., Wu, M.-C., Nolan, T.J. and Stewart, J.A., 1988a. Peripheral B lymphocyte percentage as an indicator of subclinical progression of bovine leukemia virus infection. Journal of Dairy Science. 71, 2526–2534
Lewin, H.A., Wu, M.-C., Stewart, J.A. and Nolan, T.J., 1988b. Association between BoLA and subclinical bovine leukemia virus infection in a herd of Holstein-Friesian cows. Immunogenetics, 27, 338–344
Mammerickx, M., 1987. The immunodiffusion tests for the detection of bovine leukemia virus-infected animals. In: A.Burny and M.Mammerickx (eds.), Enzootic Bovine Leukosis and Bovine Leukemia, (Nijhoff, Boston), 195–200
Manet, G., Guilbert, X., Roux, A., Vuillaume, A. and Parodi, A.L., 1989. Natural mode of horizontal transmission of bovine leukemia virus (BLV): the potential role of tabanids (Tabanus spp.). Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 22, 255–263
Mantel, N. and Haenszel, W., 1959. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 22, 719–748
Migaki, G., 1969. Hematopoietic neoplasms of slaughter animals. In: C.H.Lingeman and F.M.Garner (eds.), Comparative Morphology of Hematopoietic Neoplasms, (National Cancer Institute Monograph 32, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda), 121
Miller, L.D., 1980. Export testing for enzootic bovine leukosis. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 177, 620–622
Mix, M.E., 1979. Export significance-industry observations. Proceedings, Bovine Leukosis Symposium Washington, DC, (United States Department of Agriculture), 183–186
Reinhardt, G., Hochstein-Mintzel, V., Riedemann, S. and Niedda, H.L.M., 1988. Estudio serologico de leucosis enzootica bovina en un predio de la provincia de Valdivia y su relaciona parametro, productivos y reproductivos. Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 35(B), 178–185
Sorensen, D.K. and Beal, V.C., 1979. Prevalence and economics of bovine leukosis in the United States. Proceedings, Bovine Leukosis Symposium. College Park, MD, (US Department of Agriculture), 33–50
Stear, M.J., Dimmock, C.K., Newman, M.J. and Nicholas, F.W., 1988. BoLA antigens are associated with increased frequency of persistent lymphocytosis in bovine leukaemia virus infected cattle and with increased incidence of antibodies to bovine leukemia virus. Animal Genetics, 19, 151–158
Thurmond, M.C., 1987. Economics of enzootic bovine leukosis. In: A.Burny and M.Mammerickx (eds.), Enzootic Bovine Leukosis and Bovine Leukemia Virus, (Nijhoff, Boston), 71–84
Thurmond, M.C., Portier, K.M., Puhr, D.M. and Burridge, M.J., 1983. A prospective investigation of bovine leukemia virus infection in young dairy cattle using survival methods. American Journal of Epidemiology, 117, 621–631
Thurmond, M.C., Lapuz, G.R., Farver, T.B. and Mandac, G.C., 1985a. Retrospective study of four years of carcass condemnation rates for malignant lymphoma in California cows. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 46, 1387–1391
Thurmond, M.C., Maden, C.B. and Carter, R.L., 1985b. Cull rates of dairy cattle with antibodies to bovine leukemia virus. Cancer Research, 45, 1987–1989
Ungar-Waron, H. and Trainen, Z., 1987. Immunological aspects of enzootic bovine leukosis. In: A.Burny and M.Mammerickx (eds.), Enzootic Bovine Leukosis and Bovine Leukemia Virus, (Nijhoff, Boston), 163–173
Wu, M.-C., Shanks, R.D. and Lewin, H.A., 1989. Milk and fat production in dairy cattle influenced by advanced subclinical bovine leukemia virus infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 86, 993–996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobs, R.M., Heeney, J.L., Godkin, M.A. et al. Production and related variables in bovine leukaemia virus-infected cows. Veterinary Research Communications 15, 463–474 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346546
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346546