Summary
In a rat muscle spindle transversally cut into a series of alternating semithin and ultrathin sections, two different forms of nerve terminations were found on two neighbouring nuclear chain fibres. The two nerve terminations were connected to the same group II nerve fibre and are consequently constituents of one particular secondary sensory ending.
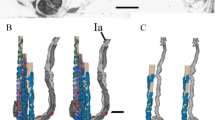
The nerve termination on one of the two nuclear chain fibres is of the anulo-spiral type.
The nerve termination on the second nuclear chain fibre shows a number of axons lying closely together between plasma membrane and basement membrane of the intrafusal muscle fibre. Not all of these axons are in direct contact with the intrafusal fibre. The terminating nerve fibre seems to be divided into several branches of rather small diameters and irregular courses. It is suggested that this kind of termination could be a correlate of the so-called “flower spray” type of sensory endings in muscle spindles.
The two morphologically different nerve terminations in the secondary ending have the following ultrastructural characteristics in common with those of the primary ending: 1) Synaptic contact between axon and intrafusal muscle fibre (synaptic gap about 200 Å) without interposition of basement membrane material; 2) terminal axons located beneath the basement membrane layer of intrafusal muscle fibres without covering by Schwann cells; 3) lack of synaptic vesicles; 4) desmosome-like structures between plasma membranes of axon and intrafusal muscle fibre, and 5) dyads of the sarcoplasmic reticulum adjacent to the synaptic cleft. According to present knowledge these features indicate that all of these endings are sensory ones.
Zusammenfassung
In einer Muskelspindel der Ratte, die an einer Serie alternierender Semidünn- und Ultradünnquerschnitte untersucht wurde, wurden zwei benachbart an „nuclear chain“-Fasern gelegene Nervenendformationen unterschiedlicher Bauweise festgestellt. Die beiden Endformationen sind mit ein und derselben Nervenfaser der Gruppe II verbunden und daher als Bestandteile einer sekundären sensorischen Endigung zu betrachten.
Die Nervenendformation an einer der beiden „nuclear chain“-Fasern hat anulo-spirale Form.
Die Nervenendformation an der anderen „nuclear chain“-Faser weist am Querschnittsbild eine Anzahl von Axonen auf, die zwischen Plasmalemm und Basalmembran der intrafusalen Muskelfaser eng aneinanderliegen. Nicht alle Axonquerschnitte stehen in direktem Kontakt mit der intrafusalen Faser. Das terminale Axon scheint sieh nach Eintritt unter die Basalmembran der intrafusalen Faser mehrfach in relativ dünne Äste unregelmäßigen Verlaufs zu teilen. Diese Form der Endigung könnte ein Korrelat der sog. „flower spray“-Endigung im Sinne Ruffinis (1898) darstellen.
Die beiden morphologisch unterschiedlichen Endformationen innerhalb der sekundären Endigung gleichen einander und den Endformationen der primären Endigung bezüglich folgender Ultrastrukturmerkmale: 1. Es besteht synaptischer Kontakt zwischen Axon und intrafusaler Muskelfaser (synaptischer Spalt durchschnittlich 200 Å) ohne Zwischenlagerung von Basalmembranmaterial; 2. die terminalen Axonabschnitte liegen direkt unter der Basalmembran der intrafusalen Muskelfaser und sind nicht von Schwannschen Zellen bedeckt; 3. Mangel an synaptischen Bläschen; 4. desmosomenartige Verhaftungen zwischen Zellmembranen von Axon und intrafusaler Faser; 5. dyadenartige Anlagerungen des sarkoplasmatischen Retikulums an die Zellmembran der intrafusalen Faser im Bereich des synaptischen Spaltes.
Nach unseren derzeitigen Vorstellungen sprechen diese Ultrastrukturmerkmale für eine rezeptorische Natur der beschriebenen Nervenendigungen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adal, M. N.: The fine structure of the sensory region of cat muscle spindles. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 332–354 (1969).
