Abstract
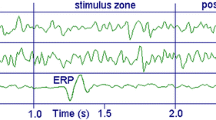
In this study, the amplitude frequency characteristics, which are obtained by application of Fourier transform to the selectively averaged evoked potentials (SAEPs) recorded from human vertex and occipital scalp electrodes upon acoustical step stimulation, are given and discussed. The resonance phenomena which we have observed in the cat brain are also demonstrated in humans by comparing the components of the single EPs with those of the spontaneous activity (EEG) just preceding the stimulus and by using the concept of amplification factor which we have recently introduced. Besides other types, special emphasis is given to the resonance phenomena in the alpha frequency range (alpha resonances). Various forms of alpha resonances are described and quantitatively demonstrated by using the data recorded during closed-eye and open-eye experiments on eight subjects. A strong resonance phenomenon is also noted in the 2–9 Hz frequency range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow, J.S., Estrin, T.: Comparative phase characteristics of induced and intrinsic alpha activity. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 30, 1–9 (1971)
Başar, E.: Biophysical and physiological systems analysis. Reading MA.: Addison-Wesley 1976
Başar, E.: Biological systems analysis and evoked potentials of the brain. T.-I.-T.J. Life Sci. 4, 37–58 (1974)
Başar, E., Gönder, A., Özesmi, Ç., Ungan, P.: Dynamics of brain rhythmic and evoked potentials I. Some computational methods for the analysis of electrical signals from the brain. Biol. Cybernetics 20, 137–143 (1975a)
Başar, E., Gönder, A., Özesmi, Ç., Ungan, P.: Dynamics of brain rhythmic and evoked potentials II. Studies in the auditory pathway, reticular formation, and hippocampus during the waking stage. Biol. Cybernetics 20, 145–160 (1975b)
Başar, E., Gönder, A., Özesmi, Ç., Ungan, P.: Dynamics of brain rhythmic and evoked potentials III. Studies in the auditory pathway, reticular formation, and hippocampus during sleep. Biol. Cybernetics 20, 161–169 (1975c)
Başar, E., Gönder, A., Rona, M., Ungan, P.: Resonance phenomena in the electrical activity of the brain. Abstract of Third European Meeting on Cybernetics and Systems Research, Vienna April 20–23, 1976 (proceedings in press)
Başar, E., Gönder, A., Ungan, P.: Important relation between EEG and brain evoked potentials I. Resonance phenomena in subdural structures of the cat brain. Biol. Cybernetics 25, 27–40 (1976)
Başar, E., Özesmi, Ç.: The hippocampal EEG activity and a systems analytical interpretation of averaged evoked potentials of the brain. Kybernetik 12, 45–54 (1972)
Başar, E., Ungan, P.: A component analysis and principles derived for the understanding of evoked potentials of the brain: Studies in the hippocampus. Kybernetik 12, 133–140 (1973)
David, E., Finkenzeller, P., Kallert S., Keidel, W.D.: Korrelations-analyse von gemittelten und ungemittelten evozierten Potentialen. Kybernetik 9, 22–26 (1971)
Davis, H., Zerlin, S.: Acoustic relations of the human vertex potential. J. acoust. Soc. Amer. 39, 109–116 (1966)
Finkenzeller, P.: Die Mittelung von Reaktionspotentialen. Kybernetik 6, 22–44 (1969)
Goldie, L., Green, J.M.: Paradoxical blocking and arousal in the drowsy state. Nature (Lond.). 187, 952–953 (1960)
Goldstein, S.: Phase coherence of alpha rhythm during photic blocking. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 29, 127–136 (1970)
Kawabata, N.: Nonstationary power spectrum analysis of the photic alpha blocking. Kybernetik 12, 40–44 (1972)
Lansing, R.W., Barlow, J.S.: Rhythmic after-activity to flashes in relation to the background alpha which precedes and follows the photic stimuli. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 32, 149–160 (1972)
Nogawa, T., Katayama, K., Tabata, Y., Ohshio, T., Kawahara, T.: Changes in amplitude of the EEG induced by a photic stimulus. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 40, 78–88 (1976)
Pfurtscheller, G., Cooper, R.: Frequency dependence of the transmission of the EEG from cortex to scalp. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 38, 93–96 (1975)
Picton, T. W., Hillyard, S. A., Krausz, H. I., Galambos, R.: Human auditory evoked potentials. I: Evaluation of components. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 36, 179–190 (1974)
Ungan, P., Başar, E.: Comparison of Winer filtering and selective averaging of evoked potentials. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 40, 516–520 (1976)
Walter, W. G.: Intrinsic rhythms of the brain. In: Handbook of Physiology, Neurophysiology, Vol. 1, pp. 279–298. Field, J. et al. (Eds.): Washington: Amer. Physiol. Soc. 1959
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Grant No. TAG-345 of the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Başar, E., Gönder, A. & Ungan, P. Important relation between EEG and brain evoked potentials. Biol. Cybernetics 25, 41–48 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337047
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337047