Summary
The structures formerly described as “blood-forming organs” or “lymph glands” in Drosophila melanogaster were re-examined by means of phase contrast, polarized light, and electron microscopy. As a result, the term “haemolymph organ” is suggested as more appropriate for these peculiar organs. Haemolymph organs of second and third instar larvae, and first stage (white) pupae from a wild strain (Varese) were studied; the methods are described in detail.
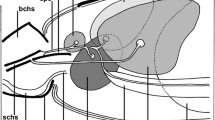
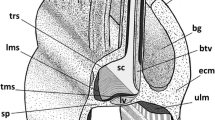
The haemolymph organ consists of two voluminous anterior lobes and several smaller posterior ones that are ovoid or tubular in shape. The anterior lobes comprise an outer capsule containing some muscle cells, a supporting stroma, and various kinds of cells. The stroma appears to consist of lamellated material of scleroprotein nature similar to that described in other organs of numerous insect species. This material must be considered as a component of the connective tissue characteristic of insect organs.
The cells are isolated or organized in groups of various sizes. The following types can be distinguished: rounded cells that are poorly differentiated, polygonal cells with well developed cytoplasm rich in organelles, polygonal cells with clear cytoplasm, and cells that appear to be intermediate form of the types mentioned above.
The morphological data presented confirm that the haemolymph organ produces and releases into the haemolymph various types of cells; of these the polygonal cells have a phagocytic and excretory function while only hypotheses can be presented at present concerning the role of the rounded cells. In addition the presence of polygonal cells with clear cytoplasm, showing signs of secretory activity, suggest that the haemolymph organ is involved in the production of substances constituting the fluid fraction of the haemolymph.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliografia
Andrè, J.: Contribution à la connaissance du chondriome. J. Ultrastruct. Res., Suppl. 3, 1–185 (1962).
Ashford, T. P., and K. R. Porter: Cytoplasmic components in hepatic cell lysosomes. J. Cell. biol. 12, 198–202 (1962).
Baccetti, B.: Lo stroma di sostegno di organi degli insetti esaminato a luce polarizzata. Redia 41, 259–276 (1959).
: Ricerche sull'ultrastruttura dell'intestino degli insetti. L'ileo di un ortottero adulto. Redia 45, 263–278 (1960).
: Primi reperti sulla struttura submicroscopica dello stroma di sostegno di alcuni organi degli insetti. Atti Acad. Sci. Torino 95, 343–350 (1961).
: Indagini ultramicroscopiche sul problema della costituzione delle tuniche peritoneali ovariche e dell'esistenza negli insetti di fibre muscolari liscie. Redia 48, 1–13 (1963).
Bairati jr., A.: Preliminary observations on the ultrastructure of the lymph gland cells of Drosophila melanogaster. In: Electron Microscopy. Fifth Int. Cong. Elec. Micr. Philadelphia 1962. vol. IIℴ, sez. 00–13. New York and London: Academic Press 1962.
Barigozzi, C.: Ereditarietà semimendeliana in Drosophila e sua relazione con la ereditarietà episomica. Atti A.G.I. 7, 9–76 (1962).
, M. C. Castiglioni and A. Di Pasquale: A complex genotype controlling the production of melanotic tumours (pseudotumours) in Drosophila. Heredity 14, 151–162 (1960).
: Melanotic tumours of Drosophila a partially Mendelian character. Heredity 17, 561–575 (1962).
Behnke, O.: Lysosomes in differentiating epithelium of the small intestine. Proc. Scand. Elec. Micr. Soc. 1962. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 8, 191 (1963).
Bennet, H. S.: The structure of striated muscle as seen by electron microscope. In: The structure and function of muscle, ed. G. H. Bourne, p. 137–181. New York and London: Academic Press 1960.
Berkaloff, A.: Contribution a l'étude des tubes de Malpighi et de l'excrétion chez les insectes. Observations au microscope électronique. Ann. Sci. natur. Zool. 12a, 869–947 (1960).
Castiglioni, M. C.: Nuove osservazioni sulla produzione degli pseudotumori in Drosophila melanogaster. Atti A.G.I. 2ℴ Riun. La Ric. Sci., Suppl. 26, 125–131 (1956).
: Le cellule dell'emolinfa di Drosophila melanogaster in relazione al genotipo e alla produzione degli pseudotumori. Atti A.G.I. 3ℴ Riun. La Ric. Sci., Suppl. 27, 51–57 (1957).
: The behaviour of the lymph gland and the migrant haemolymph cells, in different genotypes of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. X0 Int. Cong. of Genetics 2, 46 (1958).
Chauvin, R.: Physiologie de l'Insecte, p. 319. Paris: I.N.R.A. 1956.
Dalton, A. J.: A crome-osmium-fixative for electron microscopy. Anat. Rec. 121, 281 (1955).
Demerec, M.: Biology of Drosophila, p. 181. New York: J. Wiley & Sons 1950.
Duve, C. de: Lysosomes, a new group of cytoplasmic particles. In: Subcellular particles, Ed. T. Hayashi, p. 128–159. New York: Ronald Press Co. 1959.
El Shatoury, H. H.: The structure of the lymph glands of Drosophila larvae. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org. 147, 489–495 (1955a).
