Summary
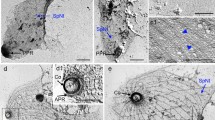
Actin-like microfilaments in the cytoplasm of trophozoites of two Entamoeba histolytica-strains, cultured monoxenically in Diamonds medium (1968), are presented in the course of electronmicroscopical studies. The thin filaments, 20–60 Å in diameter, are partly aggregated into whirl-like configurations with a more compact center, in which the individual filaments are arranged in parallel arrays. At the border between those whirls and the surrounding cytoplasm they show a more irregular distribution-pattern.
In amoebae being in the precyst stage band-like arrays of microfilaments are associated with the ribonucleoprotein or chromatoid bodies.
The significance of the microfilaments in relation to cytoplasmic streaming and cell motility of the parasites is discussed. The results of this study are compared with corresponding observations on free-living amoebae.
Zusammenfassung
Bei elektronenmikroskopischen Untersuchungen an Kulturformen von Entamoeba histolytica aus dem monoxenischen Medium nach Diamond (1968) werden im Cytoplasma der Parasiten actin-ähnliche Mikrofilamente von 20–60 Å Durchmesser dargestellt.
In den intakten Amöben der beiden untersuchten Stämme sind die Mikrofilamente teilweise zu wirbelartigen Bündeln mit zentralen Verdichtungen angeordnet, in denen die einzelnen Mikrofilamente parallel verlaufen, während sie sich beim Übergang der Wirbelfiguren in das sie umgebende Cytoplasma verlieren.
Eine Beziehung von bandförmigen Mikrofilamenten zu bestimmten Zellorganellen kann bei Amöben im „precyst“-Stadium beobachtet werden. Die Filamente liegen hier in engem Kontakt mit kristalloiden RNP-Aggregaten, die den Chromidialkörpern entsprechen.
Die Bedeutung der Mikrofilamente für die Plasmaströmung und Pseudopodienbildung der Parasiten wird diskutiert und mit den an freilebenden Amöbenarten erzielten Ergebnissen verglichen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allen, R. D.: Ameboid movement. In: The cell, vol. 11, p. 135–216 New York and London: Academic Press 1961
Bos H. J.: The problem of pathogenicity in parasitic Entamoeba. Dissertation d. Rijksuniversiteit te Leiden, Promotor: J. J. Laarmann 1973
Comly, L. T.: Mikrofilaments in Chaos carolinensis. J. Cell Biol. 58, 230–237 (1973)
Daneel, S. L.: Identifizierung der kontraktilen Elemente im Cytoplasma von Amoeba proteus. Naturwissenschaften 15, 368–369 (1964)
Diamond, L. S.: Improved method for the monoxenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae with Trypanosomatids. J. Parasit. 54, 715–719 (1968)
Doflein, F., Reichenow, E.: Lehrbuch der Protozoenkunde. Jena: Gustav Fischer 1953
Eaton, R. D., Meerovitch, P. E., Costerton, J. W.: The functional morphology of pathogenicity in Entamoeba histolytica. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 64, 299–304 (1971)
Engelmann, T. W.: Beiträge zur Physiologie des Protoplasmas. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 2, 307–322 (1869)
Goldacre, R. J., Lorch, I. I.: Folding and unfolding of protein molecules in relation to cytoplasmic streaming, ameboid movement and osmotic work. Nature (Lond.) 166, 497–500 (1950)
Grell, K. G.: Protozoologie. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1968
Griffin, J. L.: Human amebic dysentery. Electron microscopy of Entamoeba histolytica contacting, ingesting, and digesting inflammatory cells. Amer. J. trop. Med. Hyg. 21, 895–905 (1972)
Griffin, J. L., Juniper, K.: Ultrastructure of Entamoeba histolytica from human amebic dysentery. J. Parasit. 54, Sect. II, Part I, 124–125 (1970)
Griffin, J. L., Juniper, K.: Ultrastructure of Entamoeba histolytica from human amebic dysentery. Arch. Path. 21, 271–280 (1971)
Hansen, J., Huxley, H. E.: The structural basis of contraction in striated muscle. Symp. Soc. exp. Biol. 9, 228–264 (1955)
Huang, B., Pitelka, D. R.: The contractile process in the ciliate Stentor coeruleus. I. The role of microtubules and filaments. J. Cell Biol. 57, 704–728 (1973)
Jahn, R. L., Bovee, E. C.: Effects of environmental conditions on the motile behaviour of amebas. Adv. comp. Physiol. Biochem. 4, 1–35 (1971)
Käppner, W.: Bewegungsphysiologische Untersuchungen an der Amoebe Chaos chaos L. Protoplasma 53, 504–529 (1961)
Komnick, H., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E.: Das Grundplasma und die Plasmafilamente der Amoebe Chaos chaos nach enzymatischer Behandlung der Zellmembran. Z. Zellforsch. 66, 434–456 (1965)
Kriszat, G.: Die Wirkung von Adenotriphosphat auf Amoeben (Chaos chaos) Ark. Zool. 1, 81–86 (1949)
Loewy, A. G.: An actomyosin-like substance from the plasmodium of a myxomycete. J. cell. comp. Physiol. 40, 127–156 (1952)
