Summary
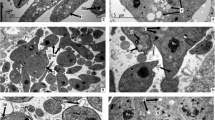
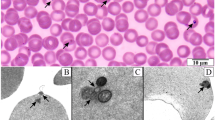
First-generation merozoites of Eimeria bovis, obtained from calves which had been inoculated 14, 14 1/2 and 15 days earlier, were inoculated into monolayers of Madin-Darby bovine kidney (MDBK) and primary embryonic bovine kidney (BEK-1), as well as kidney cell aggregates (BEK-2). Cultures were examined at intervals of 1–12 hr for 168 hr with phase-contrast microscopy and then fixed, stained and re-examined with bright-field microscopy. Fourteen-day merozoites entered all cell types, whereas 14 1/2- and 15-day merozoites did not enter any. Development beyond the first-generation merozoite stage occurred in BEK-1 and BEK-2, but not MDBK. Intermediate and mature second-generation schizonts with 24–36 merozoites were seen at 48–108 hr. Merozoites were 4.5 by 1.4 μm, with a posteriorly located nucleus. Young, intermediate, and mature microgamonts were seen at 72–96 hr, 72–120 hr, and 96–120 hr, respectively. Young, intermediate, and mature macrogamonts were seen at 48–96 hr, 72–120 hr, and 96–120 hr, respectively. Mature microgamonts and macrogamonts were 14.7 μm in diameter and 19.5 by 15 μm, respectively. At 120–168 hr, zygotes in various stages of oocyst wall formation and oocysts (24.4 by 15 μm) were seen. A crescent body was present in the parasitophorous vacuole of some schizonts and gamonts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C:
-
crescent body
- HN:
-
host cell nuclcus
- M:
-
merozoite
- MI:
-
microgamete
- N:
-
nucleus of parasite
- NU:
-
nucleolus of parasite
- PG:
-
plastic granule
- PV:
-
parasitophorous vacuole
- OW:
-
oocyst wall
- S:
-
satellite body
References
Bedrnik, P.: Further development of the 2nd generation of Eimeria tenella in tissue cultures. Folia parasit. 14, 361–363 (1967a).
Bedrnik, P.: Development of sexual stages and oocysts from the 2nd generation of Eimeria tenella merozoites in tissue culture. Folia parasit. 14, 364 (1967b).
Bedrnik, P.: Cultivation of Eimeria tenella in tissue cultures. I. Further development of second generation merozoites in tissue cultures. Acta protozool. 7, 87–98 (1969).
Bedrnik, P.: Cultivation of Eimeria tenella in tissue cultures. II. Factors influencing a further development of second generation merozoites in tissue culture. Acta protozool. 7, 253–262 (1970).
Doran, D. J.: Eimeria tenella: from sporozoites to oocysts in cell culture. Proc. helminth. Soc. Wash. 37, 84–92 (1970).
Doran, D. J.: Comparative development of five species of poultry coccidia in primary cultures of chicken kidney cells. J. Protozool. 18 (suppl.), 11 (1971).
Doran, D. J.: Cultivation of coccidia in avian embryos and cell culture, p. 183–252. In: D. M. Hammond, ed., The Coccidia; Eimeria, Isospora, Toxoplasma, and Related Genera. Baltimore: University Park Press 1973.
Fayer, R.: Sarcocystis: Development in cultured avian and mammalian cells. Science 168, 1104–1105 (1970).
Fayer, R.: Gametogony of Sarcocystis sp. in cell culture. Science 175, 65–67 (1972).
Fayer, R., Hammond, D. M.: Development of first-generation schizonts of Eimeria bovis in cultured bovine cells. J. Protozool. 14, 764–772 (1967).
Frenkel, J. K.: Toxoplasmosis: Parasite life cycle, pathology, and immunology, p. 343–410. In: D. M. Hammond, ed., The Coccidia; Eimeria, Isospora, Toxoplasma, and Related Genera. Baltimore: University Park Press 1973.
Hammond, D. M., Andersen, F. L., Miner, M. L.: The occurrence of a second-generation in the life cycle of Eimeria bovis in calves. J. Parasit. 49, 428–434 (1963).
Hammond, D. M., Fayer, R., Miner, M. L.: Further studies on in vitro development of Eimeria bovis and attempts to obtain second-generation schizonts. J. Protozool. 16, 298–302 (1969).
Kelley, G. L., Hammond, D. M.: Fine structural aspects of early development of Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae in cultured cells. Z. Parasitenk. 38, 271–284 (1972).
Levine, N. D.: Protozoan parasites of domestic animals and of man, 2nd ed., p. 167. Minneapolis: Burgess Publishing Co. 1973.
Parker, R. C.: Methods of tissue culture, 3rd ed., p. 145–151. New York: Paul B. Hoeber, Inc. 1961.
Shibalova, T. A.: Cultivation of the endogenous stages of chicken coccidia in embryos and tissue cultures. J. Parasit. 56 (4, Sect. II), 315–316 (1970).
Speer, C. A., Hammond, D. M.: Development of gametocytes and oocysts of Eimeria magna from rabbits in cell culture. Proc. helminth. Soc. Wash. 39, 114–118 (1972).
Speer, C. A., Hammond, D. M., Elsner, Y. Y.: Development of second-generation schizonts and immature gamonts of Eimeria larimerensis in cultured cells. Proc. helminth. Soc. Wash. 40, 147–153 (1973a).
Speer, C. A., Hammond, D. M., Elsner, Y. Y.: Further asexual development of Eimeria magna merozoites in cell cultures. J. Parasit. 59, in press (1973b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by PHS Research Grant No. AI-04788 from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Published as Journal Paper No. 1468, Utah Agricultural Experiment Station.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Speer, C.A., Hammond, D.M. Development of second-generation schizonts, gamonts and oocysts of Eimeria bovis in bovine kidney cells. Z. Parasitenk. 42, 105–113 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329788
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329788