Summary
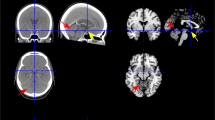
The evolution of CT signs of small, deep infarcts of the cerebral hemispheres in thirty adults, in the first five weeks, has been retrospectively studied. The relevant literature has been reviewed and an attempt has been made to present a synthesis, accompanied by a commentary. It is impossible now to give the frequency of each type of evolution, but the main data are as follows: 1. The shortest delay of visibility of an hypodense area is about 17 to 19h, but at 27 h the densities may still be normal. 2. The evolution of the hypodense area is also variable: after a minimum attenuation is reached-at approximately 72 h-there is a risk of “fogging effect”, which reduces the visibility of ischemic lesions; it could be seen from the end of the 1st week to the beginning of the 4th, but its frequency and its duration have yet to be better determined. 3. In our series, contrast enhancement has been found in the gray matter of the basal ganglia between the 8th and the 22nd days-but according to some observations recorded in the literature, it may be found from the second to the twenty sixth day-and there was no obvious contrast enhancement in the white matter. The significance of the evolving CT signs is discussed in connection with the clinical applications, principally in the management of these patients, and with the attempts to correlate the clinical and CT findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alex M, Baron EK, Goldenberg S, Blumenthal HT (1962) An autopsy study of cerebrovascular accident in diabetes mellitus. Circulation 25:663–673
Araki G, Mihara H, Shizuka M, Yunoki K, Nagata K, Yamaguchi K, Mizukami M, Kawase T, Tazawa T (1983) CT and arteriographic comparison of patients with transient ischemic attacks — Correlation with small infarction of basal ganglia. Stroke 14:276–280
Archer CR, Ilinsky IA, Goldfader PR, Smith KR, Jr (1981) Aphasia in thalamic stroke: CT stereotactic localization. J Comput Assist Tomogr 5:427–432
Aronson SM (1973) Intracranial vascular lesions in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 32:183–196
Becker H, Desch H, Hacker H, Pencz A (1979) CT fogging effect with ischemic cerebral infarcts. Neuroradiology 18: 185–192
Bergström M, Ericson K (1979) Compartment analysis of contrast enhancement in brain infarctions. J Comput Assist Tomogr 3:234–240
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F (1984) Cerebral infarction with transient signs (CITS): do TIAs correspond to small deep infarcts in internal carotid artery occlusion? Stroke 15:536–539
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F (1984) Hemiparésie avec atteinte linguale. Hématome du genou de la capsule interne. Rev Neurol (Paris) 140:587–590
Caillé JM, Guibert F, Bidabé AM, Billerey J, Piton J (1980) Enhancement of cerebral infarcts with CT. Comput Radiol 4: 73–77
Chokroverty S, Rubino FA (1975) “Pure” motor hemiplegia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38:896–899
Cole FM, Yates P (1967) Intracerebral microaneurysms and small cerebrovascular lesions. Brain 90:759–767
Critchley EMR (1983) Recognition and management of lacunar strokes. Br Med J [Clin Res] 287:777–778
Dehaene I (1982) Bilateral thalamo-subthalamic infarction. Acta Neurol Belg 82:253–261
De Renzi E, Nichelli P, Crisi G (1983) Hemiataxia and crural hemiparesis following capsular infarct. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:561–563
De Reuck J, Crevits L, De Coster W, Sieben G, vander Eecken H (1980) Pathogenesis of Binswanger chronic progressive subcortical encephalopathy. Neurology (NY) 30:920–928
De Reuck J, vander Eecken H (1976) The arterial angioarchitecture in lacunar state. Acta Neurol Belg 76:142–149
Derouesné C, Mas J-L, Bolgert F, Castaigne P (1984) Pure sensory stroke caused by a small cortical infarct in the middle cerebral artery territory. Stroke 15:660–662
Donnan GA, Tress BM, Bladin PF (1982) A prospective study of lacunar infarction using computerized tomography. Neurology (NY) 32:49–56
Drayer BP, Dujovny M, Wolfson SK, Jr., Boehnke M, Cook EE, Rosenbaum AE (1979) Comparative cranial CT enhancement in a primate model of cerebral infarction. Ann Neurol 5: 48–58
