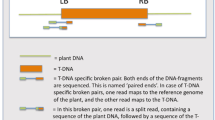
Summary
Several genomic clones from Petroselinum hortense, Zea mays and Antirrhinum majus all homologous to cloned Petroselinum chalcone synthase cDNA were isolated using the λgt WES cloning system.
Clones containing the chalcone synthase structural gene were identified by hybridization to cDNA from Petroselinum hortense, genomic wildtype, mutant and revertant DNA.
Among the 5 different clones from Petroselinum hortense, PH3 is the most likely candidate to contain at least a portion of the chalcone synthase gene.
None of the 4 Zea mays clones appeared to contain part of the chalcone synthase gene.
Among the 2 different clones from Antirrhinum majus, AM3 contains the portion of the chalcone synthase structural gene which is altered in the mutant nivea recurrens (niv rec). This mutant is considered to be due to the integration of a transposable element. In revertants of niv rec to niv + the wildtype locus is restored molecularly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dooner HK, Nelson OE (1977) Genetic control of UDP glucose: flavanol 3-O-glucosyltransferase in endosperm of maize. Biochem Genetics 15:509
Dooner HK (1980) Genetic regulation of anthocyanin biosynthetic enzymes in maize. Genetics 94:29
Fincham JRS, Sastry GRK (1974) Controlling Elements in Maize. Ann Rev Genetics 8:15
Hanson KR, Havir EA (1981) Phenylalanin ammonia lyase. In: Stumpf PK, Conn EE (eds) The biochemistry of plants, Vol 7. Academic Press New York, p 577
Harrison BJ, Carpenter RA (1973) A comparison on the instabilities at the nivea and pallida loci in Antirrhinum majus. Heredity 31:309
Heller W, Hahlbrock K (1980) Highly purified “flavanone synthase” from parsley catalyses the formation of naringenin chalcone. Arch Biochem Biophs 200:617
Hohn B (1979) In vitro packaging of λ and cosmid DNA. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds). Methods in enzymology 68:299
Kuckuck H (1936) Über vier neue Serien multipler Allele bei Antirrhinum majus. Z F indukt Abst- u Vererbungsl 71:429
Leder P, Tiemeier D, Enquist L (1977) EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organism: the λgt WES cloning system. Science 196:175
McClintock B (1956) Controlling Elements and the Gene, Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 21:197
McClintock B (1967) Regulation of pattern of gene expression by controlling elements in maize. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 65:568
McCormick SH (1968) Pigment synthesis in maize aleurone from precursor fed to anthocyanin mutants. Biochem Genetics 16:777
Paterson BM, Roberts BE, Kuff EL (1977) Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:4370
Peterson PA (1970) The En mutable system in maize. III. Transposition associated with mutational events. Theor Appl Genet 40:367
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503
Stickland RG, Harrison BJ (1974) Precursors and genetic control of pigmentation, I. Induced biosynthesis of pelagonidin, cyanidin and delphinidin in Antirrhinum majus. Heredity 33:108
Stubbe H Genetik und Zytologie von Antirrhinum L. sect, Antirrhinum. VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1966, p 97
Wienand U, Langridge P, Feix G (1981) Isolation and characterization of a genomic sequence of maize coding for a zein gene. Mol Gen Genet 182:440
Woolford JL, Rosbash M (1979) The use of R-looping for structural gene identification and mRNA purification. Nucl Acids Res 6:2483
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Schell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wienand, U., Sommer, H., Schwarz, Z. et al. A general method to identify plant structural genes among genomic DNA clones using transposable element induced mutations. Molec Gen Genet 187, 195–201 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331117
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331117