Summary
Changes of muscle weights, fiber diameters and ultrastructure were studied in the slow anterior latissimus dorsi (ALD) and in the fast posterior latissimus dorsi (PLD) of the chick three weeks after denervation and tenotomy, and after combined denervation and tenotomy of the two muscles.
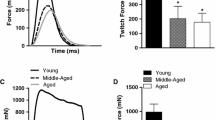
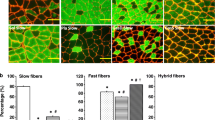
The slow ALD muscle becomes hypertrophic after denervation (Feng, Jung and Wu, 1962). Three weeks after nerve section, wet weights of ALD muscles are increased by 60% and fiber diameters become by 30% larger than those of contralateral control muscles. In spite of this hypertrophy, degenerative changes are seen in the ultrastructure, similar to those described in denervated atrophic muscles. Areas of dedifferentiation with autophagic vacuoles and aggregates of tubules are found in superficial layers of some fibers. Disintegration of Z lines and filaments along one or two sarcomeres occurs in a number of myofibrils, especially in muscles of young animals.
In contrast to denervation alone, simultaneous denervation and tenotomy of the ALD muscles results in atrophy. Decrease of muscle weights and reduction of fiber diameters are similar as after tenotomy; in both cases muscle fibers waste by degeneration and atrophy of myofibrils.
The fast PLD muscles underwent extensive atrophy in all three series of experiments. Corresponding atrophic and degenerative changes of ultrastructure were found in all instances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajusz, E.: Bed skeletal muscle fibres: Relative independence of neural control. Science 145, 938–939 (1964).
Bubenzer, H. J.: Die dünnen und die dicken Muskelfasern des Zwerchfells der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 69, 520–550 (1966).
Chang, Ch., Peng, T. P.: Comparative study on the protein and nucleic acid changes of the anterior and posterior latissimus dorsi of the chick following denervation. Acta physiol. sin. 25, 312–319 (1962).
Dreyfus, J. C., Schapira, G., Schapira, F.: Anabolisme du muscle atrophié: rôle de la croissance. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 143, 681–683 (1949).
Engel, W. K., Brooke, M., Nelson, P. G.: Histochemical studies of denervated or tenotomized cat muscle: illustrating difficulties in relating experimental animal conditions to human neuromuscular diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 138, 160–185 (1966).
Feng, T. P.: The effect of length on the resting metabolism of muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 74, 441–454 (1932).
— Jung, H. W., Wu, W. Y.: The contrasting trophic changes of the anterior and posterior latissimus dorsi of the chick following denervation. Acta physiol. sin. 25, 304–311 (1962).
—: The contrasting trophic changes of the anterior and posterior latissimus dorsi of the chick following denervation. In: The effect of use and disuse on neuromuscular functions (eds. E. Gutmann and P. Hník), p. 431–442. Prague: Publishing House of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences 1963.
Feng, T. P., Lu, D. K.: New lights on the phenomenon of transient hypertrophy in the denervated hemidiaphragm of the rat. Scientia sin. 14, 1772–1784 (1965).
Forssmann, W. G., Matter, A.: Ultrastruktureller Nachweis von zwei Myofibrillentypen in den Muskelfasern des Rattenzwerchfells. Experientia (Basel) 22, 816–817 (1966).
Gauthier, G. F., Padykula, H. A.: Cytological studies of fiber types in skeletal muscle. A comparative study of the mammalian diaphragm. J. Cell Biol. 28, 333–354 (1966).
George, J. C., Susheela, A. K.: A histophysiological study of the rat diaphragm. Biol. Bull. 121, 471–480 (1961).
Gutmann, E.: Denervation hypertrophy: the first stage in the course of the denervation changes in muscle. Physiol. bohemoslov. 9, 382–389 (1960).
—: The denervated muscle. 486 p. Prague: Publishing House of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences 1962.
— Haníková, M., Hájek, I., Klicpera, M., Syrovy, I.: The post-denervation hypertrophy of the diaphragm. Physiol. bohemoslov. 15, 508–524 (1966).
— Zelená, J.: Morphological changes in the denervated muscle. In: The denervated muscle (ed. E. Gutmann), p. 57–102 Prague: Publishing House of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences 1962.
