Summary
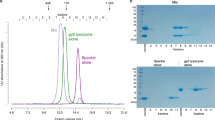
The synthesis of E. coli ribosomal proteins ceases after infection with bacteriophages T4 or T7 as does the synthesis of most other host proteins. The shut-off does not affect all ribosomal proteins to the same extent. After T7 infection no new proteins were detected in NH4Cl-washed ribosomal particles. Bacteriophage T4, however, induces 3–4 new protein bands demonstrated by one-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The appearance of these bands is prevented by the addition of rifampicin at the time of infection but not when rifampicin is added one minute after infection. The NH4Cl-washed ribosomal particles present at the time of T7 or T4 infection do not show any structural changes by sedimentation, subunit dissociation, or protein analysis on two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels. However, by labeling the T7 infected cells with 32P-phosphate, it is seen that the ribosomes become phosphorylated. The 32P-label comigrates with ribosomal proteins. This phosphorylating activity depends on a T7 gene. The T7 protein phosphokinase utilizes ribosomes as phosphate acceptor in vitro. The T7 ribosomes (NH4Cl-washed) still function in vitro as do ribosomal particles from uninfected cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Echols, H., Garen, A., Garen, G., Torriani, A.: Genetic control of repression of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli. J. molec. Biol. 3, 425–438 (1961)
Gordon, J.: Determination of an upper limit to the phosphorus content of polypeptide chain elongation factor and ribosomal proteins in E. coli. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 44, 579–585 (1971)
Herrlich, P., Rahmsdorf, H. J., Pai, S. H., Schweiger, M.: Translational control induced by bacteriophage T7. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.), in press (1974)
Herrlich, P., Schweiger, M.: DNA- and RNA-directed synthesis in vitro of phage enzymes. Meth. Enzymol. 30, in press (1973)
Hill, R. F.: A radiation-sensitive mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 30, 636–637 (1958)
Kaltschmidt, E., Wittmann, H. G.: Ribosomal proteins, XII. Number of proteins of small and large ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli as determined by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 67, 1276–1282 (1970)
Mathews, C. K.: Bacteriophage biochemistry. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., 1971
Rahmsdorf, H. J., Herrlich, P., Tao, M., Schweiger, M.: Interference of phage with host DNA, RNA and protein synthesis. In: Cell-virus interactions (Raspé and Bernhard, eds.), Adv. in the biosciences, vol 12. Braunschweig: Pergamon Press-Vieweg 1973
Rahmsdorf, H. J., Pai, S. H., Ponta, H., Herrlich, P., Schweiger, M.: Protein phosphokinase induction in E. coli by bacteriophage T7. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.), in press (1974)
Scherzinger, E., Herrlich, P., Schweiger, M., Schuster, H.: The early region of the DNA of bacteriophage T7. Europ. J. Biochem. 25, 341–348 (1972)
Schweiger, M., Herrlich, P.: DNA directed enzyme synthesis in vitro. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. (in press)
Smith, F. A., Haselkorn, R.: Protein associated with the ribosomes in T4 infected E. coli. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 34, 91–94 (1969)
Studier, F. W.: The genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T7. Virology 39, 562–574 (1969)
Studies, F. W.: Analysis of bacteriophage T7 RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J. molec. Biol. 79, 237–248 (1973)
Tao, M., Salas, M. L., Lipmann, F.: Mechanism of activation by cyclic 3′, 5′-AMP of a protein phosphokinase from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 67, 408–414 (1970)
Tishler, P. V., Epstein, C. J.: A convenient method of preparing polyacrylamide gels for liquid scintillation spectrometry. Analyt. Biochem. 22, 89–98 (1968)
Traub, P.: Structure, function and in vitro reconstitution of E. coli ribosomes. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 52, 1–93 (1970)
Traugh, J. A., Traut, R. R.: Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli by protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochemistry 11, 2503–2509 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by E. Bautz
Paper No. 83 on “Ribosomal Proteins”. Preceding paper is by Isono et al., Mol. gen. Genet. 127, 191–195 (1973).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmsdorf, H.J., Herrlich, P., Pai, S.H. et al. Ribosomes after infection with bacteriophage T4 and T7. Molec. gen. Genet. 127, 259–271 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333766
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333766