Summary
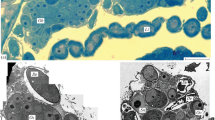
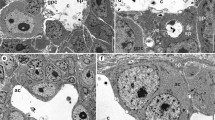
The development of the human thyroid gland was studied by light- and electron microscopy in 20 embryos with a crown-rump length from 1.4–12 cm. An ultimobranchial body was found outside the thyroid gland in embryos of less than 1.9 cm length. With the junction of the ultimobranchial body and the dorsal part of the reticular medial thyroid anlage a compact bilateral thyroid anlage arises. In this lateral anlage the development of thyroid follicles, of branchiogenic cysts and of thyroid C-cells could be demonstrated. The primitive cavity of the thyroid follicles originates from an invagination of the cytomembrane. This seems to be the result of beginning secretion and polar differentiation of the follicular cells. Colloid could not be demonstrated in embryos less than 6 cm long. Thyroid C-cells rather late develop from undifferentiated cells which are distributed in the lateral anlage. They could be identified only in an rather immature stage in embryos of 12 cm length by electron microscopy and could not be demonstrated by specific staining methods in light microscopy.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 20 menschlichen Keimlingen mit einer Scheitel-Steißlänge (SSL) von 1,4–12 cm wurde die Entwicklung der Schilddrüse lichtund elektronenoptisch untersucht. Bei Embryonen von weniger als 1,9 cm SSL kann außerhalb der Schilddrüse ein ultimobranchialer Körper (UBK) nachgewiesen werden. Aus der Vereinigung des UBK mit den dorsalen Anteilen der primär unpaarigen medialen Schilddrüsenanlage entsteht beiderseits eine laterale Schilddrüsenanlage. Während die mediale Organanlage einen reticulären Aufbau hat und Schilddrüsenfollikel bildet, hat die laterale Schilddrüsenanlage einen kompakten Aufbau. Aus der lateralen Schilddrüsenanlage gehen hervor:
-
1.
Schilddrüsenfollikel.
-
2.
branchiogene Cysten.
-
3.
die C-Zellen.
Die primitiven Follikellichtungen entstehen durch Einstülpungen der Zelloberfläche als Ergebnis der beginnenden Sekretion und polaren Differenzierung der Follikelzellen. Kolloid ist erst bei Embryonen ab SSL 6 cm nachweisbar. Die C-Zellen differenzieren sich wesentlich später erst am Ende der Embryonalperiode und sind auch bei Embryonen von SSL 12 cm noch nicht ausgereift. Sie entstehen aus undifferenzierten Stammzellen, die im Bereich der lateralen Schilddrüsenanlage verteilt sind. Der lichtoptische Nachweis von C-Zellen mit spezifischen Färbemethoden ist bei Embryonen von SSL bis 12 cm noch nicht möglich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bargmann, W.: Die Schilddrüse. In: Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen hrsg von. W. v. Möllendorff, Bd. VI/2. Berlin: Springer 1939.
Braunstein, H., Stephens, Ch. L.: Parafollicular cells of human thyroid. Arch. Path. 86, 659–666 (1968).
Copp, D. H., Brooks, C. E., Low, B. S., Newsome, F., Odor, R. K., Parkes, C. O., Walker, V., Watts, E. G.: Calcitonin and ultimobranchial function in lower vertebrates. In: Calcitonin 1969. Proceedings of the second internat. Symposion, p. 281–294. London: William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd. 1970.
Ekholm, R., Ericson, L. E.: The ultrastructure of the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland in the rat. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 378–402 (1968).
Geyer, G.: Histochemischer Nachweis von Carboxylgruppen mit der Carbodiimidreaktion. Acta histochem. (Jena) 19, 73–77 (1964).
Godwin, M. C.: Complex IV in the dog with special emphasis on the relation of the ultimobranchial body to the interfollicular cells in the postnatal thyroid gland. Amer. J. Anat. 60, 299–339 (1937).
Heidenhain, M.: Über verschiedene Typen im Bau der Schilddrüse. Anat. Anz., Erg.-Bd. 54, 141–151 (1921).
Heimann, P.: Ultrastructure of human thyroid. Acta endocrin. (Kbh.) 53, Suppl. 110, 1–102 (1966).