: A genetically controlled malignant tumours in Drosophila. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org. 147, 496–510 (1955b).
: Functions of the lymph glands cells during the larval period of Drosophila. J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 5, 122–133 (1957).
Gay, H.: Chromosome-nuclear menbrane-cytoplasmic interrelations in Drosophila. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 407–415 (1956).
Grandi, G.: Introduzione allo studio dell'entomologia, p. 188. Bologna: Ed. Agricole 1951.
Guidotti, G., E. Clerici e E. Bazzano: Incorporazione, in aerobiosi ed in anaerobiosi, della glicina-I-14C nelle proteine del fegato normale e rigenerante di ratto. Ricerca in vitro. Minerva nucl. 2, 14–17 (1958).
joyHalfer, C.: Esperimenti di selezione sul ceppo „e 144 melanotic“ di Drosophila melanogaster. Tesi di Laurea. Ist. Genetica Univ. Milano 1959.
: Risposta allc selezione di diversi livelli di struttura microscopica dei tumori melanotici di Drosophila melanogaster (ceppo melanotic e 144). Ist. Lomb. (Red. Sci.) B 95, 3–25 (1961).
Hruban, Z., H. Swift and R. W. Wissler: Analog-induced inclusions in pancreatic acinar cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 7, 273–285 (1962).
King, R. C.: Oogenesis in adult Drosophila melanogaster. IX. Studies on the cytochemistry and ultrastructure of developing oocytes. Growth 24, 265–323 (1960).
Kurosumi, K.: Electron microscopic analysis of the secretion mechanism. In: Int. Rev. Cytol, Ed. Bourne and Danielli, vol. XI, p. 1–124. New York and London: Academic Press 1961.
Luft, J. H.: Permanganate a new fixative for electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 799–801 (1956).
: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Millonig, G.: Further observations on a phosphate buffer for osmium solutions. In: Electron Microscopy. Fifth Int. Cong. Elec. Micr. Philadelphia 1962, vol. 2ℴ, sez. P-8. New York and London: Academic Press 1962.
Moe, H., and O. Behnke: Cytoplasmic bodies containing mitochondria, ribosomes and rough surfaced endoplasmic menbranes in the epithelium of small intestine of newborn rats. J. Cell biol. 13, 168–171 (1962).
Novikoff, A. B.: Lysosomes and related particles. In: The Cell, Ed. Brachet e Mirsky, vol. 2ℴ, p. 423–488. New York and London: Academic Press 1961.
, and E. Essner: Cytolysomes and mitochondrial degeneration. J. Cell biol. 15, 140–146 (1962).
Oftedal, P.: The histogenesis of a new tumor in Drosophila melanogaster and a comparison with tumors of five other stocks. Z. indukt. Abstamm.- u. Vererb.-L. 85, 408–422 (1953).
Palade, G. E.: A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J. exp. Med. 95, 285–298 (1952).
Parks, H. F.: Morphological study on the extrusion of secretory materials by the parotid gland of Mouse and Rats. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 6, 449–465 (1962).
Rizki, M. T.: Alterations in the haemocyte population of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Morph. 100, 437–458 (1957a).
: Tumor formation in relation to metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Morph. 100, 459–472 (1957b).
: The influence of glucosamine-hydrochloride on cellular adhesiveness in Drosophila melanogaster. Exp. Cell. Res. 24, 111–119 (1961).
Roeder, K. D.: Insect Physiology. New York: J. Wiley & Sons 1953.
Röhrborn, G.: Untersuchungen zur Phänogenetik der melanotischen Drosophila-Tumoren. Dtsch. entom. Z. 9, 478–487 (1962).
Rosenbluth, J., and S. L. Palay: The fine structure of nerve cell bodies and their myelin sheath in the eighth nerve ganglion of the Goldfish. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 853–877 (1961).
Smith, D. S.: The structure of insect fibrillar flight muscle. A study made with special reference to the membrane systems of the fiber. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 10, 123–158 (1961).
, and V. C. Littau: Cellular specialization in the excretory epithelia of an insect, Macrosteles fascifrons Stal (Homoptera). J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 8, 103–133 (1960).
Stark, M. B., and A. K. Marshall: The blood-forming organ of the larva of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Amer. Inst. Homeopathy 23, 1204–1206 (1930).
Susumu, Ito: The lamellar systems of cytoplasmic membranes in dividing spermatogenic cells of Drosophila virilis. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 433–442 (1960).
Tsubo, I., and P. W. Brandt: An electron microscopic study of the malpighian tubules of the Grasshoper, Dissosteira Carolina. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 6, 28–35 (1962).
Wigglesworth, V. B.: The principles of Insect physiology. London: Methuen Ed. 1953.
: The haemocytes and connective tissue formation in an insect Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera). Quart. J. micr. Sci. 97, 89–98 (1956).
Yasuzumi, G., W. Fujimura and H. Ishida: Spermatogenesis in animal as revealed by electron microscopy. Vℴ Spermatid differentiation of Drosophila and Grasshopper. Exp. Cell. res. 14, 268–285 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Ricerca eseguita con i sussidi del C.N.R. (Impresa Genetica).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bairati, A. L'ultrastruttura dell'organo dell'emolinfa nella larva di Drosophila melanogaster . Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 61, 769–802 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342624
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342624