Summary
Certain E. coli K12 strains are able to secrete a plasmid encoded 107 K protein into the culture medium. During exponential growth of the cells this protein represents approximately 1% of total cell protein.
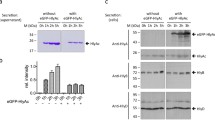
The presence of the 107 K polypeptide was demonstrated through the fortuitous use of strain MC4100. This gave a largely protein-free culture supernatant, presumably due to minimal lysis of whole cells. Pulse-labelling experiments showed that the secretion of the 107 K polypeptide reached a maximum during the stationary phase of growth, where it represented substantially more than 1% of total cell protein. The 107 K polypeptide is coded by the haemolytic plasmid pHly167, and appears to be related to a previously reported intracellular “precursor” form of the α-haemolysin (Goebel and Hedgpeth 1982). However, additional extracellular factors appear to be required for α-haemolysin activity since several nonhaemolytic mutants still secrete this protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glenn AR (1976) Production of extracellular proteins in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 30:41–62
Goebel W, Hedgpeth J (1982) Cloning and functional characterization of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin determinant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 151:1290–1298
Hirst TR, Hardy SJS, Randall LL (1983) Assembly in vivo of enterotoxin from Escherichia coli: formation of the B subunit oligomer. J Bacteriol 153:21–26
Noegel A, Rdest U, Springer W, Goebel W (1979) Plasmid cistrons controlling synthesis and excretion of the exotoxin α-haemolysin of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 175:343–350
Noegel A, Rdest U, Goebel W (1981) Determination of the functions of hemolytic plasmid pHly152 of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 145:233–247
Poole K, Hancock REW (1983) Secretion of alkaline phosphatase and phospholipase C in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is specific and does not involve an increase in outer membrane permeability. FEMS Microbiol Lett 16:25–29
Rennie RP, Arbuthnott JP (1974) Partial characterization of Escherichia coli haemolysin. J Med Microbiol 7:179–188
Sancar A, Hack AM, Rupp WD (1979) Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol 137:692–693
Smith HW (1963) The haemolysins of Escherichia coli. J Pathol Bacteriol 85:197–211
Springer W, Goebel W (1980) Synthesis and secretion of hemolysin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 144:53–59
Williams P (1979) Determination of the molecular weight of Escherichia coli α-haemolysin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 5:21–24
Yamada M, Miki T, Nakazawa A (1982) Translocation of colicin E1 through cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. FEBS lett 150:465–468
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G.A. O'Donovan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackman, N., Holland, I.B. Secretion of a 107 K dalton polypeptide into the medium from a haemolytic E. coli K12 strain. Molec Gen Genet 193, 312–315 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00330686
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00330686