Summary
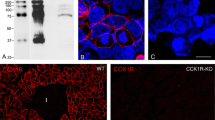
Region-specific antibodies against synthetic N-terminal fragments of cardiodilatin (CDD) were raised in rabbits and used for the immunohistochemical detection of this new peptide hormone in the myoendocrine cells within the cardiac atria of several species. The peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) immunohistochemical methods gave identical results of cardiodilatin-immunoreactivity (CDD-IR) within the tissue. In addition to the porcine right atrial appendage, myoendocrine cells with CDD-IR were also detected in the left atrium of porcine heart, as well as in other species such as dog and cat. The exact localization of the immunoreactivity in specific secretory granules was mostly related to the Golgi-area which is located on both nuclear poles of auricular myoendocrine cells. The results confirm that cardiodilatin is stored in secretory granules observed through electron microscopical means. This hormone is most likely synthesized and released in myoendocrine cells, exerting its important cardiovascular effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger JM, Rona G (1971) Functional and fine structural heterogeneity of atrial cardiocytes. In: Bajusz E, Jasmin G (eds) Meth Achievm exp Pathol 5. Karger, Basel, pp 540–590
Bompiani GD, Rouiller C, Hatt PY (1959) Le tissu de conduction du cœur chez le rat. Etude au microscope électronique. Arch Maladies Cœur et Vaisseaux 52. 1257
Briggs JP, Steipe B, Schubert G, Schnermann J (1982) Micropuncture studies of the renal effects of atrial natriuretic substance. Pflügers Arch 395:271–276
Cantin M, Benchimol S, Castonguay Y, Berlinguet J-C, Huet M (1975) Ultrastructural cytochemistry of atrial muscle cells. V. Characterization of specific granules in the human left atrium. J Ultrastruct Res 52:179–192
Coons AH (1978) Fluorescent antibody methods. In: Danielli JF (ed) General cytochemical methods. Academic Press, New York, pp 399–422
Currie MG, Geller DM, Cole BR, Boylan JG, Jusheng W, Holmberg SW, Needleman P (1983) Bioactive cardiac substances: potent vasorelaxant activity in mammalian atria. Science 221:71–73
Currie MG, Geller DM, Cole BR, Siegel NR, Fok KF, Adams SP, Eubanks SR, Gallupi GR, Needleman P (1984) Purification and sequence analysis of bioactive atrial peptides (atriopeptins). Science 223:67–69
De Bold AJ (1979) Heart atria granularity effects of changes in water-electrolyte balance. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 161:508–511
De Bold AJ (1982) Tissue fractionation studies on the relationship between an atrial natriuretic factor and specific atrial granules. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60:324–330
Forssmann WG (1981) General methods in transmission electron microscopy of the nervous system. In: Heym Ch, Forssmann WG (eds) Techniques in neuroanatomical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 21–40
Forssmann WG, Girardier L (1970) A study of the T system in rat heart. J Cell Biol 44:1–19
Forssmann WG, Pickel V, Reinecke M, Hock D, Metz J (1981) Immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry of nervous tissue. In: Heym Ch, Forssmann WG (eds) Techniques in neuroanatomical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 171–205
Forssmann WG, Reinecke M, Weihe E (1982) Cardiac innervation. In: Bloom SR, Polak M, Lindenlaub E (eds) Systemic role of regulatory peptides. Schattauer, Stuttgart New York, pp 329–349
Forssmann WG, Hock D, Lottspeich F, Henschen A, Kreye V, Christmann M, Reinecke M, Metz J, Carlquist M, Mutt V (1983) The right auricle of the heart is an endocrine organ: cardiodilatin as a peptide hormone candidate. Anat Embryol 168:307–313
Forssmann WG, Birr C, Carlquist M, Christmann M, Finke R, Henschen A, Hock D, Kirchheim H, Kreye V, Lottspeich F, Metz J, Mutt V, Reinecke M (1984) The auricular myocardiocytes of the heart constitute an endocrine organ: Characterization of a porcine cardiac peptide hormone, cardiodilatin-126. Cell Tissue Res (in press)
