Summary
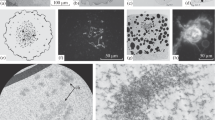
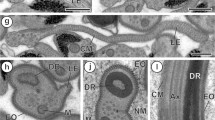
Macronuclear envelopes were isolated from the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis GL, negatively stained and examined in the electron microscope. The frequency of central granules in the macronuclear pores was evaluated in five different physiological states: (1) stationary phase of growth, (2) exponential phase of growth, (3) heat-synchronized cultures at the end of the heat-synchronization treatment, (4) heat-synchronized cultures at the beginning of the first division, (5) heat-synchronized cultures at the end of the first division.
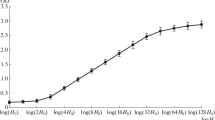
The percentage of pores containing a central granule was markedly enhanced in heatsynchronized cultures at the end of the first division, i.e. a state known for an increase in ribosome formation. Actinomycin D was found to cause a significant decrease in central granule frequency.
The observed alterations in central granule frequency seem to confirm the hypotheses which consider the central granule as representing a ribonucleoprotein particle in transit from nucleus to cytoplasm through the nuclear pore.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzelius, B. A.: The ultrastructure of the nuclear membrane of the sea urchin oocyte as studied with the electron microscope. Exp. Cell Res. 8, 147–158 (1955).
Allen, E. R., Cave, M. D.: Formation, transport, and storage of ribonucleic acid containing structures in oocytes of Acheta domesticus (Orthoptera). Z. Zellforsch. 92, 477–486 (1968).
Anderson, E., Beams, H. W.: Evidence from electron micrographs for the passage of material through pores of the nuclear membrane. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 439–443 (1956).
Beermann, W.: Control of differentiation at the chromosomal level. J. exp. Zool. 157, 49–61 (1964).
Belitsina, N. V., Ajtkhozhin, M. A., Gavrilova, L. P., Spirin, A. S.: Messenger RNA of differentiating animal cells. Biokhimiya 29, 363 (1964).
Byfield, J. E., Scherbaum, O. H.: Temperature-dependent decay of RNA and of protein synthesis in a heat-synchronized protozoan. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 57, 602–606 (1967).
Comes, P., Kleinig, H., Franke, W. W.: Composition, structure and function of the Hela cell nuclear envelope. I. Structural data. (In preparation.)
Feldherr, C. M.: The nuclear annuli as pathways for nucleocytoplasmic exchanges. J. Cell Biol. 14, 65–72 (1962).
—: Binding within the nuclear annuli and its possible effect on nucleocytoplasmic exchanges. J. Cell Biol. 20, 188–192 (1964).
—: The effect of the electron opaque pore material on exchange through the nuclear annuli. J. Cell Biol. 25, 43–53 (1965).
—, Harding, C. V.: The permeability characteristics of the nuclear envelope at interphase. In: Protoplasmatologia (M. Alfert, H. Bauer and C. V. Harding, eds.). 5, 35–50. Wien: Springer 1964.
Franke, W. W.: Isolated nuclear membranes. J. Cell Biol. 31, 619–623 (1966).
—: Zur Feinstruktur isolierter Kernmembranen aus tierischen Zellen. Z. Zellforsch. 80, 585–593 (1967).
Scheer, U.: The ultrastructure of the nuclear envelope of amphibian oocytes: A reinvestigation. I. The mature oocyte. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1969a (in press).
- - The ultrastructure of the nuclear envelope of amphibian oocytes: A reinvestigation. II. The immature oocyte and dynamic aspects. J. Ultrastruct. Res. (in press) (1969b).
Gall, J. G.: Observations on the nuclear membrane with the electron microscope. Exp. Cell Res. 7, 197–200 (1954).
—: Electron microscopy of the nuclear envelope. In: Protoplasmatologia (M. Alfert, H. Bauer and C. V. Harding, eds.), vol. 5, p. 4–25. Wien: Springer 1964.
Girard, M., Latham, H., Penman, S., Darnell, J. E.: Entrance of newly formed messenger RNA and ribosomes into Hela cell cytoplasm. J. molec. Biol. 11, 187–201 (1965).
Goldberg, J. H., Rabinowitz, M., Reich, E.: Basis of actinomycin action. I. DNA binding and inhibition of RNA-polymerase synthetic reactions by actinomycin. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 48, 2094–2101 (1962).
Hurwitz, J., Furth, J. J., Malamy, M., Alexander, M.: The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonueleic acid synthesis. III. The inhibition of the enzymatic synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid by actinomycin D and proflavin. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 48, 1222–1230 (1962).
Kessel, R. G.: Annulate lamellae. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 24, Suppl. 10, 1–82 (1968a).
—: Fine structure of annulate lamellae. J. Cell Biol. 36, 658–664 (1968b).
—: Fine structure of the pore-annulus complex in the nuclear envelope and annulate lamellae of germ cells. Z. Zellforsch. 94, 441–453 (1969).
Krishan, A., Hsu, D., Hutchins, P.: Hyperthrophy of granular endoplasmic reticulum and annulate lamellae in Earle's L cells exposed to vineblastine sulfate. J. Cell Biol. 39, 221–216 (1968).
Kumar, A.: Patterns of ribosomal RNA synthesis in Tetrahymena. J. Cell Biol. 35, 74A (1967).
