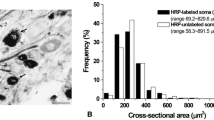
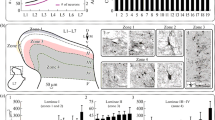
Abstract
Three distinct clusters of crustacean cardioactive-peptide-immunoreactive neurones occur in the terminal abdominal ganglion of the crayfish species Orconectes limosus, Astacus leptodactylus, Astacus astacus and Procambarus clarkii, as revealed by immunocytochemistry of whole-mount preparations and sections. They exhibit similar topology and projection patterns in all four studied species. An anterior ventral lateral and a posterior lateral cluster contain one small, strongly stained perikaryon and two large, less intensely stained perikarya, each showing contralateral projections. A posterior medial lateral cluster of up to six cells also contains these two types of perikarya. Whereas the small type perikarya belong to putative interneurones, the large type perikarya give rise to extensive neurohaemal plexuses in perineural sheaths of the third roots of the fifth abdominal ganglia, the connectives, the dorsal telson nerves, the ganglion itself, its roots and arteriolar supply. Thin fibres from these plexuses reach newly discovered putative neurohaemal areas around the hindgut and anus via the intestinal and the anal nerves, and directly innervate the phasic telson musculature. A comparison with earlier investigations of motoneurones and segmentation indicates that these three cell groups containing putative neurosecretory neurones may be members of at least three neuromeres in this ganglion. Crustacean cardioactive peptide released from these neurones may participate in the neurohumoral and modulatory control of different neuronal and muscle targets, thereby exceeding its previously established hindgut and heart excitatory effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AG :
-
abdominal ganglion
- adpl :
-
arteria dorsalis pleica
- Ala :
-
arreria lateralis abdominalis
- Asub :
-
arteria subneuralis
- CCAP :
-
crustacean cardioactive peptide
- CNS :
-
central nervous system
- IR :
-
immunoreactive
- LG :
-
lateral giant axon
- LTr :
-
lateral tract
- MDT :
-
medial dorsal tract
- MG :
-
medial giant axon
- M Tr :
-
medial tract
- mcan :
-
musculus compressor ani
- mfltp :
-
museulus flexor telsonos posterior
- nan :
-
nervus ani (AG6 N5)
- nant :
-
nervus anterior (AG6 N1, N2)
- nia :
-
nervus intestinal anterior
- nin :
-
nervus intestinalis (AG6 N7)
- nip :
-
nervus intestinalis posterior
- nteld :
-
nervus telsonos dorsalis (AG6 N6)
- nielv :
-
nervus telsonos ventralis (AG6 N4)
- nur :
-
nervus uropedalis (AG6 N3)
- nven :
-
nervus ventralis (AG5 N3)
- PIR :
-
peri-intestinal ring
- PTF :
-
posterior telson flexor
- VLT :
-
ventral lateral tract
- VMT :
-
ventral medial tract
- VNC :
-
ventral nerve cord
- VIF :
-
ventral telson flexor
- AVLC, PLC, PMLC :
-
anterior ventral lateral, posterior lateral, posterior medial lateral CCAP-immunoreactive cell cluster
- A6AVC, A7AVC :
-
anterior ventral commissures
- A7DCI :
-
dorsal commissure I
- A7PVC :
-
posterior ventral commissure
- A7SCII :
-
sensory commissure II
- A7VCII, A7VCIII :
-
ventral commissures II and III of the sixth (A6) and seventh (A7) abdominal neuromer
References
Alexandrowicz JS (1909) Zur Kenntnis des sympatischen Nerven-systems bei Crustaceen. Jena Z Naturwiss 45:395–444
Altman JS, Tyrer NM (1980) Filling selected neurons with cobalt through cut axons. In: Strausfeld NJ, Miller TA (eds) Neuroanatomical techniques. Insect nervous system. Springer, New York Heidelberg Berlin, pp 373–402
Audehm U, Dircksen H, Keller R (1991) Projections of crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP)-immunoreactive neurons of the sixth abdominal ganglion of crayfishes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 82:284
Baumann H (1918) Das Gefäßsystem von Astacus fluviatilis (Potamobius astacus L.). Z Wiss Zool 118:246–312
Bishop CA, Wine JJ, O'Shea M (1984) Neuropeptide proctolin in postural motoneurones of the crayfish. J Neurosci 4:2001–2009
