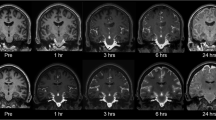
Summary
The incidence of post-myelographic sideeffects has been significantly reduced since the advent of the new generation of water-soluble, non-ionic, contrast media (CM). One of these CM, iopamidol, has recently been released for clinical intrathecal use in Australia. Clinical evaluations have shown iopamidol to give excellent diagnostic results. However, many adverse side-effects have been cited in the literature. Reactions to iopamidol following myelography are thought to be due to the lack of a physiologic barrier between the extracellular fluid of the brain parenchyma and the CSF, thereby allowing CM to penetrate the brain parenchyma tissue, following subarachnoid injection. This study investigates the rate of clearance of intrathecal iopamidol from the brain in dogs by performing coronal CT scans at intervals over a 48 h, post-injection period. Analysis of similar regions of interest (ROI) for each time period indicate that iopamidol can be detected in canine brains for at least 48 h following intrathecal injection (P<0.05). Furthermore, the disappearance of iopamidol from the brain parenchyma is approximately logarithmic in form, with a half-life of approximately 22 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Felder E, Pitre D, Tirone P (1977) Radiopaque contrast media: XLIV Preclinical studies with a new nonionic contrast agent. II Farmaco (Sci) 32:834–844
Drayer B, Suslavich F, Luther J, Rommel A, Allen S, Dubois P, Heinz R, Bates M (1982) Clinical trial of iopamidol for lumbosacral myelography. AJNR 3:59–64
Drayer BP, Warner MA, Sudilovsky A, Luther J, Wilkins R, Allen S, Bates M (1982) Iopamidol vs metrizamide: a double blind study for cervical myelography. Neuroradiology 24: 77–84
Trevisan C, Malaguti C, Manfredini M, Tampieri D (1983) Iopamidol vs metrizamide myelography: clinical comparison of side effects. AJNR 4:306–308
Gonsette RE, Brucher JM (1980) Neurotoxicity of novel water-soluble contrast media for intrathecal application. Invest Radiol 15:S254-S259
Carella A, Federico F, Di Cuonzo F, Vissjau E, Lamberti P (1982) Adverse side effects of metrizamide and iopamidolo in myelography. Neuroradiology 22:247–249
Oldendorf WH, Davson H (1967) Brain extracellular space and the sink action of the cerebrospinal fluid. Measurement of rabbit brain extracellular space using sucrose labelled with carbon 14. Arch Neurol 17:196–205
Bradbury M (1979) The concept of a blood-brain barrier. Wiley, Chichester
Sage MR, Wilcox J, Evill CA, Benness GT (1982) Brain parenchyma penetration by intrathecal ionic and nonionic contrast media. AJNR 3:481–483
Sage MR, Wilcox J (1983) Brain parenchyma penetration by intrathecal nonionic iopamidol. AJNR 4:1181–1183
Drayer BP, Rosenbaum AE (1977) Metrizamide brain penetrance. Acta Radiol [Suppl] (Stockh) 355:280–293
Caille JM, Guibert-Tranier F, Howa JM, Billerey J, Calabet A, Piton J (1980) Cerebral penetration following metrizamide myelography. J Neuroradiol 7:3–12
Potts DG, Gomez DG, Shaw DD (1985) Cranial and spinal cerebrospinal fluid absorption and the clearance of water-soluble myelographic contrast media: A review. Invest Radiol [Suppl] 20:S51-S54
Hammer B, Lackner W (1980) Iopamidol, a new non-ionic hydrosoluble contrast medium for neuroradiology. Neuroradiology 19:119–121
Hammer B, Deisenhammer E (1985) Iotrol, a new water-soluble non-ionic dimeric contrast medium for intrathecal use. Neuroradiology 27:337–341
Richert S, Sartor K, Holl B (1979) Subclinical organic psychosyndromes on intrathecal injection of metrizamide for lumbar myelography. Neuroradiology 18:177–184
Cronqvist SE, Holtas SL, Laike T, Ozolins A (1984) Psychologic tests in the evaluation of psychic changes after myelography with metrizamide. Acta Radiol [Diagn] 25:257–260
Cronqvist SE, Holtas SL, Laike T, Ozolins A (1984) Psychic changes following myelography with metrizamide and iohexol: a comparative investigation with psychologic tests. Acta Radiol [Diagn] 25:369–373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilcox, J., Evill, C.A. & Sage, M.R. Rate of clearance of intrathecal iopamidol in the dog. Neuroradiology 28, 359–361 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333446
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333446