Forssmann WG, Hock D, Kirchheim H, Metz J, Mutt V, Reinecke M (1984) Cardiac hormones: Morphological and functional aspects. Clin. Exp. Hypertension (in press)
Flynn TG, de Bold ML, de Bold AJ (1983) The amino acid sequence of an atrial peptide with potent diuretic and natriuretic properties. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 117:859–865
Garcia R, Cantin M, Thibault G, Ong H, Genest J (1982) Relationship of specific granules to the natriuretic and diuretic activity of rat atria. Experientia 15:1071–1073
Gu J, Polak JM, Adrian TE, Allen JM, Tatemoto K, Bloom SR (1983) Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY) — a major cardiac neuropeptide. Lancet I:1008–1010
Hibbs RG, Ferrans VJ (1969) An ultrastructural and histochemical study of rat atrial myocardium. Am J Anat 124:251–280
Jamieson JD, Palade GE (1964) Specific granules in atrial muscle cells. J Cell Biol 23:151–172
Kangawa K, Matsuo H (1984) Purification and complete amino acid sequence of-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (α-hANF). Biochem Biophys Res Comm 118:131–139
Kisch B (1956) Electron microscopy of the atrium of the heart. I. Guinea pig. Exp Med Surg 14:99–112
Kuhn H, Richards JG, Tranzer JP (1975) The nature of rat “specific heart granules” with regard to catecholamines: an investigation by ultrastructural cytochemistry. J Ultrastruct Res 50:159–166
Marie J-P, Guillemot H, Hatt P-Y (1976) Le degré de granulation des cardiocytes auriculaires. Etude planimétrique au cours de différents apports d'eau et de sodium chez le rat. Pathol Biol 24:549–554
McNutt NS, Fawcett DW (1969) The ultrastructure of the cat myocardium. II. Atrial muscle. J Cell Biol 42:46–67
Papka RE, Furness JB, Della NG, Costa M (1981) Depletion by capsaicin of substance P — immunoreactivity and acetylcholinesterase activity from nerve fibres in the guinea-pig heart. Neurosci Lett 27:47–53
Poche R (1957) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen des Lipofuscin im Herzmuskel des Menschen. Zbl Allg Pathol 96:395
Reinecke M, Weihe E, Forssmann WG (1980) Substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the heart. Neurosci Lett 20:265–269
Reinecke M, Weihe E, Carraway RE, Leeman SE, Forssmann WG (1982) Localization of neurotensin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the guinea pig heart: evidence derived by immunohistochemistry, radioimmunoassay and chromatography. Neuroscience 7:1785–1795
Sosa-Lucero JC, de la Iglesia FA, Lumb G, Berger JM, Bencosme S (1969) Subcellular distribution of catecholamines and specific granules in rat heart. Lab Invest 21:19–26
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd. edition. Wiley, New York
Tatemoto K (1982) New peptides, their structures and functions. In: Bloom SR, Polak JM, Lindenlaub E (eds) Systemic role of regulatory peptides. Schattauer, Stuttgart New York, pp 507–531
Thibault G, Garcia R, Cantin M, Genest J, Lazure C, Seidah NG, Chrétien M (1984) Primary structure of a high M r form of rat atrial natriuretic factor. FEBS Lett 167:352–357
Weihe E, Reinecke M, Forssmann WG (1984) Multilocal distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide immunoreactivity in the heart: immunohistochemical evidence for an interaction with neurotensin-immunoreactive and substance P-immunoreactive cardiac nerves. Cell Tissue Res [in press]
Weihe E, Reinecke M, Opherk D, Forssmann WG (1981) Peptidergic innervation (substance P) in the human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 13:331–333
Wharton J, Polak JM, McGregor GP, Bishop AE, Bloom SR (1981) The distribution of substance P-like immunoreactive nerves in the guinea-pig heart. Neuroscience 11:2193–2204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Carvas SFB 90
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metz, J., Mutt, V. & Forssmann, W.G. Immunohistochemical localization of cardiodilatin in myoendocrine cells of the cardiac atria. Anat Embryol 170, 123–127 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318996
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318996