Bishop CA, Wine JJ, Nagy F, O'Shea M (1987) Physiological consequences of a peptide cotransmitter in a crayfish nerve-muscle preparation. J Neurosci 7:1769–1779
Boer HH, Schot LPC, Roubos EW, Maat A ter, Lodder JC, Reichelt D, Swaab DF (1979) ACTH-like immunoreactivity in two electronically coupled giant neurons in the pond snail Lymnea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 202:231–240
Breidbach O, Dircksen H (1991) Crustacean cardioactive peptide-immunoreactive neurons in the ventral nerve cord and the brain of the meal beetle Tenebrio molitor during postembryonic development. Cell Tissue Res 265:129–144
Breidbach O, Kutsch W (1990) Structural homology of identified motoneurones in larval and adult stages of hemi-and holometabolous insects. J Comp Neurol 297:392–409
Brown SK, Sherwood DN (1981) Vascularization of the crayfish abdominal cord. J Comp Physiol 143:93–101
Dircksen H, Breidbach O (1991a) Crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP)-immunoreactive neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system of the locust Locusta migratoria and the metamorphosing meal beetle Tenebrio molitor. Gen Comp Endocrinol 82:286
Dircksen H, Breidbach O (1991b) Peripheral projection sites of crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP)-immunoreactive neurons of the central nervous system of the locust Locusta migratoria and the metamorphosing meal beetle Tenebrio molitor. In: Elsner N, Penzlin H (eds) Synapse-transmission-modulation. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 14
Dircksen H, Keller R (1988) Immunocytochemical localisation of CCAP, a novel crustacean cardioactive peptide, in the nervous system of the shore crab, Carcinus meanas L. Cell Tissue Res 254:347–360
Dircksen H, Müller A, Keller R (1991) Crustacean cardioactive peptide in the nervous system of the locust, Locusta migratoria: an immunocytochemical study on the ventral nerve cord and peripheral innervation. Cell Tissue Res 263:439–457
Dumont JPC, Wine JJ (1987) The telson flexor neuromuscular system of the crayfish. I. Homology with the fast flexor system. J Exp Biol 127:249–277
Elekes F, Florey E, Cahill MA (1988) Morphology and central synaptic connections of the efferent neurons innervating the crayfish hindgut. Cell Tissue Res 254:369–379
Hagiwara G, Wheat G (1983) Cited in Reichert et al. (1983), below
Homberg U (1991) Neuroarchitecture of the central complex in the brain of the locust Schistocerca gregaria and S. americana as revealed by serotonin immunocytochemistry. J Comp Neurol 303:245–254
Keim W (1915) Das Nervensystem von Astacus fluviatilis (Potamobius astacus L.). Z Wiss Zool 113:485–545
Kobierski LA, Beltz BS, Trimmer BA, Kravitz EA (1987) FMRFamide-like peptides of Homarus americanus: distribution, immunocytochemical mapping and ultrastructural localisation in terminal varicosities. J Comp Neurol 266:1–15
Kondoh Y, Hisada M (1986) Neuroanatomy of the terminal (sixth abdominal) ganglion of the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii (Girard). Cell Tissue Res 243:273–288
Kondoh Y, Hisada M (1987) The topological organization of primary efferents in the terminal ganglion of crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Cell Tissue Res 247:17–24
Kornberg T (1981) engrailed: A gene controlling compartment and segment formation in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:1095–1099
Larimer JL, Kennedy D (1969) Innervation patterns of fast and slow muscle in the uropods of crayfish. J Exp Biol 51:119–133
Leise E, Mulloney B (1986) The osmium-ethyl gallate procedure is superior to silver impregnations for mapping neuronal pathways. Brain Res 367:265–272
Mittenthal JE, Wine JJ (1978) Segmental homology and variation in flexor motoneurons of the crayfish abdomen. J Comp Neurol 117:311–334
Muramoto A (1971) The afferent nerve response of the movement receptor around the anal region of the crayfish. J Fac Sci Hokkaido Univ Ser VI Zool 17:545–563
Muramoto A (1977) Neural control of rhythmic anal contraction in the crayfish. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 56:551–557