Hennenberg, B.: Beitrag zur Kenntnis der lateralen Schilddrüsenanlage. Anat. H. 28, 287–302 (1905).
Kingsbury, B. F.: On the fate of the ultimobranchial body within the human thyroid gland. Anat. Rec. 61, 155–173 (1935).
Klinck, G. H., Oertel, J. E., Winship, T.: Ultrastructure of normal human thyroid. Lab. Invest. 22, 2–22 (1970).
Kracht, J., Hachtmeister, U., Kruse, J., Matthaes, P.: C-Zellen in der Schilddrüse des Menschen. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Path. 52, 485–490 (1968).
Lietz, H.: Zur Ultrastruktur der C-Zellen in der Rattenschilddrüse bei gestörtem Calciumstoffwechsel. Virchows Arch. Abt. A Path. Anat. 350, 136–149 (1970).
—, Donath, K.: Zur Ultrastruktur und Entstehung des Amyloids im medullären Schilddrüsencarcinom. Virchows Arch. Abt. A Path. Anat. 350, 261–274 (1970).
Luciano, L., Reale, E.: Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen der parafollikulären Zellen der Rattenschilddrüse. Z. Zellforsch. 64, 751–766 (1964).
Meyer, J. S.: Fine structure of two amyloid-forming medullary carcinomas of thyroid. Cancer (Philad.) 21, 406–425 (1968).
Norris, E. H.: The morphogenesis of the follicles of the human thyroid gland. Amer. J. Anat. 20, 411–418 (1916).
—: The early morphogenesis of the human thyroid gland. Amer. J. Anat. 24, 443–465 (1918).
Olin, P.: Human fetal thyreoglobulin: characterization and in vitro biosynthesis studies. Endocrinology 86, 1041–1048 (1970).
Pearse, A. G. E.: Common cytochemical and ultrastructural characteristics of cells producing polypeptide hormones (the APUD-series) and their relevance to thyroid ultimobranchial C cells and calcitonin. Proc. roy. Soc. B 170, 71–80 (1968).
—: The characteristics of the C cells and their significance in relation to those of other endocrine polypeptide cells and to the synthesis, storage and secretion of calcitonin. In: Calcitonin 1969. Proceedings of the second internat. Symposion, p. 125–140. London: William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd. 1970.
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Sato, T., Ishikawa, K., Aoi, T., Kito, J., Sugiyama, S.: Electron microscopic observations on the development of the parafollicular cells from the ultimobranchial cysts in the thyroid gland of the mouse. Okajimas Fol. anat. jap. 42, 91–105 (1966).
Schiebler, T. H., Schiessler, S.: Über den Nachweis von Insulin mit den metachromatisch reagierenden Pseudoisocyaninen. Histochemie l, 445–465 (1959).
Shepard, T. H.: Development of the human fetal thyroid. Gen. comp. Endocr. 10, 174–181 (1968).
Solcia, E., Vassallo, G., Capella, C.: Selective staining of endocrine cells by basis dyes after acid hydrolysis. Stain Technol. 73, 257–263 (1968).
Stenpak, J. G., Ward, P. T.: An improved staining method for electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 22, 697–701 (1964).
Stoeckel, M. E., Porte, A.: Origine embryonnaire et différentiation sécrétoire des cellules à calcitonine (cellules C) dans la thyroïde foetale du rat. Étude au microscope électronique. Z. Zellforsch. 106, 251–268 (1970).
Sugiyama, S., Taki, A., Machida, Y., Furihata, N.: The significance and fate of the ultimobranchial body in man in relation to the development of the thyroid gland. Okajimas Fol. anat. jap. 32, 329–340 (1959).
—, Sugiyama, N., Yamamoto, Y.: Histological studies of the human thyroid gland in middle and late prenatal life. Okajimas Fol. anat. jap. 33, 75–84 (1959).
Watzka, M.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über den ultimobranchialen Körper. Z. mikr.anat. Forsch. 34, 485–533 (1933).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lietz, H., Wöhler, J. & Pomp, H. Zur Entwicklung und Ultrastruktur der embryonalen Schilddrüse des Menschen. Z. Zellforsch. 113, 94–110 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331204
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331204