Summary
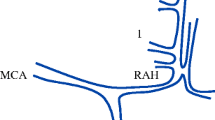
In a group of 50 proselected examples of venous phase of carotid angiography the definition and delining of the position of the posterior ventricular branches of the internal cerebral and basilar vein in 2 projections was made. The relative frequences of these veins were recorded. The medial atrial vein was found to be the prevailing vessel in this region.
Résumé
L'étude de 50 phlébogrammes profonds nous a permis de définir les branches postérieures ventriculaires de la veine cérébrale interne et de la veine basilaire de Rosenthal. La relative fréquence de ces veines a été estimée, la veine médiale atriale ou veine médiane du carrefour ventriculaire étant la plus fréquente.
Zusammenfassung
Anhand von 50 ausgewählten, technisch einwandfreien Carotis-Angiogrammen wurde versucht, die hintern ventrikulären Äste der V. cerebralis interna und der V. basilaris in 2 Ebenen zu bestimmen. —Die in dieser Region am häufigsten auftretende Vene war: The medial atrial vein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, Y.P., Wolf, B.S.: Veins of the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres. (The medullary veins). Amer. J. Roentgenol. 92, 739–755 (1964).
Johanson, C.: The central veins and deep dural sinuses. An anatomical and angiographic study. Acta radiol. Suppl. 107, 1–1084 (1954).
Laine, E., Delandtsheer, J., Galibert, P., Delandtsheer-Arnott, G.: Les données plébographiques dans les tumeurs des hémisphères cérébraux et des noyaux gris centraux. J. Radiol. Électrol. 37, 368–374 (1956).
Padget, D.H.: The cranial venous system in man in reference to development, adult configuration, and relation to the arteries. Amer. J. Anat. 98, 307–340 (1956).
Paturet, G.: Système nerveux. T. IV, 452–454. Paris: Masson 1964.
Schlesinger, B.: Venous drainage of brain, with special reference to galenic system. Brain 62, 274–291 (939).
Wolf, B.S., Huang, Y.P.: Subependymal veins of lateral ventricles. Amer. J. Roentgenol. 91, 406–426 (1964).
—, Newman, C.M., Schlesinger, B.: Diagnostic value of deep cerebral veins in cerebral angiography. Radiology 64, 161–177 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billewicz, O., Ben-Amor, M. The posterior ventricular branches of the internal cerebral and basilar vein. Neuroradiology 2, 37–45 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345870
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345870