—: Kinetics of RNA synthesis in Tetrahymena: Appearance of polysome-associated RNA and ribosomal subunits in the cytoplasm. J. Cell Biol. 39, 76A (1968).
Lane, N. J.: Spheroidal and ring nucleoli in amphibian oocytes. Patterns of uridine incorporation and fine structural features. J. Cell Biol. 35, 421–434 (1967).
Leick, V.: Effect of actinomycin D and DL-p-fluorophenylalanine on ribosome formation in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Europ. J. Biochem. 8, 215–220 (1969a).
—: Formation of subribosomal particles in the macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Europ. J. Biochem. 8, 221–228 (1969b).
—, Plesner, P.: Formation of ribosomes in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 169, 398–408 (1968a).
—: Precursors of ribosomal subunits in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 169, 409–415 (1968b).
Mentre, P.: Présence d'acide ribonucléique dans l'anneau osmiophile et le granule central des pores nucléaires. J. Microscopic 8, 51–68 (1969).
Merriam, R. W.: On the fine structure and composition of the nuclear envelope. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 11, 559–570 (1961).
—: Some dynamic aspects of the nuclear envelope. J. Cell Biol. 12, 79–90 (1962).
Mita, T.: Effects of actinomycin D on the RNA synthesis and the synchronous cell division of Tetrahymena pyriformis GL. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 103, 182–185 (1965).
Moner, J. G.: Temperature, RNA synthesis and cell division in heat-synchronized cells of Tetrahymena. Exp. Cell Res. 45, 618–630 (1967).
Monroe, J. H., Schidlovsky, G., Chandra, S.: Membrane pores and herpesvirus-type particles in negatively stained whole cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 134–144 (1967).
Nemer, M., Infante, A. A.: Early control of gene expression. In: The control of nuclear activity (L. Goldstein, ed.), p. 101–127. London: Prentice-Hall 1967.
Nørrevang, A.: Electron microscopic morphology of oogenesis. In: Int. Rev. Cytol. 23, 113–186 (1968).
Perry, R. P.: The cellular sites of synthesis of ribosomal and 4 S RNA. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 48, 2179–2186 (1962).
Perry, R. P.: Selective effects of actinomycin D on the intracellular distribution of RNA synthesis in tissue culture cells. Exp. Cell Res. 29, 400–406 (1963).
Pollister, A., Gettner, M., Ward, R.: Nucleocytoplasmic interchange in oocytes. Science 120, 789 (1954).
Samarina, O. P., Lukanidin, E. M., Georgiev, G. P.: On the structural organization of the nuclear complexes containing messenger RNA. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 142, 561–564 (1967).
Scheer, U., Franke, W. W.: Negative staining and adenosine triphosphatase activity of annulate lamellae of newt oocytes. J. Cell Biol. 42, 519–593 (1969).
Scherbaum, O., Zeuthen, E.: Induction of synchronous cell division in mass cultures of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Exp. Cell Res. 6, 221–227 (1954).
Stevens, A. R.: Machinery for exchange across the nuclear envelope. In: The control of nuclear activity (L. Goldstein, ed.), p. 189–271. London: Prentice-Hall 1967.
Stevens, B., Swift, H.: RNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm in Chironomus salivary glands. J. Cell Biol. 31, 55–78 (1966).
Takamoto, T.: Ultrastructural transport mechanism of messenger ribonucleic acid in the young oocytes of amphibians. Nature (Lond.) 211, 772–773 (1966).
Vaughan, M. H., Warner, J. R., Darnell, J. E.: Ribosomal precursor particles in the Hela cell nucleus. J. molec. Biol. 25, 235–251 (1967).
Verhey, C. A., Moyer, F. H.: Fine structural changes during sea urchin oogenesis. J. exp. Zool. 164, 195–226 (1967).
Vivier, E.: Observations ultrastructurales sur l'enveloppe nucléaire et ses ≪dpores≫ chez des sporozoaires. J. Microscopie 6, 371–390 (1967).
Watson, M. L.: Further observations on the nuclear envelope of the animal cell. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 6, 147–156 (1959).
Wunderlich, F.: The macronuclear envelope of Tetrahymena pyriformis GL in different physiological states. I. Quantitative structural data. Exp. Cell Res. 56, 369–374 (1969).
—, Franke, W. W.: Structures of macronuclear envelopes of Tetrahymena pyriformis in the stationary phase of growth. J. Cell Biol. 38, 458–462 (1968).
Yoo, B. Y., Bayley, S. T.: Studies on the substructure of the pores in isolated pea nuclei. Amer. J. Bot. 53, 610 (1966).
—: The structure of pores in isolated pea nuclei. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 18, 651–660 (1967).
Zeuthen, E., Scherbaum, O.: Synchronous divisions in mass cultures of the ciliate protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis as induced by temperature changes. In: Recent developments in cell physiology (J. A. Kitching, ed.), p. 141–155. London: Butterworths 1954.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
For careful technical assistance I am indebted to Miss Marianne Whiter as well as to Drs. H. Falk, W.W. Franke and P. Sitte for helpful discussions. This work was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wunderlich, F. The macronuclear envelope of Tetrahymena pyriformis GL in different physiological states. Z.Zellforsch. 101, 581–587 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335270
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335270