Abstract
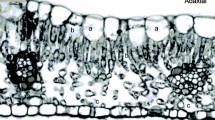
The azimuth of vertical leaves of Silphium terebinthinaceum profoundly influenced total daily irradiance as well as the proportion of direct versus diffuse light incident on the adaxial and abaxial leaf surface. These differences caused structural and physiological adjustments in leaves that affected photosynthetic performance. Leaves with the adaxial surface facing East received equal daily integrated irradiance on each surface, and these leaves had similar photosynthetic rates when irradiated on either the adaxial or abaxial surface. The adaxial surface of East-facing leaves was also the only surface to receive more direct than diffuse irradiance and this was the only leaf side which had a clearly defined columnar palisade layer. A potential cost of constructing East-facing leaves with symmetrical photosynthetic capcity was a 25% higher specific leaf mass and increased leaf thickness in comparison to asymmetrical South-facing leaves. The adaxial surface of South-facing leaves received approximately three times more daily integrated irradiance than the abaxial surface. When measured at saturating CO2 and irradiance, these leaves had 42% higher photosynthetic rates when irradiated on the adaxial surface than when irradiated on the abaxial surface. However, there was no difference in photosynthesis for these leaves when irradiated on either surface when measurements were made at ambient CO2. Stomatal distribution (mean adaxial/abaxial stomatal density = 0.61) was unaffected by leaf orientation. Thus, the potential for high photosynthetic rates of adaxial palisade cells in South-facing leaves at ambient CO2 concentrations may have been constrained by stomatal limitations to gas exchange. The distribution of soluble protein and chlorophyll within leaves suggests that palisade and spongy mesophyll cells acclimated to their local light environment. The protein/chlorophyll ratio was high in the palisade layers and decreased in the spongy mesophyll cells, presumably corresponding to the attentuation of light as it penetrates leaves. Unlike some species, the chlorophyll a/b ratio and the degree of thylakoid stacking was uniform throughout the thickness of the leaf. It appears that sun-shade acclimation among cell layers of Silphium terebinthinaceum leaves is accomplished without adjustment to the chlorophyll a/b ratio or to thylakoid membrane structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson HY, Chow WS, Anderson JM, Vesk M, Sutherland MW (1991) Photosynthetic acclimation of Trasescantia albiflora to growth irradiance: morphological, ultrastructural and growth responses. Physiol Plant 82: 353–359
Aro EM, Rintamäki E, Korhonen P, Mäenpää P (1986) Relationship between chloroplast structure and O2 evolution rate of leaf discs in plants from different biotypes in South Finland. Plant Cell Environ 9: 87–94
Boardman NK (1977) Comparative photosynthesis of sun and shade plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 28: 355–377
Bjorkman O (1981) Responses to different quantum flux densities. In: Lange OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Zeigler H (eds) Physiological plant ecology. I. (Ency in plant physiology, NS, vol 12A) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 57–107
Bornman JF, Vogelmann TC, Martin G (1991) Measurement of chlorophyll fluorescence within leaves using a fibreoptic microprobe. Plant Cell Environ 14: 719–725
Cui M, Vogelmann TC, Smith WK (1991) Chlorophyll and light gradients in sun and shade leaves of Spinacia oleracea. Plant Cell Environ 14: 493–500
Day TA, DeLucia EH, Smith WK (1990) Dorsiventrality of the photosynthetic-light response in naturally occurring C3 dicots. Proceedings of the VIIIth International Congress of Photosynthesis. IV: 883–886
Delieu T, Walker DA (1981) Polarographic measurement of photosynthetic oxygen evolution by leaf discs. New Phytol 89: 165–178
DeLucia EH, Shenoi HD, Naidu SL, Day TA (1991) Photosynthetic symmetry of sun and shade leaves of different orientations. Oecologia 87: 51–57
Donahue RA (1991) Interactions of ambient light directionality with leaf anatomy and effects on photosynthesis of sun and shade leaves of Thermopsis montana. PhD. Dissertation, University of Wyoming USA
Evans JR (1988) Acclimation by the thylakoid membranes to growth irradiance and the partitioning of nitrogen between soluble and thylakoid proteins. Aust J Plant Physiol 15: 93–106
Evans JR (1989) Partitioning of nitrogen between and within leaves grown under different irradiances. Aust J Plant Physiol 16: 533–548
