Abstract
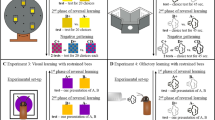
Bees were trained on a black disc (rewarded) against a smaller grey disc (unrewarded). Thus the bees had the choice of distinguishing between the two training figures by relying on the difference in size or on the difference in greyness or on both parameters. The aim of the present investigation was whether the relative weight of these parameters depended upon the differences in size and greyness presented during the training phase. 1. During the first two days of training the relative rating of these parameters changed in some, though not all individuals. In these cases the size of the discs rose in importance while the greyness was rated uniformly high (Fig. 3). Later, from the third day of training onwards the parameters were rated constantly. 2. Whenever size and greyness of the two training figures differed noticeably the bee relied on both parameters. The bee rated both parameters independently of the quantity of the differences in size and greyness presented during the training (Fig. 5). Thus the bee's analysis of the tested patterns cannot be attributed solely to the training paradigm, but seems to rely also on given (innate) “analyzers” (cf. Sutherland and Mackintosh, 1971). The type of training patterns only determines which “analyzers” influence the choice reaction. 3. The bee's “analyzer for size” had an influence on the choice reaction only if there was a noticeable size-difference between the training figures. The “analyzer for shades of grey”, however, strongly influenced the choice reactions also in those cases where the training figures showed no difference in greyness but only differences in size (Fig. 2).
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Cruse, H.: An application of the cross-correlation coefficient to pattern recognition of honey bees. Kybernetik 15, 73–84 (1974)
Daumer, K.: Reizmetrische Untersuchungen des Farbensehens der Biene. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 38, 413–486 (1956)
Frisch, K. v.: Der Farbensinn und Formensinn der Biene. Zool. Jb. Allg. Zool Physiol. 35, 1–182 (1915)
Frisch, K. v.: Über den Geruchssinn der Bienen und seine blütenbiologische Bedeutung. Zool. Jb. (Physiol.) 37, 1–238 (1919)
Hassenstein, B. Bedingungen für Lernprozesse-teleonomisch geschen. In: Informatik, Scharf, J.H. (Hrsg.). Leipzig: Joh. Abr. Barth-Verlag 1972
Hassenstein, B.: Instinkt, Lernen, Spielen, Einsicht: Einführung in die Verhaltensbiologie. München: Piper 1980
Helversen, O. v.: Zur spektralen Unterschiedsempfindlichkeit der Honigbiene. J. Comp. Physiol. 80, 439–472 (1972)
Helversen, O. v.: The relationship between difference in stimuli and choice frequency in training experiments with the honey bee. In: Information processing in the visual system of arthropods, Wehner, R. (ed.). Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1972
Hertz, M.: Über figurale Intensitäten und Qualitäten in der optischen Wahrnehmung der Biene. Biol. Zbl. 53, 10–40 (1933)
Koltermann, R.: Rassen-bzw. artspezifische Duftbewertung bei der Honigbiene und ökologische Adaptation. J. Comp. Physiol. 85, 327–360 (1973)
Kriston, I.: Zum Problem des Lernverhaltens von Apis mellifica L. gegenüber verschiedenen Duftstoffen. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 74, 169–189 (1971)
Kriston, I.: Die Bewetung von Duft-und Farbsignalen als Orientierungshilfen an der Futterquelle durch Apis mellifera L. J. Comp. Physiol. 84, 77–94 (1973)
Lindauer, M.: Lernen und Gedächtnis-Versuche an der Honigbiene. Naturwissenschaften 57, 463–467 (1970)
Mackintosh, N.J.: The psychology of animal learning. London, New York, San Francisco: Academic Press 1974
Menzel, R.: Untersuchungen zum Erlernen von Spektralfarben durch die Honigbiene. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 56, 22–62 (1967)
Micko, H.C., Fischer, W.: The metric of multidimensional psychological space as a function of differential attention to subjective attributes. J. Math. Psychol. 7, 118–143 (1970)
Ronacher, B.: Äquivalenz zwischen Größen-und Helligkeitsunter-schieden im Rahmen der visuellen Wahrnehmung der Honigbiene. Biol. Cybern. 32, 63–75 (1979)
Ronacher, B.: Beitrag einzelner Parameter zum wahrnehmungsgemäßen Unterschied von zusammengesetzten Reizen bei der Honigbiene. Biol. Cybern. 32, 77–83 (1979)
Ronacher, B.: Ein einfacher Zusammenhang zwischen der Äquivalenzbeziehung und der Unterschiedsempfindlichkeit für zwei Musterparameter bei der Honigbiene. Biol. Cybern. 36, 51–61 (1980)
Saraga, E., Shallice, T.: Parallel processing of the attributes of single stimuli, Percept Psychophys. 13, 261–270 (1973)
Schnetter, B.: Visuelle Formunterscheidung der Honigbiene im Bereich von Vier- und Sechsstrahlsternen. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 59, 90–109 (1968)
Schnetter, B.: Experiments on pattern discrimination in honey bees. In: Information processing in the visual system of arthropods, Wehner, R. (ed.) Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1972
Schnetter, B.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zum Lernverhalten der Bienen und Hummeln unter besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer Blütenstetigkeit. Habilitationsschrift, Würzburg 1979
Sutherland, N.S., Mackintosh, N.J.: Mechanisms of Animal Discrimination learning. New York, London: Academic Press 1971
Tversky, A., Krantz, D.H.: The dimensional representation and the metric structure of similarity data. J. Math. Psychol. 7, 572–596 (1970)
Wagner, A.R.: Incidental stimuli and discrimination learning. In: Animal discrimination learning, Gilbert, R.M., Sutherland, N.S. (eds.). New York, London: Academic Press 1969
Wagner, A.R.: Stimulus validity and stimulus selection in associative learning. In: Animal discrimination learning, Gilbert, R.M., Sutherland, N.S. (eds.) New York, London: Academic Press 1969
Wehner, R.: Die Bedeutung der Streifenbreite für die optische Winkelmessung der Biene. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 58, 322–343 (1968)
Wehner, R.: The generalization of directional visual stimuli in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. J. Insect Physiol. 17, 1579–1591 (1971)
Wehner, R.: Pattern recognition. In: compound eye and vision of insects, Horridge, G.A. (ed.) Oxford: Clarendon Press 1975
Wehner, R., Lindauer, M.: Zur Physiologie des Formensehens bei der Honigbiene. I. Winkelunterscheidung an vertikal orientierten Streifenmustern. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 52, 290–324 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Meinem wissenschaftlichen Lehrer, Prof. Dr. Bernhard Hassenstein, anläßlich seines 60. Geburtstages gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronacher, B. Unabhängigkeit der bewertung zweier musterparameter von deren unterschiedlichkeitsgrad bei der Dressur. Biol. Cybern. 46, 173–182 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336799
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336799