Abstract
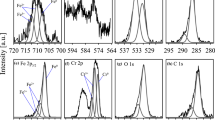
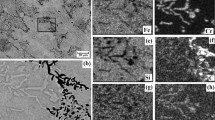
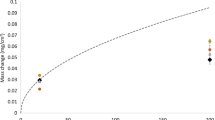
ESCA examination of films formed on Si-Fe alloys after immersion in 0.1 M NaCl for 24 h has hown that the thickness of passive films decreased with an increase in silicon content. A thick passive film containing oxidized silicon and oxidized iron was formed on Fe-20 wt% Si and the oxidized iron was about three times higher than the oxidized silicon in the passive film. However, an obvious reduction in the oxidized iron in the film on Fe-30 wt % Si was observed. Oxidized iron was detected up to a depth of 1.0 nm and at a depth greater than 1.0 nm from the surface, the film was exclusively in oxidized silicon. The film was exclusively silicon oxide when the silicon content was increased to 50 wt %. Electrochemical techniques according to ASTM G59 and ASTM G5 were used for the determination of the relative corrosion rate. Fe-50 wt % Si was found to have a corrosion rate smaller than those lower silicon alloys. This relates to the surface film composition and structure as determined by ESCA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.S. Greiner et al.: The Alloys of Iron and Silicon (McGraw-Hill, New York 1933)
L.L. Shreir: Corrision, Vol. 1 (Butterworths, London 1976) p. 119
V. Brusic et al.: In Passivity of Metals, ed. by R.P. Frankenthal, J. Kruger (Electrochemical Society, Princeton, NJ 1978) p. 170
S. Jin, A. Atrens. Appl. Phys. A 42, 149–165 (1987)
M. Stern, R.M. Roth: J. Electrochem. Soc. 104, 390 (1967)
M. Stern: Corrosion 14, 440t (1958)
F. Mansfeld: In Corrosion Science and Technology (Plenum, New York 1976) Vol. VI, p. 163
C.D. Wagner et al: In Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, ed. by G.E. Muilenberg (Perkin-Elmer, Eden Prairie 1978)
N.S. McIntyre: In Practical Surface Analysis, ed. by D. Briggs, N.P. Seah (Wiley, Chichester 1983)
K. Asami, K. Hashimoto: Corros. Sci. 17, 559 (1977)
D. Briggs, J. Riviere: In Practical Surface Analysis, ed. by D. Briggs, N.P. Seah (Wiley, Chichester 1983) p. 131
C.D. Wagner: J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 32, 99 (1983)
S. Hofmann: Surf. Int. Anal. 2, 148 (1980)
P. Bruesch et al.: Appl. Phys. A 38, 1 (1985)
I. Abbati et al.: J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 21, 409 (1982)
A. Cros et al.: Surf. Sci. 110, 352 (1981)
J. Derrien et al.: Passivity of Metals and Semiconductors, ed. by M. Froment (1983) p. 457