Abstract
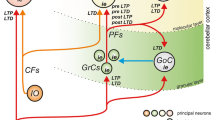
A dynamic model of learning that is based on the specific neuronal system of the cerebellum, including some of its structural-functional peculiarities, is proposed. It allows to simulate modification processes of the parallel fiber synapse that influences the Purkinje cell. Regularities of synaptic modifications are obtained by extrapolating well-known experimental data about changes of synaptic efficiency as resulting from release, refilling and mobilization of the mediator. It is shown that a mathematical description of synaptic processes corresponds to experimental data on the changes of synaptic efficiency under rhythmical stimulation and gives objective quantitative estimates for long-term (refilling of the mediator) and short-term (mobilization of the mediator) effects which are caused by presynaptic stimulation. Computer simulations have been conducted to investigate the characteristics of learning for different values of the following parameters: intensity of unconditioned stimulus (US, activity of the climbing fibre), intensity of conditioned stimulus (CS, activity of the parallel fibre), temporal shift between US and CS, temporal interval between reinforcements. It is shown that the temporal shift between CS and US is one of the major factors that influence the learning procedures. Analysis of the data obtained shows that the model enables us to simulate the main regularities of establishment and extinction of conditioned reflexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albus, J.S.: A theory of cerebellar function. Math. Biosci.10, 25–61 (1971)
Asratyan, E.A.: On the physiology of reinforcement of the conditioned reflex. Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. Im.I.P. Pavlova21, 3–13 (1971) (in Russian)
Brindley, G.S.: The use made by the cerebellum of the information that it receives from sense organs. IBRO Bull.3, 80 (1964)
Brindley, G.S.: The classification of modifiable synapses and their use in models for conditioning. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B168, 361–376 (1967)
Čapek, R., Esplin, B.: Homosynaptic depression and transmitter turnover in spinal monosynaptic pathway. J. Neurophysiol.40, 95–105 (1977)
Curtis, D.R., Eccles, J.C.: Synaptic action during and after repetitive stimulation. J. Physiol.150, 374–398 (1960)
Del Castillo, J., Katz, B.: Quantal components of the endplate potentail. J. Physiol.124, 560–573 (1954)
Dunin-Barkowski, W.L.: The operational theory of the cerebellum. In: Neuronal mechanisms of integrative action of the cerebellum, Fanardjian, V.V. (ed.), pp. 220–226. Yerevan: Publ. House of Armenian Academy of Sciences 1979 (in Russian)
Eccles, J.C.: The physiology of synapses. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1964
Eccles, J.C.: An instruction-selection theory of learning in the cerebellar cortex. Brain Res.127, 327–352 (1977)
Eccles, J.C., Ito, M., Szentagothai, J.: The cerebellum as a neuronal machine. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1967
Fedor, P., Majernik, V.: A neuron model as an universal element of self-learning networks for pattern recognition. Biol. Cybern.26, 25–33 (1977)
Fukushima, K.: Cognitron: a self-organizing multilayered neural network. Biol. Cybern.20, 121–136 (1975)
Gilbert, P.F.C.: A theory of memory that explaines the function and structure of the cerebellum. Brain Res.70, 1–18 (1974)
Grossberg, S.: Pavlovian pattern learning by nonlinear neural networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (Wash.).68, 828–831 (1971)
Hebb, D.O.: The organization of behaviour. New York: Wiley 1949
Hirai, Y.: A new hypothesis for synaptic modification: an interactive processes between postsynaptic competition and presynaptic regulation. Biol. Cybern.36, 41–50 (1980)
Ito, M.: Neural design of the cerebellum motor control system. Brain Res.40, 81–84 (1972)
Kandel, E.R.: Cellular basis of behaviour. San Francisco: Freeman 1976
Katz, R., Miledi, R.: Tetrodoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J. Physiol.203, 459–487 (1969)
Kohonen, T.: Associative memory. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1977
Kostyuk, P.G., Vasilenko, D.A., Zadorozhny, D.A.: Reactions of lumbar motoneurons produced by actions of propriospinal pathways. Neirophysiologia1, 5–14 (1969) (in Russian)
Kostyuk, P.G., Savoskina, L.A.: Functional peculiarities of degenerating central synaptic endings. Sechenov Physiol. J. USSR52, 793–803 (1969) (in Russian)
Kreps, E.M.: To the possibility of conditioned reflex formation when unconditioned stimulus precedes the indifferent one. Tr. Fiziol. Lab. I.P. Pavlova5, 3–20 (1954) (in Russian)
Liley, A.M., North, K.A.: An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J. Neurophysiol.16, 509–527 (1953)
Malsburg von der, C.: Self-organization of orientation sensitive cells in the striate cortex. Kybernetik14, 85–100 (1973)
Marr, D.: A theory of cerebellar cortex. J. Physiol.202, 437–470 (1969)
Melkonian, D.S., Mkrtchian, H.H., Chondkarian, N.S.: Mathematical description of synapse behaviour in the course of repetitive stimulation. Dokl. Acad. Nauk. Arm. SSR65, 59–64 (1977) (in Russian)
Melkonian, D.S., Mkrtchian, H.H., Chondkarian, N.S.: Mathematical description of some regularities of transmitter release from presynaptic terminals. Biol. J. Arm.31, 375–382 (1978) (in Russian)
Pavlov, I.P.: Conditioned reflexes, London: Oxford University Press 1927
Stent, G.S.: A physiological mechanism for Hebb's postulate of learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)70, 997–1001 (1973)
Willshaw, D.J., Buneman, O.P., Longuet-Higgins, H.C.: Non-holographic associative memory. Nature (Lond.)222, 960–962 (1969)
Wilson, H.R.: A synaptic model for spatial frequency adaptation. J. Theor. Biol.50, 327–352 (1975)
Woodson, P.B.J., Schlapfer, W.T., Tremblay, J.P., Barondes, S.H.: Resting and stimulated values of model parameters governing transmitter release at a synapse in Aplisia californica. Brain Res.109, 21–40 (1976)
Zadeh, L.A.: Time-varying networks. I. Proc. I.R.E.49, 1488–1503 (1961)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melkonian, D.S., Mkrtchian, H.H. & Fanardjian, V.V. Simulation of learning processes in neuronal networks of the cerebellum. Biol. Cybern. 45, 79–88 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335233
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335233