Summary
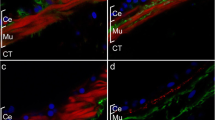
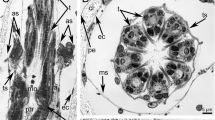
The structure of the cerebral ganglion of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas, is investigated by conventional electron miscroscope techniques, with particular emphasis on the relation of intracerebral blood vessels to other elements in the brain. The ganglion is permeated by a continuous network of channels which may be interpreted as invaginations of the ganglion surface. The afferent vessel (cerebral artery) is of mesodermal origin, but apparently terminates as an open-ended vessel soon after entering the brain, where it runs within the invaginated channels. The greater part of the cerebral vasculature, therefore, has no mesodermal endothelial lining. Tissue components in the diffusion path between blood and brain which could conceivably restrict diffusion, are the thick glial basement membrane, junctions between perivascular and between interstitial glia, and polymeric material in the extracellular space. However, apart from a barrier to large colloidal particles at the basement membrane, the present EM observations do not decisively pinpoint sites of diffusional restriction, nor can they be interpreted as evidence that such restriction exists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, N. J.: Absence of blood-brain barrier in a crustacean, Carcinus maenas L. Nature (Lond.) 225, 291–293 (1970).
—: The organization of the cerebral ganglion in the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. I. Morphology. Z. Zellforsch. 120, 386–400 (1971a).
- Access of ferritin to the interstitial space of Carcinus brain from intracerebral blood vessels. (In preparation.)
- Uptake of ions and molecules by the cerebral ganglion of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. (In preparation.)
- Efflux of 22Na from the cerebral ganglion of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. (In preparation.)
Barber, V. C., Graziadei, P.: The fine structure of cephalopod blood vessels. II. The vessels of the nervous system. Z. Zellforsch. 77, 147–161 (1967).
Beaulaton, J.: Étude ultrastructurale et cytochimique des glandes prothoraciques de vers à soie aux quatrième et cinquième âges larvaires. I. La tunica propria et ses relations avec les fibres conjonctives et les hémocytes. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 474–498 (1968).
Brightman, M. W.: The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebro-spinal fluid compartments. Amer. J. Anat. 117, 193–220 (1965).
—, Reese, T. S.: Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J. Cell Biol. 40, 648–677 (1969).
—, Feder, N.: Assessment with the electronmicroscope of the permeability to peroxidase of cerebral endothelium and epithelium in mice and sharks. In: Alfred Benzon Symposium II Capillary permeability, ed. by C. Crone and N. A. Lassen. Copenhagen: Munksgaard 1970.
Bullivant, S., Loewenstein, W. R.: Structure of coupled and uncoupled cell junctions. J. Cell Biol. 37, 621–632 (1968).
Claus, C.: Zur Kenntnis der Kreislaufsorgane der Schizopoden und Decapoden. Arb. zool. Inst. Univ. Wien 5, 271–318 (1884).
Copeland, D. E., Fitzjarrell, A. T.: The salt absorbing cells in the gills of the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun) with notes on modified mitochondria. Z. Zellforsch. 92, 1–22 (1968).
Danilova, L. V., Rokhlenko, K. D., Bodryagina, A. V.: Electron microscopic study on the structure of septate and comb desmosomes. Z. Zellforsch. 100, 101–117 (1969).
Danini, E. S.: Beiträge zur vergleichenden Histologie des Blutes und des Bindegewebes. III. Über die entzündliche Bindegewebsneubildung beim Flußkrebs. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 3, 558–608 (1925).
Davson, H.: Physiology of the cerebrospinal fluid. London: Churchill 1967.
Edwards, G. A., Ruska, H., De Harven, É.: Electron microscopy of peripheral nerves and neuromuscular junctions in the wasp leg. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 107–114 (1958).
Gilula, N. B., Branton, D., Satir, P.: The septate junction: a structural basis for intercellular coupling. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 67, 213–220 (1970).
Gray, E. G.: Electron microscopy of the glio-vascular organization of the brain of Octopus. Phil. Trans. B 255, 13–32 (1969).
—, Guillery, R. W.: An electron microscopical study of the ventral nerve cord of the leech. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 826–849 (1963).
Haeckel, E.: Über die Gewebe des Flußkrebses. Arch. Anat. Physiol. (1857), 469–568 (1857).
Hama, K.: The fine structure of some blood vessels of the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 717–723 (1960).
Heuser, J. E., Doggenweiler, C. F.: The fine structural organization of nerve fibers, sheaths, and glial cells in the prawn, Palaemonetes vulgaris. J. Cell Biol. 30, 381–403 (1966).