Lowe, C. Y., Maegraith, B. G.: Further electron microscopic studies of Entamoeba histolytica. Trans. roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 63, 11 (1969)
Lowe, C. Y., Maegraith, B. G.: Electron microscopy of Entamoeba histolytica in culture. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 64, 283–291 (1970a)
Lowe, C. Y., Maegraith, B. G.: Electron microscopy of an axenic strain of Entamoeba histolytica. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 64, 293–298 (1970b)
Lowe, C. Y., Maegraith, B. G.: Electron microscopy of Entamoeba histolytica in host tissue. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 64, 469–473 (1970c)
Ludvik, J., Shipstone, A. C.: The ultrastructure of Entamoeba histolytica. Bull. Org. mond. Santé-Bull. Wld Hlth Org. 43, 301–308 (1970)
Mast, S. O.: Mechanics of locomotion in amoeba Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 9, 258 (1923)
Mast, S. O.: Structure, movement, locomotion, and stimulation in Amoeba. J. Morph. Physiol. 41, 347–425 (1926)
Mast, S. O.: Locomotion in Amoeba proteus. Protoplasma 14, 312 (1931)
Michel, R., Westphal, A.: Extraintestinale Infektionsversuche beim Goldhamster mit Entamoeba histolytica aus bakterienfreien Kulturen. Z. Tropenmed. Parasit. 21, 230–239 (1970a)
Michel, R., Westphal, A.: Zytochemische Untersuchungen an Entamoeba histolytica in bakterienhaltigen und bakterienfreien Kulturen. Z. Tropenmed. Parasit. 21, 372–382 (1970b)
Miller, J. H., Swartzwelder, J. C., Deas, J. E.: An electron microscope study of Entamoeba histolytica. J. Parasit. 47, 577–587 (1961)
Nachmias, V. T.: Fibrillar structures in the cytoplasma of Chaos chaos. J. Cell. Biol. 23, 183 (1964)
Nachmias, V. T.: Further electron microscope studies on fibrillar organization of the ground cytoplasm of Chaos chaos. J. Cell Biol. 38, 40 (1968)
Nachmias, V. T.: Electron microscope observations on myosin from Physarum polycephalum. J. Cell Biol. 52, 648 (1972)
Nakajima, H.: Some properties of a contractile protein in a myxomycete plasmodium. Protoplasma 52, 413–436 (1960)
Osada, M.: Electron microscopic studies on Protozoa. I. Fine structure of Entamoeba histolytica. Keio. J. Med. 8, 99–108 (1959)
Pollard, R. D., Shelton, E., Weihing, R. R., Korn, E. D.: Ultrastructural characterization of F-actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii and identification of cytoplasmic filaments as F-actin by reaction with rabbit heavy meromyosin. J. molec. Biol. 50, 91 (1970)
Pollard, T. D., Korn, E. D.: Filaments of Amoeba proteus. II. Binding of heavy meromyosin by thin filaments in motile cytoplasmic extracts. J. Cell Biol. 48, 216 (1971)
Proctor, E. M., Gregory, M. A.: The ultrastructure of axenically cultivated trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to an observed variation in structural pattern. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 66, 335–338 (1972a)
Proctor, E. M., Gregory, M. A.: The observation of a surface active lyosome in the trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica from the human colon. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 66, 339–342 (1972b)
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as electronopaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Rosenbaum, R. M., Wittner, M.: Ultrastructure of bacterized and axenic trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to helical bodies. J. Cell Biol. 45, 367–382 (1970)
Schäfer-Daneel, S.: Strukturelle und funktionelle Voraussetzung für die Bewegung von Amoeba proteus. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 441–462 (1967)
Siddiqui, W. A., Rudzinska, M. A.: The fine structure of axenically-grown trophozoites of Entamoeba invadens with special reference to the nucleus and helical ribonucleoprotein bodies. J. Protozool. 12, 448–459 (1965)
Treviño-García, Manzo N., Feria-Velaxco, A., Ruiz de Chavez, J., de la Torre, M.: Lisosomas en entamoeba histolytica. Arch. Invest. Med. 2, Suppl. 179–186 (1971)
Westphal, A., Michel, R.: Phagozytose und Pinozytose der Entamoeba histolytica. Z. Tropenmed. Parasit. 22, 82–91 (1971)
Westphal, A., Michel, R., Mühlpfort, H.: Elektronenoptische Darstellung der Invaginationsphagozytose bei Entamoeba histolytica. Z. Tropenmed. Parasit. 23, 117–127 (1972)
Wolpert, L., Thompsen, C. M., O'Neill, C. H.: Studies on the isolated membrane and cytoplasm of Amoeba proteus in relation to ameboid movement. In: Primitive motile systems in cell biology, 143–171. New York-London: Academic Press 1964
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michel, R., Schupp, E. Darstellung von Mikrofilamenten im Cytoplasma von Entamoeba histolytica . Z. Parasitenk. 43, 285–298 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328883
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328883