Summary
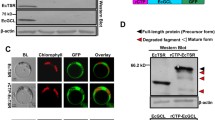
Transport of foreign proteins into chloroplasts was studied in a transgenic plant expressing two different fusion proteins, the transit peptide (TP) of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit (SS) fused to neomycin phosphotransferase (TP-NPT II) and, the same transit peptide plus the amino-terminal 23 amino acids of mature SS linked to NPT II. The second fusion protein (TP-SS-NPT II) was found in isolated chloroplasts but accumulated to a lesser degree than the first (TP-NPT II). This finding does not support the hypothesis that the highly conserved amino acid sequence surrounding the cleavage site between the transit peptide (TP) and mature SS is required for efficient transport. This cleavage region shows a markedly higher conservation than either the mature protein or the TP sequences in SS genes from different plant species. Evidence is presented indicating that the transport of the TP-SS-NPT II precursor is diminished as a result of competition between the rate of its uptake and the rate of its degradation by cytosolic proteases. In an attempt to identify further regions in the TP involved in transport and processing, we designed derivatives of both the TP-SS-NPT II and TP-NPT II precursors. A derivative of TP-SS-NPT II lacking the amino acids at the processing site was expressed in plants and was shown to be transported and processed. A derivative of TP-NPT II comprising the first 41 amino acids (out of 57) of the transit peptide linked to NPT II was also expressed in plants. This protein was not imported into the organelles; however a significant amount of partially processed fusion protein was found to be attached to the outer membrane of the chloroplast.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett SG, Grossman AR, Chua N-H (1982) In vitro synthesis and uptake of cytoplasmically-synthesized chloroplast proteins. In: Edelmann M, Hallick RB, Chua N-H (eds) Methods in chloroplast molecular biology. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford, pp 1081–1002
Cashmore AR (1983) Nuclear genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. In: Kosuge T, Meredith CP, Hollaender A (eds) Genetic engineering of plants —An agricultural perspective. Plenum, New York, pp 29–38
Cashmore A, Szabo L, Timko M, Kausch A, Van den Broeck G, Schreier P, Bohnert H, Herrera-Estrella L, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1985) Import of polypeptides into chloroplasts. Bio/Technology 3:803–808
Cline K, Werner-Washburne M, Lubben TH, Keegstra K (1985) Precursors to two nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins bind to the outer envelope membrane before being imported into chloroplasts. J Biol Chem 260:3691–3696
Deblaere R, Bytebier BN, De Greve H, DeBoeck F, Schell J, Van Montagu M, Leemans J (1985) Efficient octopine TI plasmidderived vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer to plants. Nucleic Acids Res 13:4777–4788
Dobberstein B, Blobel G, Chua N-H (1977) In vitro synthesis and processing of a putative prescursor for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase of Chlamydomonas reinharditii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:1082–1085
Gronenborn B, Messing J (1978) Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature 272:375–377
Grossman AR, Bartlett SG, Chua N-H (1980) Energy-dependent uptake of cytoplasmically synthesized polypeptides by chloroplasts. Nature 285:625–628
Gruissem W, Greenberg BM, Zurawski G, Prescott DM, Hallick RB (1983) Biosynthesis of chloroplast transfer RNA in a spinach chloroplast transcription system. Cell 35:815–828
Hain R, Stabel P, Czernilofsky AP, Steinbiß HH, Herrera-Estrella L, Schell J (1985) Uptake, integration, expression and genetic transmission of a selectable chimaeric gene by plant protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet 199:161–168
Highfield PE, Ellis RJ (1978) Synthesis and transport of the small subunit of chloroplast ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Nature 271:420–424
Horwich AL, Kalousek F, Mellman I, Rosenberg LE (1985) A leader peptide is sufficient to direct mitochondrial import of a chimeric protein. EMBO J 4:1129–1135
Hurt EC, Pesold-Hurt B, Schatz G (1984) The cleavable prepiece of an imported mitochondrial protein is sufficient to direct cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the mitochondrial matrix. FEBS Lett 178:306–310
Hurt EC, Pesold-Hurt B, Suda K, Opplinger W, Schatz G (1985) The first twelve amino acids (less than half of the pre-sequence) of an imported mitochindrial protein can direct mouse cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the yeast mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J 4:2061–2068
Langley KE, Villarejo MR, Fowler AV, Zamenhof PJ, Zabin I (1975) Molecular basis of β-galactosidase α-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1254–1257
Norrander J, Kempe T, Messing J (1983) Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene 26:101–106
Reiss B, Sprengel R, Will H, Schaller H (1984a) Nucleotide sequence and exact localisation of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 30:211–218
Reiss B, Sprengel R, Schaller H (1984) Protein fusions with the kanamycin resistance gene from transposon Tn5. EMBO J 3:3317–3322
Robinson C, Ellis RJ (1984) Transport of proteins into chloroplasts. The precursor of small subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase is processed to the mature size in two steps. Eur J Biochem 142:343–346
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Soulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Schreier PH, Cortese R (1979) A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol 129:169–172
Schreier PH, Seftor EA, Schell J, Bohnert HJ (1985) The use of nuclear encoded sequences to direct the light-regulated synthesis and transport of a foreign protein into plant chloroplasts. EMBO J 4:25–32
Shillito RD, Paszkowski J, Potrykus I (1983) Agarose plating and bead type culture technique enable and stimulate development of protoplast-derived colonies in a number of plant species. Pl Cell Rep 2:244–247
Simpson J, Timko MP, Cashmore AR, Schell J, Van Montagu M, Herrera-Estrella L (1985) Light-inducible and tissue-specific expression of a chimaeric gene under control of the 5′-flanking sequence of a pea chlorophyll a/b-binding protein gene. EMBO J 4:2723–2729
Van den Broeck G, Timko MP, Kausch AP, Cashmore AR, Van Montagu M, Herrera-Estrella L (1985) Targeting of a foreign protein to chloroplasts by fusion to the transit peptide from the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Nature 313:358–363
Van Haute E, Joos H, Maes M, Warren G, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1983) Intergeneric transfer and exchange recombination of restriction fragments cloned in pBR322: a novel strategy for the reversed genetics of the Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J 2:411–417
Wasmann CC, Reiss B, Bartlett SG, Bohnert HJ (1986) The importance of the transit peptide and the transported protein for protein import into chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet (MS 260)
Winnacker EL, Dorper T (1982) Solid-phase synthesis of oligonucleotides using the phosphoamidite mehtod. In: Gassen HG, Lang A (eds) Chemical and enzymatic synthesis of gene fragments. Verlag Chemie Weinheim, pp 79–192
Zambryski P, Herrera-Estrella L, De Block M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1984) The use of the Ti-plasid of A. tumefaciens to study the transfer and expression of foreign DNA in plant cells: new vectors and methods. Genetic engineering, Vol VI, Eds Hollaender A, Setlow J. Plenum Press, pp 253–278
Zoller MJ, Smith M (1982) Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 10:6487–6500
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Saedler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuntz, M., Simons, A., Schell, J. et al. Targeting of protein to chloroplasts in transgenic tobacco by fusion to mutated transit peptide. Mol Gen Genet 205, 454–460 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00338082
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00338082