Kappers, Ariëns, C. U., Huber, G. C., Crosby, E. C.: The comparative anatomy of the nervous system of vertebrates, including man. New York: Macmillan 1936.
Kuffler, S. W., Potter, D. D.: Glia in the leech central nervous system: physiological properties and neuron-glia relationships. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 290–320 (1964).
Kumé, M., Dan, K. (eds.): Invertebrate embryology. Belgrade: Nolit 1968.
Laurent, T. C.: The interaction between polysaccharides and other macromolecules. 9. The exclusion of molecules from hyaluronic acid gels and solutions. Biochem. J. 93, 106–112 (1964).
Locke, M.: The structure of septate desmosomes. J. Cell Biol. 25, 166–169 (1965).
Luft, J. H.: Fine structure of capillary and endocapillary layer as revealed by ruthenium red. Fed. Proc. 25, 1773–1783 (1966).
Malzone, W. F., Collins, G. H., Cowden, R. R.: Neuroglial relationships in the thoracic ganglion of the fiddler crab, Uca. J. comp. Neural. 127, 511–530 (1966).
Marinozzi, V., Gautier, A.: Essais de cytochimie ultrastructurale. Du rôle de l'osmium réduit dans les “colorations” électroniques. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 253, 1180–1182 (1961).
Maroudas, A.: Physicochemical properties of cartilage in the light of ion exchange theory. Biophys. J. 8, 575–595 (1968).
Nicholls, J. G., Kuffler, S. W.: Extracellular space as a pathway for exchange between blood and neurons in the central nervous system of the leech: ionic composition of glial cells and neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 645–671 (1964).
Oppelt, W. W., Rall, D. P.: Brain extracellular space as measured by diffusion of various molecules into brain. In: Brain edema (eds. I. Klatzo and F. Seitelberger). Symposium in Vienna, 1965. Wien-New York: Springer 1967.
Pantin, C. F. A.: Notes on microscopical technique for zoologists. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1946.
Rechardt, L.: Electronmiscroscopic and histochemical observations on the supraoptic nucleus of normal and dehydrated rats. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 329, 1–79 (1969).
Rehberg, S.: Über den Feinbau der Abdominalganglien von Leucophaea maderae mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Transportwege und der Organellen des Stoffwechsels. Z. Zellforsch. 72, 370–389 (1966).
Sandeman, D. C.: The vascular circulation in the brain, optic lobes and thoracic ganglion of the crab Carcinus. Proc. roy. Soc. B 168, 82–90 (1967).
Scharrer, B.: Neurosecretion. XIII. The ultrastructure of the corpus cardiacum of the insect Leueophaea maderae. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 761–796 (1963).
—: Neurosecretion. XIV. Ultrastructural study of sites of release of neurosecretory material in Blatterian insects. Z. Zellforsch. 89, 1–16 (1968).
Skaer, R. J.: Personal communication.
Smith, D. S., Treherne, J. E.: Functional aspects of the organization of the insect nervous system. In: Advances in insect physiology (eds. J. W. L. Beament, J. E. Treherne and V. B. Wigglesworth), vol. 1, pp. 401–484. London: Academic Press 1963.
Treherne, J. E.: The distribution and exchange of some ions and molecules in the central nervous system of Periplaneta americana L. J. exp. Biol. 39, 193–217 (1962).
—, Moreton, R. B.: The environment and function of invertebrate nerve cells. Int. Rev. Cytol. 28, 45–88 (1970).
—, Smith, D. S.: The metabolism of acetylcholine in the intact central nervous system of an insect (Periplaneta americana L.). J. exp. Biol. 43, 441–454 (1965).
Vignal, W.: Sur l'endothélium de la paroi interne des vaisseaux des invertébrés. Arch. Physiol. norm. et path. 8, 1–6 (1886).
Wiener, J., Spiro, D., Loewenstein, W. R.: Studies on an epithelial (gland) cell junction. II. Surface structure. J. Cell Biol. 22, 587–598 (1964).
Wood, R. L.: Intercellular attachment in the epithelium of Hydra as revealed by electronmicroscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 6, 343–352 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
I wish to thank Dr. J. E. Treherne for encouragement and advice, Dr. A. M. Mullinger and Dr. B. L. Gupta for help and discussion concerning the electron microscopy, and Prof. E. G. Gray for reading the manuscript. This work was supported by an SRC Research Studentship.
Fig. 6 is reproduced from “Nature” by permission of Macmillan (Journals) Ltd.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbott, N.J. The organization of the cerebral ganglion in the shore crab, Carcinus maenas . Z. Zellforsch. 120, 401–419 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324900
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324900