Englander RN, Netsky MG, Adelman LS (1975) Location of human pyramidal tract in the internal capsule: anatomic evidence. Neurology (NY) 25:823–826
Fisher CM (1965) Pure sensory stroke involving face, arm, and leg. Neurology (NY) 15:76–80
Fisher CM (1965) Lacunes: small, deep cerebral infarcts. Neurology (NY) 15:774–784
Fisher CM (1969) The arterial lesions underlying lacunes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 12:1–15
Fisher CM (1972) Cerebral miliary aneurysms in hypertension. Am J Pathol 66:313–342
Fisher CM (1978) Thalamic pure sensory stroke: a pathologic study. Neurology (NY) 28:1141–1144
Fisher CM (1979) Capsular infarcts. The underlying vascular lesions. Arch Neurol 36:65–73
Fisher CM (1982) Pure sensory stroke and allied conditions. Stroke 13:434–447
Fisher CM (1982) Lacunar strokes and infarcts: a review. Neurology (NY) 32:871–876
Fisher CM, Curry HB (1965) Pure motor hemiplegia of vascular origin. Arch Neurol 13:30–44
Gado M, Danziger WL, Chi D, Hughes CP, Coben LA (1983) Brain parenchymal density measurements by CT in demented subjects and normal controls. Radiology 147:703–710
Goldenberg G, Reisner Th (1983) Angiographic findings in relation to clinical course and results of computed tomography in cerebrovascular disease. Eur Neurol 22:124–130
Goto K, Ishii N, Fukasawa H (1981) Diffuse white-matter disease in the geriatric population. A clinical, neuropathological, and CT study. Radiology 141:687–695
Goto K, Tagawa K, Uemura K, Ishii K, Takahashi S (1979) Posterior cerebral artery occlusion: clinical, computed tomographic, and angiographic correlation. Radiology 132:357–368
Graff-Radford NR, Eslinger PJ, Damasio AR, Yamada T (1984) Nonhemorrhagic infarction of the thalamus: behavioral, anatomic, and physiologic correlates. Neurology (NY) 34: 14–23
Hakim AM, Ryder-Cooke A, Melanson D (1983) Sequential computerized tomographic appearance of strokes. Stroke 14: 893–897
Houser OW, Campbell JK, Baker HL, Jr, Sundt TS, Jr (1982) Radiologic evaluation of ischemic cerebrovascular syndromes with emphasis on computed tomography. Radiol Clin North Am 20:123–142
Huang CY, Lui FS (1984) Ataxic-hemiparesis, localization and clinical features. Stroke 15:363–366
Ichikawa K, Tsutsumishita A, Fujioka A (1982) Capsular ataxic hemiparesis. A case report. Arch Neurol 39:585–586
Inoue Y, Takemoto K, Miyamoto T, Yoshikawa N, Taniguchi S, Saiwai S, Nishimura Y, Komatsu T (1980) Sequential computed tomography scans in acute cerebral infarction. Radiology 135:655–662
Iragui VJ, McCutchen CB (1982) Capsular ataxic hemiparesis. Arch Neurol 39:528–529
Jacome DE (1983) Homolateral ataxia and crural paresis. Arch Neurol 40:659–660
Jokelainen M, Pilke A (1983) Ataxic hemiparesis. Arch Neurol 40:326
Kase CS, Maulsby GO, de Juan E, Mohr JP (1981) Hemichorea-hemiballism and lacunar infarction in the basal ganglia. Neurology (NY) 31:452–455
Kawase T, Mizukami M, Araki G (1981) Mechanisms of contrast enhancement in cerebral infarction: computerized tomography, regional cerebral blood flow, fluorescein angiography, and pathological study. Adv. Neurol 30:149–158
Kendall BE, Pullicino P (1980) Intravascular contrast injection in ischaemic lesions. II. Effect on prognosis. Neuroradiology 19:241–243
Manelfe C, Clanet M, Gigaud M, Bonafé A, Guiraud B, Rascol A (1981) Internal capsule: normal anatomy and ischemic changes demonstrated by computed tomography. AJNR 2: 149–155
Masuda J, Tanaka K, Omae T, Ueda K, Sadoshima S (1983) Cerebrovascular diseases and their underlying vascular lesions in Hisayama, Japan — A pathological study of autopsy cases. Stroke 14:934–940
Miller VT (1983) Lacunar stroke. A reassessment. Arch Neurol 40:129–134
Mohr JP (1982) Lacunes. Stroke 13:3–11
Mohr JP, Caplan LR, Melski JW, Goldstein RJ, Duncan GW, Kistler JP, Pessin MS, Bleich HL (1978) The Harvard cooperative stroke registry: a prospective registry. Neurology (NY) 28: 754–762
Mohr JP, Kase CS, Meckler RJ, Fisher CM (1977) Sensorimotor stroke due to thalamocapsular ischemia. Arch Neurol 34: 739–741