Hájek, I., Gutmann, E., Syrový, I.: Changes of proteolytic activity of proteins following denervation in the anterior and posterior latissimus dorsi of the chicken. Physiol. bohemoslov. 15, 1–6 (1966).
Hess, A.: Structural differences of fast and slow extrafusal muscle fibers and their nerve endings in chickens. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 157, 221–231 (1961).
—: The structure of vertebrate slow and twitch muscle fibers. Invest. Ophthal. 6, 217–228 (1967).
Hník, P., Jirmanová, I., Vyklický, L., Zelená, J.: Fast and slow muscles of the chick after nerve cross-union. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 193, 309–325 (1967).
Jirmanová, I., Zelená, J.: Effect of denervation and tenotomy on slow and fast muscles of the chicken. [In Czech.] Čs. fysiol. 15, 507 (1966).
Lee, J. C.: Observations on lamelated structures and their formation in denervated skeletal muscle. J. roy. micr. Soc. 82, 17–22 (1963).
Martin, A. W., Sola, O. M.: The rate of atrophy of rat diaphragm. Fed. Proc. 7, 78 (1948).
—, Stewart, D. M.: Analysis of hypertrophy of denervated skeletal muscle. Fed. Proc. 13, 95 (1954).
Muscatello, TL, Margreth, A., Aloisi, M.: On the differential response of sarcoplasm and myoplasm to denervation in frog muscle. J. Cell Biol. 27, 1–24 (1965).
Nachmias, V. T., Padykula, H. A.: A histochemical study of normal and denervated red and white muscles of the rat. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 47–54 (1958).
Padykula, H. A., Gauthier, G. F.: Morphological and cytochemical characteristics of fiber types in normal mammalian skeletal muscle. In: Exploratory concepts in muscular dystrophy and related disorders (ed. A. T. Milhorat). Inter. Congr. Ser. 147, p. 117–128. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation 1968.
Page, S. G.: Structure and some contractile properties of fast and slow muscles of the chicken. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 205, 131–145 (1969).
— Slater, C. R.: Observations on fine structure and rate of contraction of some muscles from the chicken. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 179, 58–59P (1965).
Pellegrino, C., Franzini, C.: An electron microscope study of denervation atrophy in red and white skeletal muscle fibers. J. Cell Biol. 17, 327–349 (1963).
—, Franzini-Armstrong, C.: Recent contributions of electron microscopy to the study of normal and pathological muscle. Inter. Rev. exp. Path. 7, 139–226 (1969).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Sabatini, D. D., Bensch, K., Barrnett, R. J.: Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J. Cell Biol. 17, 19–58 (1963).
Shafiq, S.A., Gorycki, M. A., Asiedu, S., Milhorat, A. T.: Tenotomy: Effect on the fine structure of the soleus of the rat. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 20, 625–633 (1969).
Shafiq, S. A., Milhorat, A. T., Gorycki, M. A.: Pine structure of human muscle in neurogenic atrophy. Neurology (Minneap.) 17, 934–948 (1967).
Sola, O. M., Martin, A. W.: Denervation hypertrophy and atrophy of the hemidiaphragm of the rat. Amer. J. Physiol. 172, 324–332 (1953).
Stewart, D. M.: Effect of age on the response of four muscles of the rat to denervation. Amer. J. Physiol. 214, 1139–1146 (1968).
— Martin, A. W.: Hypertrophy of the denervated hemidiaphragm. Amer. J. Physiol. 186, 497–500 (1956).
Walker, S. M. Schrodt, G. R., Truong, X. T., Wall, E. J.: Electron microscope study of sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofilaments of tenotomized rat muscle. Amer. J. phys. Med. 44, 176–192 (1965).
Zelená, J.: The effect of denervation on muscle development. In: The denervated muscle (ed. E. Gutmann), p. 103–126. Prague: Publishing House of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences 1962.
—: Development of muscle receptors after tenotomy. Physiol. bohomoslov. 12, 30–36 (1963).
— Hník, P.: Muscle atrophy in young rats. Physiol. bohemoslov. 6, 193–199 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to acknowledge gratefully the skillful technical assistance of Mrs. M. Sobotková and Ing. M. Doubek, and editorial assistance of Miss Virginia Hamilton.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jirmanová, I., Zelená, J. Effect of denervation and tenotomy on slow and fast muscles of the chicken. Z. Zellforsch. 106, 333–347 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335777
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335777