Orlov J (1926) Die Innervation des Darmes des Flusskrebses. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 4:101–149
Patel NH, Marin-Blanco E, Coleman KG, Poole SJ, Ellis MC, Kornberg TB, Goodman CG (1989a) Expression of engrailed proteins in arthropods, annelids, and chordates. Cell 58:955–968
Patel NH, Kornberg TB, Goodman CS (1989b) Expression of engrailed during segmentation in grasshopper and crayfish. Development 107:201–212
Paul DH (1989) A neurophylogenist's view of decapod Crustacea. Bull Mar Sci 45:487–504
Paul DH, Then AM, Magnuson DS (1985) Evolution of the telson neuromusculature in decapod Crustacea. Biol Bull 168:106–124
Reichert H, Plummer MR, Wine JJ (1983) Lateral inhibition mediated by a non-spiking interneuron: circuit properties and consequences for behavior. J Physiol (Paris) 78:786–792
Sandeman DC (1982) Organization of the central nervous system. In: Bliss DE (ed) The biology of Crustacea. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–61
Schmidt W (1915) Die Muskulatur von Astacus fluviatilis (Potamobius astacus L.). Z Wiss Zool 113:166–251
Selverston AJ, Remler MP (1972) Neural geometry and activation of crayfish fast flexor motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 35:797–814
Stangier J (1991) Biological effects of crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP), a putative neurohormone/neurotransmitter from crustacean pericardial organs. In: Stefano GB, Florey E (eds) Comparative aspects of neuropeptide function. Manchester University Press, Manchester New York, pp 201–210
Stangier J, Keller R (1990) Occurrence of the crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) in the nervous system of the crayfish Orconectes limosus. In: Wiese K, Krenz WD, Tautz J, Reichert H, Molloney B (eds) Frontiers in crustacean neurobiology. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 394–400
Stangier J, Hilbich C, Beyreuther K, Keller R (1987) Unusual cardioactive peptide (CCAP) from pericardial organs of the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:575–579
Stangier J, Hilbich C, Keller R (1989) Occurrence of crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) in the nervous system of an insect, Locusta migratoria. J Comp Physiol [B] 159:5–11
Stefanini M, De Martino C, Zamboni L (1967) Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature 216:173–174
Stoll E (1925) Über den Bau des Zentralnervensystems von Astacus fluviatilis (Potamobius astacus L.). Z Wiss Zool 126:145–179
Trube A, Dircksen H, Keller R (1991a) CCAP-(crustacean cardioactive peptide-) immunoreactive structures in the central nervous system of crayfishes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 82:284
Trube A, Audehm U, Dircksen H (1991b) Crustacean cardioactive peptide-immunoreactive structures in the nervous system of crayfish. In: Elsner N, Penzlin H (eds) Synapse-transmission-modulation. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 408
Van Harreveld A (1936) A physiological solution for freshwater crustaceans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 34:428–432
Wine JJ, Mittenthal JE, Kennedy D (1974) The structure of tonic flexor motoneurons in the crayfish abdominal ganglia. J Comp Physiol 93:313–335
Winlow W, Laverack MS (1972a) The control of hindgut motility in the lobster, Homarus gammarus (L.). I. Analysis of hindgut movements and receptor activity. Mar Behav Physiol 1:1–27
Winlow W, Laverack MS (1972b) The control of hindgut motility in the lobster, Homarus gammarus (L.). III. Structure of the sixth abdominal ganglion (6 A.G.) and associated ablation and microelectrode studies. Mar Behav Physiol 1:93–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Audebm, U., Trube, A. & Dircksen, H. Patterns and projections of crustacean cardioactive-peptide-immunoreactice neurones of the terminal ganglion of crayfish. Cell Tissue Res 272, 473–485 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318553
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318553