Andres, K. H.: Zur Methodik der Perfusionsfixierung des Zentralnervensystems von Säugern. Tagg. der Niederländ. u. Dtsch. Elektronenmikroskopischen Gesellschaften, Aachen 1965.
Barker, D.: The innervation of mammalian skeletal muscle. In: Ciba Foundation Symposium on myotatic, kinesthetic and vestibular mechanisms (A. V. S. de Reuck and J. Knight, eds.), p. 3–15. London: J. & A. Churchill Ltd. 1967.
—, Ip, M. C.: The primary and secondary endings of the mammalian muscle spindle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 153, 8P-10P (1960).
Boyd, I. A.: The structure and innervation of the nuclear bag muscle fibre system and the nuclear chain muscle fibre system in mammalian muscle spindles. Phil. Trans. B 245, 81–136 (1962).
Corvaja, N., Marinozzi, V., Pompeiano, O.: Muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscle of the cat. Arch. ital. Biol. 107, 365–543 (1969).
During, M. v., Andres, K. H.: Zur Feinstruktur der Muskelspindel von Mammalia. Anat. Anz. 124, 566–573 (1969).
Gruner, J.-E.: La structure fine du fuseau neuromusculaire humain. Rev. neurol. 104, 490–507 (1962).
Hennig, G.: Die Nervenendigungen der Rattenmuskelspindel im elektronen- und phasenkontrastmikroskopischen Bild. Z. Zellforsch. 96, 275–294 (1969).
Karlsson, U., Andersson-Cedergren, E.: Motor myoneural junction on frog intrafusal muscle fibers. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 14, 191–211 (1966).
Landon, D. N.: Electron microscopy of muscle spindles. In: Control and innervation of skeletal muscle (B. L. Andrew, ed.), p. 96–110. Dundee, Scotland: D. C. Thomson & Co., Ltd. 1966.
Lloyd, D., Chang, H.: Afferent fibres in muscle nerves. J. Neurophysiol. 11, 199–208 (1948).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Mayr, R.: Untersuchungen an isolierten Muskelspindeln der Ratte nach Cholinesterasedarstellung und Sudanschwarz-Färbung. Z. Zellforsch. 93, 594–606 (1969).
—, Zenker, W.: Narrowings of the synaptic cleft in myoneural junctions. Experientia (Basel) 25, 1319–1321 (1969).
Merrillees, N. C. R.: The fine structure of muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscles of the rat. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 725–742 (1960).
Mukuno, K., Nomura, T.: Fine structure of muscle spindles in the human extraocular muscles. Acta Soc. Ophthalmol. Jap. 73, 2119–2127 (1969).
Rexed, B., Therman, P.: Calibre spectra of motor and sensory nerve fibers to flexor and extensor muscles. J. Neurophysiol. 11, 133–139 (1948).
Ruffini, A.: On the minute anatomy of the neuromuscular spindles of the cat, and on their physiological significance. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 23, 190–208 (1898).
Rumpelt, H.-J., Schmalbruch, H.: Zur Morphologie der Bauelemente von Muskelspindeln bei Mensch und Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 102, 601–630 (1969).
Teräväinen, H.: Axonal protrusions in the small multiple endings in the extraocular muscles of the rat. Z. Zellforsch. 96, 206–211 (1969).
Zenker, W., Krammer, E.: Untersuchungen über Feinstruktur und Innervation der inneren Augenmuskulatur des Huhnes. Z. Zellforsch. 83, 147–168 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Gekürzt vorgetragen an der gemeinsamen Tagung der Österreichischen Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Ultrastrukturforschung und der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Elektronenmikroskopie e.V., Wien, 22.–25. 9. 69.
Für wertvolle technische Mitarbeit danke ich Frau Gudrun Schran.
Derzeit am 2. Anatomischen Institut der Universität Wien (Prof. Dr. W. Zenker).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayr, R. Zwei elektronenmikroskopisch unterscheidbare Formen sekundärer sensorischer Endigungen in einer Muskelspindel der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 110, 97–107 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00343988
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00343988