Summary
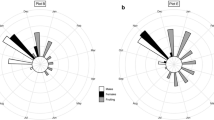
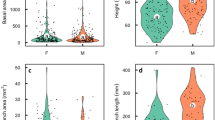
We examined the relationship between size variability and the distribution of functional gender in stands of the monoecious, wind-pollinated annual Ambrosia artemisiifolia. Populations of 60 individuals were grown in the greenhouse at a density of 372 m−2 and at two nutrient levels. Among the surviving plants, after self-thinning, variability in above-ground biomass and gender was higher in the high nutrient treatment. Among individuals there was a significant positive correlation between maleness and both height and biomass. Fecundity was also positively correlated with both measures of size. Based on the pattern of distribution of male and female flowers within the plant, it appears that the increase in maleness in larger plants is due to increased branching and axis elongation. These results demonstrate that competitive interactions, which lead to increased variability in biomass and fecundity, can also generate variability in gender within populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abul-Fatih HA, Bazzaz FA, Hunt R (1979) The biology of Ambrosia trifida L. III. Growth and biomass allocation. New Phytol 83:829–838
Barker P, Freeman DC, Harper KT (1982) Variation in the breeding system of Acer grandidentatum. For Sci 28:563–572
Bazzaz FA (1974) Ecophysiology of Ambrosia artemisiifolia: a successional dominant. Ecology 55:112–119
De Jong TJ, Klinkhamer PGL (1989) Size-dependency of sex-allocation in hermaphroditic, monocarpic plants. Functional Ecology 3:201–206
Frank SA (1987) Individual and population sex allocation patterns. Theor Pop Biol 31:47–74
Freeman DC, Harper KT, Charnov EL (1980) Sex change in plants: old and new observations and new hypotheses. Oecologia (Berlin) 47:222–232
Freeman DC, McArthur ED, Harper KT, Blauer AC (1981) Influence of environment on the floral sex ratio of monoecious plants. Evolution 35:194–197
Harper JL (1977) Population biology of plants. Academic Press, London
Heywood JS (1986) The effects of plant size variation on genetic drift in populations of annuals. Am Nat 127:851–861
Lande R, Barrowclough GF (1987) Effective population size, genetic variation, and their use in population management. In: Soulé ME (ed) Viable populations for conservation. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, pp 87–123
Lloyd DG (1980) Sexual strategies in plants. III. A quantitative method for describing the gender of plants. NZJ Bot 18:103–108
Lloyd DG, Bawa KS (1984) Modification of the gender of seed plants in varying conditions. Evol Biol 17:255–338
Łomnicki A (1988) Population ecology of individuals. Princeton University Press, Princeton
McKone MJ, Tonkyn DW (1986) Intrapopulation gender variation in common ragweed (Asteraceae: Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.), a monoecious, annual herb. Oecologia (Berlin) 70:63–67
Payne WW (1963) The morphology of the inflorescence of ragweeds (Ambrosia-Franseria: Compositae). Am J Bot 50:872–880
Schultz BB (1985) Levene's test for relative variation. Syst Zool 34:449–456
Solbrig OT, Solbrig DJ (1984) Size inequalities and fitness in plant populations. Oxford Surv Evol Biol 1:141–159
Solomon BP (1989) Size-dependent sex ratios in the monoecious, wind-pollinated annual, Xanthium strumarium. Am Midl Nat 121:209–218
Uchmański J (1985) Differentiation and frequency distributions of body weights in plants and animals. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 310:1–75
Weiner J (1988) The influence of competition on plant reproduction. In: Lovett-Doust J, Lovett-Doust L (eds) Plant reproductive ecology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 228–245
Weiner J, Thomas SC (1986) Size variability and competition in plant monocultures. Oikos 47:211–222
Wilson JB, Levin DA (1986) Some genetic consequences of skewed fecundity distributions in plants. Theor Appl Genet 73:113–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ackerly, D.D., Jasieński, M. Size-dependent variation of gender in high density stands of the monoecious annual, Ambrosia artemisiifolia (Asteraceae). Oecologia 82, 474–477 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319788
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319788