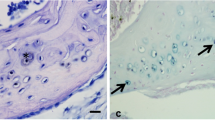
Summary
The cartilage matrix in which the early calcium salts are deposited has been studied in the tibial epiphyses and in the costo-chondral junctions of 30-day-old guinea pigs. The results may be summarized as follows:
(1) Structures of globular shape (“globules”) are to be found throughout the entire epiphyseal plate. (2) They have a homogeneous matrix and are bounded by a membrane. (3) Early calcification occurs in globules. Calcification of collagen fibrils seems to occur later. (4) The earliest mineral deposited would seem to consist of tiny granules about 20 Å in diameter. Then apatite crystals are laid down, initially in small clusters and later filling the globules completely. (5) The globules are strongly osmiophilic. They seem to contain a fair amount of neutral polysaccharides, but no acid polysaccharides except a coating on their outer membrane. Hyaluronidase digestion does not affect globules. Papain digestion makes them more reactive to uranium and lead. (6) Globules are of cellular origin but they are almost certainly not pre-formed in the chondrocytes. Finally, the present paper advances the hypothesis that some globules derive from degenerating chondrocytes and others from the processes of normal chondrocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amprino, R., Bairati, A.: Studi sulle trasformazioni delle cartilagini dell'uomo nell'accrescimento e nella senescenza. Z. Zellforsch. 20, 143–205 (1933).
Anderson, D. R.: The ultrastructure of elastic and hyaline cartilage of the rat. Amer. J. Anat. 114, 403–433 (1964).
Anderson, H. C.: Vesicles in the matrix of epiphyseal cartilage: fine structure, distribution and association with calcification. In: Electron microscopy 1968 (D. S. Bocciarelli, ed.). Fourth Europ. Reg. Conf. Electr. Microsc. Rome: Tipografia Poliglotta Vaticana 1968.
—: Vesicles associated with calcification in the matrix of epiphyseal cartilage. J. Cell Biol. 41, 59–72 (1969).
Barnett, C. H., Cochrane, W., Palfrey, A. J.: Age changes in articular cartilage of rabbits. Ann. rheum. Dis. 22, 389–400 (1963).
Bonucci, E.: Fine structure of early cartilage calcification. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 20, 33–50 (1967).
—: Further investigation on the organic/inorganic relationships in calcifying cartilage. Calc. Tiss. Res. 3, 38–54 (1969).
Cameron, D. A.: The fine structure of bone and calcified cartilage. Clin. Orthop. 26, 199–228 (1963).
Fitton Jackson, S.: The fine structure of developing bone in the embryonic fowl. Proc. roy. Soc. B. 146, 270–280 (1957).
—: Fibrogenesis and the formation of matrix. In: Bone as a tissue (K. Rodahl, J. T. Nicholson and E. M. Brown, eds.). New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co. 1960.
Follis, R. H., Jr.: Calcification of cartilage. In: Calcification in biological systems (R. F. Sognnaes, ed.). Washington: Amer. Ass. Adv. Sci. 1960.
Ghadially, F. N., Meachim, G., Collins, D. H.: Extra-cellular lipid in the matrix of human articular cartilage. Ann. rheum. Dis. 24, 136–146 (1965).
Ham, A. W.: Histology. London and Philadelphia: Pitman Medical Publishing Co. and J. B. Lippincott Co. 1965.
Knese, K.-H., Knoop, A.-M.: Über den Ort der Bildung des Mukopolysaccharid-Proteinkomplexes im Knorpelgewebe. Elektronenmikroskopische und histochemische Untersuchungen. Z. Zellforsch. 53, 201–258 (1961a).
—: Chondrogenese und Osteogenese. Elektronenmikroskopische und lichtmikroskopische Untersuchungen. Z. Zellforsch. 55, 413–468 (1961b).
Marinozzi, V.: Silver impregnation of ultrathin sections for electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 121–133 (1961).
Matukas, V. J., Krikos, G. A.: Evidence for changes in protein polysaccharide associated with the onset of calcification in cartilage. J. Cell Biol. 39, 43–48 (1968).
—, Panner, B. J., Orbison, J. L.: Studies on ultrastructural identification and distribution of protein-polysaccharide in cartilage matrix. J. Cell Biol. 32, 365–377 (1967).
Palfrey, A. J., Davies, D. V.: The fine structure of chondrocytes. J. Anat. (Lond.) 100, 213–226 (1966).
Pascher, M.: Zur Kenntnis der Altersveränderungen in den menschlichen Kehlkopfknorpeln, insbesondere der körnigen Entartung der Knorpelgrundsubstanz, der Vascularisations-, Resorptions- und Verknöcherungsbefunde. Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 246, 198–238 (1923).
Rambourg, A.: An improved silver methenamine technique for the detection of periodic acid — reactive complex carbohydrates with the electron microscope. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 409–412 (1967).
Robinson, R. A., Cameron, D. A.: Electron microscopy of cartilage and bone matrix at the distal epiphyseal line of the femur in the newborn infant. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 253–260 (1956).
Schaffer, J.: Die Stützgewebe. In: Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen (W. v. Möllendorff, ed.), Bd. II, H. 2. Berlin: Springer 1930.
Schenk, R. K., Spiro, D., Wiener, J.: Cartilage resorption in the tibial epiphyseal plate of growing rats. J. Cell Biol. 34, 275–291 (1967).
Scherft, J. P.: The ultrastructure of the organic matrix of calcified cartilage and bone in embryonic mouse radii. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 333–343 (1968).
Scott, B. L., Pease, D. C.: Electron microscopy of the epiphyseal apparatus. Anat. Rec. 126, 465–495 (1956).
Stäubli, W.: A new embedding technique for electron microscopy, combining a water-soluble epoxy resin (Durcupan) with water-insoluble Araldite. J. Cell Biol. 16, 197–201 (1963).
Takuma, S.: Electron microscopy of the developing cartilagenous epiphysis. Arch. oral Biol. 2, 111–119 (1960).
Tousimis, A. J., Follis, R. H., Jr.: Studies on the ultrastructure of rat epiphysial cartilage. Fed. Proc. 17, 460 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author is indebted to Mr. A. Benvenuti for his technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Italian Research Council.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonucci, E. Fine structure and histochemistry of “calcifying globules” in epiphyseal cartilage. Z. Zellforsch. 103, 192–217 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337312
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337312