Abstract
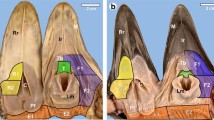
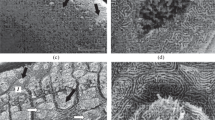
The taste disc of the red-bellied toad Bombina orientalis (Discoglossidae) has been investigated by light and electron microscopy and compared with that of Rana pipiens (Ranidae). Unlike the frog, B. orientalis possesses a disc-shaped tongue that cannot be ejected for capture of prey. The taste discs are located on the top of fungiform papillae. They are smaller than those in Ranidae, and are not surrounded by a ring of ciliated cells. Ultrastructurally, five types of cells can be identified (mucus cells, wing cells, sensory cells, and both Merkel cell-like basal cells and undifferentiated basal cells). Mucus cells are the main secretory cells of the taste disc and occupy most of the surface area. Their basal processes do not synapse on nerve fibers. Wing cells have sheet-like apical processes and envelop the mucus cells. They contain lysosomes and multivesicular bodies. Two types of sensory cells reach the surface of the taste disc; apically, they are distinguished by either a brush-like arrangement of microvilli or a rod-like protrusion. They are invaginated into lateral folds of mucus cells and wing cells. In contrast to the situation in R. pipiens, sensory cells of B. orientalis do not contain dark secretory granules in the perinuclear region. Synaptic connections occur between sensory cells (presynaptic sites) and nerve fibers. Merkel cell-like basal cells do not synapse onto sensory cells, but synapse-like connections exist between Merkel cell-like basal cells (presynaptic site) and nerve fibers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beidler LM (1961) Taste receptor stimulation. In: Butler JAV, Huxley HE, Zirkle RE (eds) Progress in biophysics and biophysical chemistry, vol 12. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 107–151
Chernetski KE (1964) Sympathetic enhancement of peripheral sensory input in the frog. J Neurophysiol 27:493–515
Delay RJ, Roper SD (1988) Ultrastructure of taste cells and synapses in the mud-puppy Necturus maculosus. J Comp Neurol 277:268–280
Düring M von, Andres KH (1976) The ultrastructure of taste and touch receptors of the frog's taste organ. Cell Tissue Res 165:185–198
Engelmann TW (1872) Die Geschmacksorgane. In: Stricker S (ed) Handbuch der Lehre von den Geweben des Menschen und der Thiere, vol 2. Engelmann, Leipzig, pp 822–838
Esakov Al, Solovieva NA, Krokhina EM (1984) Effects of tryptophan and 5-hydroxy-trytophan on the number of monoamine-containing cells in the frog taste bud. Chem Senses 9:303–309
Fährmann W (1967) Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an der Geschmacksknospe des neotenen Axolotls. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 77:117–152
Getchell TV, Margolis FL, Getchell ML (1984) Perireceptor and receptor events in vertebrate olfaction. Prog Neurobiol 23:317–345
Graziadei PPC, De Han RS (1971) The ultrastructure of frog's taste organs. Acta Anat 80:563–603
Gubo G, Lametschwandtner A, Simonsberger P, Adam H (1978) Licht- und rasterelektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Gaumen und Zunge der Gelbbauchunke, Bombina variegata L. Anat Anz 144:169–178
Hartschuh W, Weihe E, Reinecke M (1986) The Merkel cell. In: Bereiter-Hahn J, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS (eds) Biology of the integument: 2. Vertebrates. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 605–620
Hirata K, Nada O (1975) A monoamine in the gustatory cell of the frog's taste organ. A fluorescence histochemical and electron microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 159:101–108
Hirata K, Nada O (1977) Cytoarchitecture of monoamine-containing cell in the frog's gustatory epithelium. Experientia 33:1223–1224
Jakubowski M, Whitear M (1990) Comparative morphology and cytology of taste buds in teleosts. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 104:529–560
Jasinski A (1979) Light and scanning microscopy of the tongue and its gustatory organs in the common toad, Bufo bufo (L.). Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 93:465–476
Kimura K (1961) Factors affecting the response of taste receptors of rat. Kumamoto Med J 14:95–99
