Summary
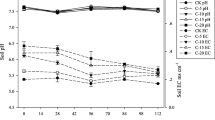
The effect of incorporating sesbania and rice straw and of period of decomposition on urea hydrolysis was studied in a wetland soil under laboratory conditions. Urea hydrolysis proceeded more rapidly in the crop residue-amended soil than in the control soil, and increased with increases in the rate of addition of crop residues and with longer periods of decomposition. Irrespective of amendment treatment, urea hydrolysis followed first-order reaction kinetics, and rate constants in the unamended soil ranged from 0.021 to 0.024 h-1 after urea application of 200 μg N g-1 soil. In the amended soil, hydrolysis rates ranged from 0.033 to 0.149 h-1 with sesbania and 0.071 and 0.250 h-1 with rice straw, depending on the length of decomposition period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajpai S, Srivastava OP, Pathak AN (1984) Effect of organic matter on urea hydrolysis in soil. In: Nitrogen in soils, crops and fertilizers. Bull 13, Indian Soc Soil Sci, New Delhi, pp 115–159
Bolten H Jr, Elliot LF, Papandick RT, Bezdicek DF (1985) Soil microbial biomass and selected enzyme activities: Effect of fertilizers and cropping practices. Soil Biol Biochem 17:297–302
Bremner JM, Mulvaney RL (1978) Urease activity in soils. In: Burns RG (ed) Soil enzymes. Academic Press, London, pp 149–166
Carmona G, Christianson CB, Byrnes BH (1990) Temperature and low concentration effect of the urease inhibitors N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide (nBTPT) on ammonia volatilization from urea. Soil Biol Biochem 22:933–937
Douglas LA, Bremner JM (1970) Extraction and colorimetric determination of urea in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 34:859–862
Kumar V, Wagenet RJ (1984) Urease activity and kinetics of urea transformations in soils. Soil Sci 137:263–269
Mulvaney RL, Bremner JM (1979) A modified diacetyl monoxime method for colorimetric determination of urea in soil extracts. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 10:1163–1170
Saini P (1990) In situ leaching and transformation of urea applied to wetland rice soils. MSc thesis, Punjab Agric Univ, Ludhiana, India
Sankhayan SD, Shukla UC (1976) Rates of urea hydrolysis in five soils of India. Geoderma 16:171–178
Thomas GV, Shantaram MV (1984) In situ cultivation and incorporation of green manure legumes in coconut basins. Plant and Soil 80:373–380
Yadvinder-Singh, Khind CS, Bijay-Singh (1991) Efficient management of leguminous green manures in wetland rice. Adv Agron 45:135–189
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khind, C.S., Bajwa, M.S. Urea hydrolysis in wetland soil amended with Sesbania aculeata green manure and rice straw. Biol Fertil Soils 15, 65–67 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336291
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336291