Geller GH, Smith WK (1982) Influence of leaf size, orientation and arrangement on temperature and transpiration in three high elevation large-leaved herbs. Oecologia 53: 227–234
Gutschick VP, Barron MH, Waechter DA, Wolf MA (1985) Portable monitor for solar radiation that accumulates irradiance histograms for 32 leaf-mounted sensors. Agri For Meteor 33: 281–290
Iqbal M (1983) An introduction to solar radiation. Academic press, Toronto New York London, pp. 362–365
Jurik TW, Zhang H, Pleasants JM (1990) Ecophysiological consequences of non-random leaf orientation in the prairie compass plant, Silphium laciniatum Oecologia 82: 180–186
Knapp AK, Vogelmann TC, McClean TM, Smith WK (1988) Light and chlorophyll gradients within Cucurbita cotyledons. Plant Cell Environ 11: 257–263
Kulandaivelu G, Noorudeen AM, Sampath P, Periyanan S, Raman K (1983) Assessment of the photosynthetic electron transport properties of upper and lower leaf sides in vivo by fluorometric method. Photosynthetica 17: 204–209
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1954) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 267–275
Lowther JR (1980) Use of a single sulphuric acid-hydrogen peroxide digest for the analysis of Pinus radiata needles. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 11: 175–188
McClendon JH (1984) The micro-optics of leaves-I. Patterns of reflection from the epidermis. Am J Bot 71: 1391–1397
Moss DN (1964) Optimum lighting of leaves. Crop Sci 4: 131–136
Mott KA and Michaelson O (1991) Amphistomaty as an adaptation to high light intensity in Ambrosia cordifolia (Compositae) Am J Bot 78: 76–79
Ögren E, Sjörström M (1990) Estimation of the effect of photoinhibition on the carbon gain in leaves of a willow canopy. Planta 181: 560–567
Pearcy RW (1989) Radiation and light measurements. In: Pearcy RW, Ehleringer J, Mooney HA, Rundel PW (eds) Plant Physiological Ecology: field methods and instrumentation. Chapman and Hall, NY pp. 97–116
Porra RJ, Thompson WA, Kriedemann PE (1989) Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 975: 384–394
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17: 208–212
Schreiber U, Fink R, Vidaver W (1977) Fluorescence induction in whole leaves: differentiation between the two leaf sides and adaptation to different light regimes. Planta 133: 121–129
Sharkey TD (1985) Photosynthesis in intact leaves of C3 plants: physics, physiology and rate limitations. Botanical Rev 51: 53–105
Smith M, Ullberg D (1989) Effect of leaf angle and orientation on photosynthesis and water relations in Silphium terebinthinaceum. Am J Bot 76: 1714–1719
Syvertsen JP, Cunningham GL (1979) The effects of irradiating adaxial or abaxial leaf surface on the rate of net photosynthesis of Perezia nana and Helianthus annuus. Photosynthetica 13: 287–293
Terashima I (1986) Dorsiventrality in photosynthetic light response curves of a leaf. J Exp Bot 37: 399–405
Terashima I (1989) Productive structure of a leaf. In: WR Briggs (ed) Plant biology vol 8, Photosynthesis. Alan R. Liss Inc. New York, pp 207–226
Terashima I, Evans JR (1988) Effects of light and nitrogen nutrition on the organization of the photosynthetic apparatus in spinach. Plant Cell Physiol 29: 143–155
Terashima I, Inoue Y (1984) Comparative photosynthetic properties of palisade tissue chloroplasts and spongy tissue chloroplasts of Camellia japonica L.: functional adjustment of the photosynthetic apparatus to light environment within a leaf. Plant Cell Physiol 25: 555–563
Terashima I, Inoue Y (1985) Palisade tissue chloroplasts and spongy tissue chloroplasts in spinach: biochemical and ultrastructural differences. Plant Cell Physiol 26: 63–75
Terashima I, Takenaka A (1986) Organization of photosynthetic system of dorsiventral leaves as adapted to the irradiation from the adaxial side. In: Marcell R, Clijsters H, Van Poucke M (eds) Biological control of photosynthesis. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht pp. 219–230
Václavík J (1984) Photosynthetic CO2 uptake by Zea mays leaves as influenced by unilateral irradiation of adaxial and abaxial leaf surfaces. Biol Plant 26: 206–214
Vogelmann TC, Bornman JF, Josserand S (1989) Photosynthetic light gradients and spectral regime within leaves of Medicago sativa. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 323: 411–421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poulson, M.E., DeLucia, E.H. Photosynthetic and structural acclimation to light direction in vertical leaves of Silphium terebinthinaceum . Oecologia 95, 393–400 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00320994
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00320994