Merkel F (1880) Über die Endigungen der sensiblen Nerven in der Haut der Wirbeltiere. Stiller, Rostock
Olson KR, Fromm PO (1973) A scanning electron microscopic study of secondary lamellae and chloride cells of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Z Zellforsch 143:439–449
Pappas GD, Waxman SG (1972) Synaptic fine structure — morphological correlates of chemical and electrotonic transmission. In: Pappas GD, Purpura DP (eds) Structure and function of synapses. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–44
Raviola E, Osculati F (1967) La line struttura dei recettori gustativi della lingua di rana. Inst Lomb (Rend Sc) B 101:599–627
Retzius G (1892) Die Nervenendigungen in dem Geschmacksorgan der Säugetiere und Amphibien: B. Das Geschmacksorgan der Amphibien. In: Biologische Untersuchungen. NF. IV. Samson and Wallin, Stockholm, pp 26–32
Reutter K (1971) Die Geschmacksknospen des Zwergwelses Amiurus nebulosus (Lesueur). Morphologische und histochemische Untersuchungen. Z Zellforsch 120:280–308
Reutter K (1986) Chemoreceptors. In: Bereiter-Hahn J, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS (eds) Biology of the integument: 2. Vertebrates. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 586–604
Richter H-P, Avenet P, Mestres P, Lindemann B (1988) Gustatory receptors and neighbouring cells in the surface layer of an amphibian taste disc: in situ relationship and response to cell isolation. Cell Tissue Res 254:83–96
Röhlich P, Pevzner RA (1982) The chemoreceptor surface of the taste organ in the frog Rana esculenta. A freeze-fracture analysis. Cell Tissue 224:409–420
Royer SM, Kinnamon JC (1991) HVEM serial-section analysis of rabbit foliate taste buds: I. Type III cells and their synapses. J Comp Neurol 306:49–72
Sagmeister H, Gubo G, Lametschwandtner A, Simonsberger P, Adam H (1977) A new cell type in the taste buds of anurans. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 183:553–556
Sbarbati A, Franceschini F, Zancanaro C, Cecchini T, Ciaroni S, Osculati F (1988) The fine morphology of the basal cell in the frog's taste organ. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 20:73–79
Sbarbati A, Zancanaro C, Franceschini F, Osculati F (1989) Basal cells of the frog's taste organ: fluorescence histochemistry with the serotonin analogue 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine in supravital conditions. Basic Appl Histochem 33:289–297
Sbarbati A, Ceresi E, Accordini C (1991) Surfactant-like material on the chemoreceptorial surface of the frog's taste organ: an ultrastructural and electron spectroscopic imaging study. J Struct Biol 107:128–135
Stensaas LJ (1971) The fine structure of fungiform papillae and epithelium of the tongue of a South American toad, Calyptocephalella gayi. Am J Anat 131:443–462
Suzuki Y, Takeda M (1989) Filaments in the cells of frog taste organ. Zool Sci 6:487–497
Toyoshima K, Shimamura A (1987) Monoamine-containing basal cells in the taste buds of the newt Triturus pyrrhogaster. Arch Oral Biol 32:619–621
Toyoshima K, Shimamura A (1988) An immunohistochemical demonstration of neuron-specific enolase in the Merkel cells of the frog taste organ. Arch Histol Cytol 51:295–297
Toyoshima K, Honda E, Nakahara S, Shimamura A (1984) Ultrastructural and histochemical changes in the frog taste organ following denervation. Arch Histol Jpn 47:31–42
Toyoshima K, Miyamoto K, Shimamura A (1987) Fine structure of taste buds in the tongue, palatal mucosa and gill arch of the axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum. Okaj Folia Anat Jpn 64:99–110
Waller A (1849) Minute structure of the papillae and nerves of the tongue of the frog and toad. Communicated by R. Owen. Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol]:139–149
Witt M, Reutter K (1990) Electron microscopic demonstration of lectin binding sites in the taste buds of the European catfish Silurus glanis (Teleostei). Histochemistry 94:617–628
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witt, M. Ultrastructure of the taste disc in the red-bellied toad Bombina orientalis (Discoglossidae, Salientia). Cell Tissue Res 272, 59–70 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323571
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323571