Nelson RF, Pullicino P, Kendall BE, Marshall J (1980) Computed tomography in patients presenting with lacunar syndromes. Stroke 11:256–261
Newton TH, Potts DG (eds) (1981) Radiology of the skull and brain vol V. Technical aspects of computed tomography. Mosby, St Louis Toronto London
Norton GA, Kishore PRS, Lin J (1978) CT contrast enhancement in cerebral infarction. AJR 131:881–885
Olsen TS, Christensen J, Skriver EB, Lassen NA (1983) Brain scintigraphy with Tc99-pertechnetate in the evaluation of patients with cerebrovascular lesions. The diagnosic value related to age of the lesion and to the size, type and localisation revealed by CT-scan. Acta Neurol Scand 67:229–234
Pentlow KS (1981) Dosimetry in computed tomography. In: Newton TH, Potts DG (eds) pp 4228–4258
Perman GP, Racy A (1980) Homolateral ataxia and crural paresis: case report. Neurology (NY) 30:1013–1015
Pullicino P, Kendall BE (1980) Contrast enhancement in ischaemic lesions. I. Relationship to prognosis. Neuroradiology 19:235–239
Pullicino P, Nelson RF, Kendall BE, Marshall J (1980) Small deep infarcts diagnosed on computed tomography. Neurology (NY) 30:1090–1096
Rascol A, Clanet M, Manelfe C, Guiraud B, Bonafé A (1982) Pure motor hemiplegia: CT study of 30 cases. Stroke 13:11–17
Roehmholdt ME, Palumbo PJ, Whisnant JP, Elveback LR (1983) Transient ischemic attack and stroke in a communitybased diabetic cohort. Mayo Clin Proc 58:56–58
Rosenberg NL, Koller R (1981) Computerized tomography and pure sensory stroke. Neurology (NY) 31:217–220
Skriver EB, Olsen TS (1981) Transient disappearance of cerebral infarcts on CT scan, the so-called fogging effect. Neuroradiology 22:61–65
Skriver EB, Olsen TS (1982) Contrast enhancement of cerebral infarcts. Incidence and clinical value in different states of cerebral infarction. Neuroradiology 23:259–265
Soisson T, Cabanis EA, Iba-Zizen MT, Bousser MG, Laplane D, Castaigne P (1982) Pure motor hemiplegia and computed tomography. 19 cases. J Neuroradiol 9:304–322
Spertell RB, Ransom BR (1979) Dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome produced by capsular infarct. Ann Neurol 6:263–265
Terent A, Ronquist G, Bergström K, Hällgren R, Åberg H (1981) Ischemic edema in stroke. A parallel study with computed tomography and cerebrospinal fluid markers of disturbed brain cell metabolism. Stroke 12:33–40
Thaler HT, Rottenberg DA, Pentlow KS, Allen JC (1979) A method of correcting for linear drift in computed tomography brain scans. J Comput Assist Tomogr 3:251–255
Tohgi H, Mochizuki H, Yamanouchi H, Iio M, Yamada H, Chiba K, Tomonaga M (1981) A comparison between the computed tomogram and the neuropathological findings in cerebrovascular disease. J Neurol 224:211–220
Torack RM (1982) Computed tomography and stroke edema: case report with an analysis of water in acute infarction. Comput Radiol 6:35–41
Tredici G, Pizzini G, Bogliun G, Tagliabue M (1982) The site of motor corticospinal fibres in the internal capsule of man. A computerised tomographic study of restricted lesions. J Anat 134:199–208
van Gijn J, Kraaijeveld CL (1982) Blood pressure does not predict lacunar infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45: 147–150
Wall SD, Brant-Zawadzki M, Jeffrey RB, Barnes B (1981 and 1982) High frequency CT findings within 24 hours after cerebral infarction. AJNR 2:553–557 and AJR 138:307–311
Weisberg LA (1979) Computed tomography and pure motor hemiparesis. Neurology (NY) 29:490–495
Weisberg LA (1982) Lacunar infarcts: clinical and computed tomographic correlations. Arch Neurol 39:37–40
Zatz LM (1981) General overview of computed tomography instrumentation. In: Newton TH, Potts DG (eds), pp 4025–4057
Zatz LM, Jernigan TL, Ahumada AJ (1982) White matter changes in cerebral computed tomography related to aging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 6:19–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Launay, M., N'Diaye, M. & Bories, J. X-ray computed tomography (CT) study of small, deep and recent infarcts (SDRIs) of the cerebral hemispheres in adults. Neuroradiology 27, 494–508 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340845
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340845