Summary
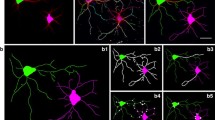
Ultrastructural examination of neurons treated with the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) confirmed our previous finding that TPA promoted neurite differentiation. At the low concentration of 16 nM TPA, the outgrowth of long neurites was correlated with the increased appearance of membrane-filled varicosities and filopodial extensions along the axons. In contrast, treatment with high concentrations of TPA (160 nM) produced dense outgrowths which were shorter in length and organized as thick fascicles. Increased neurite fasciculation appeared to result from the enhanced side-to-side interactions of neighboring neurites by a neural cell adhesion molecule. Axons within these fascicles were retracted and appeared congested with cytoskeletal and membranous components. Treatment with the antibody to the neural cell adhesion molecule defasciculated the thick outgrowths and permitted further axonal elongation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benowitz L and Routtenberg A (1987) A membrane phosphoprotein associated with neural development, axonal regeneration, phospholipid metabolism and synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 10:527–532
Bottenstein JE, Skaper SP, Varon SS, Sato GH (1980) Selective survival of neurons from chick embryo sensory ganglionic dissociates utilizing serum-free supplemented medium. Exp Cell Res 125:185–190
Bray D (1979) Mechanical tension produced by nerve cells in tissue culture. J Cell Sci 37:391–410
Bunge M (1973) Fine structure of nerve fibres and growth cones of isolated sympathetic neurons in culture. J Cell Biol 56:713–735
Castagna M, Takai Y, Kaibuchi K, Sano K, Kikkawa U, Nishizuka Y (1982) Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid dependent protein kinase by tumor promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem 257:7847–7851
Diamond L, O'Brien TG and Baird WM (1980) Tumor promoters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Adv Cancer Res 32:1–74
Graham RC and Karnovsky MJ (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horse-radish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Heath JW, Hill CE and Burnstock G (1974) Axon retraction following guanethidine treatment: studies of sympathetic neurons in tissue culture. J Neurocytol 3:263–276
Hinek A, Thyberg J and Fridberg U (1977) Electron microscopic studies on embryonic chick spinal ganglion cells: relationship between microtubules and the Golgi complex. J Neurocytol 6:13–15
Hsu L, Natyzak D, Trupin GL (1982) A simple microculture system of neuronal explants. J Tissue Cult Methods 7:143–145
Hsu L, Natyzak D and Laskin JD (1984) Effects of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on neurile outgrowth from chick embryo sensory ganglia. Cancer Res 44:4607–4616
Hsu L (1985) Neurite-promoting effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on chick embryo neurons. Neurosci Lett 62:283–289
Hsu L, Jeng A-Y, Chen KY (1989) Induction of neurite outgrowth from chick embryonic ganglia explants by activators of protein kinase C. Neurosci Lett (in press)
Ishii DN (1978) Effects of tumor promoters on the response of cultured embryonic chick ganglia to nerve growth factor. Cancer Res 38:3886–3893
Levi-Montalcini R, Caramia F, Luce SA, Angeletti PU (1968) In vitro effects of the nerve growth factor on the fine structure of the sensory nerve cells. Brain Res 8:347–362
Masurovsky EB, Peterson ER (1973) Photoreconstituted collagen gel from tissue culture substrates. Exp Cell Res 76:447–448
Meiri KF, Pfenninger KH, Willard MB (1986) Growth associated protein, GAP 43 a polypeptide that is induced when neurons extend axons, is a component of growth cones and corresponds to pp 46, a major polypeptide of a subcellular fraction enriched in growth cones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3537–3541
Nishizuka Y (1984) Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science 225:1365–1370
Pannese E (1974) The histogenesis of the spinal ganglia. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 47:1–91
Rutishauser U, Gall WE, Edelman GM (1978) Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. IV. Role of the cell surface molecule CAM in the formation of neurite bundles in cultures of spinal ganglia. J Cell Biol 79:382–393
Rutishauser U, Edelman GM (1980) Effects of fasciculation on the outgrowth of neurites from spinal ganglia in culture. J Cell Biol 87:370–378
Rutishauser U (1988) The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) as a regulator of cell-cell interactions. Science 240:53–57
Skene JHP, Jacobson RD, Snipes GJ, Mcquire GB, Norden JJ and Freeman JA (1986) A protein-induced during nerve growth (GAP 43) is a major component of growth cone membranes. Science 233:783–786
Yamada KM, Spooner BS, Wessells NK (1971) Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells. J Cell Biol 49:614–635
Yamasaki H (1984) Modulation of cell differentiation by tumor promoters. In: Slaga TJ (ed) Mechanism of Tumor Promotion IV. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 1–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, L. The effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) on axonal elongation and fasciculation. Anat Embryol 179, 511–518 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319595
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319595