Summary
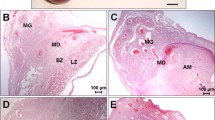
An electron microscopic study was made of the changes of the trophoblast and the uterine epithelium at early implantation. During delay of implantation in mice, only a small amount of secretion was present in the uterine lumen, and the trophoblast-epithelial space was narrow. The luminal part of the uterine epithelial cells contained a 0.1 μm deep layer of dense ground cytoplasm devoid of organelles and inclusions. Below this juxtaluminal layer many apical vesicles were seen. The luminal part of the trophoblast cells contained several endocytic vesicles, indicating that in spite of its low metabolic activity, the blastocyst is actively taking up substances at this stage. This also implies that the uterine epithelium is secreting, although at a low rate. At the luminal surface of the uterine epithelium, however, tests for alkaline phosphatase and glucose-6-phosphatase reactions were negative.
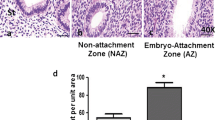
During early oestrogen-induced activation for implantation, uterine secretion was present in a moderate amount in the lumen and the blastocyst lay separated from the epithelial surface. The apical vesicles of the epithelial cells now also occupied the juxtaluminal layer of cytoplasm, which had previously been free of vesicles. The luminal part of the trophoblast cells still contained many endocytic vesicles. A positive reaction to the alkaline phosphatase test was seen at the epithelial cell surface between 4 and 8 h after injection of oestrogen and still persisted at 16 h. No positive reaction indicating glucose-6-phosphatase was seen. One single implantation site was found at the 16-h stage and this showed a positive reaction to the alkaline phosphatase test at the trophoblast-epithelial border in the embryonal part, but not abembryonically.
These findings suggest that a marked increase occurs in the secretory activity of the uterine epithelium only a few hours after initiation of blastocyst activation for implantation. Considering the mode of uterine control of blastocyst activity, the present results would seem to favour the view that the uterine control of implantation is dependent upon the amount and nutritional value of the uterine secretion made available to the blastocyst.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergström, S.: Experimentally delayed implantation. In: Methods in mammalian embryology (J.E. Daniels, ed.) (in press) New York: Academic Press 1977
Casanova, S., Marchetti, M., Bovina, C., Laschi, R.: A study of the effects of fixation on liver glucose-6-phosphatase activity for electron microscope cytochemistry. J. Submicr. Cytol. 4, 261 (1972)
Christie, G.A.: Implantation of the rat embryo: glycogen and alkaline phosphatases. J. Reprod. Fert. 12, 279 (1966)
Crane, R.K.: The substrate specificity of liver glucose-6-phosphatase. Biophys. Acta 17, 443 (1955)
Crane, R.K.: The substrate specificity of liver glucose-6-phosphatase. Biophys. Acta 17, 443 (1955)
Enders, A.C., Nelson, D.M.: Pinocytotic activity of the uterus of the rat. Am. J. Anat. 138, 277 (1973)
Ericsson, J.L.E., Biberfeld, P.: Studies on aldehyde fixation. Fixation rates and their relation to fine structure and some histochemical reactions in liver. Lab. Invest. 17, 281 (1967)
Fernley, H.: Mammalian alkaline phosphatases. In: The enzymes, vol. 4 (P.D. Boyer, ed.), p. 417. London, New York: Academic Press (1971)
Hall, K.: 5-nucleotidase acid phosphatase and phosphorylase during normal delayed and induced implantation of blastocysts in mice: a histochemical study. J. Endocr. 51, 291 (1971)
Holländer, H.: The section embedding (SE) technique. A new method for the combined light microscopy and electron microscopy of central nervous tissue. Brain Res. 20, 39 (1970)
Hugon, J., Borgers, M.: Ultrastructural localization of alkaline phosphatase activity in the absorbing cells of the duodenum of mouse. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 629 (1966)
Humphrey, K.W.: The induction of implantation in the mouse after ovariectomy. Steroids 10, 591 (1967)
Izquierdo, L., Marticorena, P.: Alkaline phosphatase in preimplantation mouse embryos. Exp. Cell Res. 92, 399 (1975)
Johnson, L.V., Calarccco, P.G., Siebert, M.: Alkaline phosphatase activity in the preimplantation mouse embryo. J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 40, 83 (1977)
Kanamura, S.: Sensitivity of glucose 6-phosphatase activity to glutaraldehyde. Histochem. 41, 257 (1975)
Leiser, R., Wille, K.-H.: Alkaline phosphatase in the bovine endometrium and trophblast during the early phase of implantation. Anat. Embryol. 148, 145 (1975)
Lundkvist, Ö., Ljungkvist, I.: Morphology of the rat endometrial stroma at the appearance of the Pontamine blue reaction during implantation after an experimental delay. Cell Tiss. Res. 184, 453 (1977)
McLaren, A.: Blastocyst activation. In: The regulation of mammalian reproduction (S.J. Segal, R. Crozier, P.A. Corfman and P.G. Condliffe, eds.), p. 321. Springfield: C. Thomas 1973
Menke, T.M.: Changes in mouse blastocyst carvon dioxid production as a function of time postcoitum in delay of implantation during lactation or following ovariectomy. Biol. Reprod. 7, 414 (1972)
Mulnard, J., Huygens, R.: Ultrastructural localization of non-specific alkaline phosphatase during cleavage and blastocyst formation in the mouse. J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 44, 121 (1978)
Nilsson, O.: Ultrastructure of the process of secretion in the rat uterine epithelium at preimplantation. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 40, 572 (1972)
Nilsson, O.: The morphology of blastocyst implantation. J. Repord. Fert. 39, 187 (1974)
Nilsson, B.O.: Ultrastructure of trophoblast-epithelium relationship during implantation in the mouse. In press (1978)
Nilsson, B.O., Östensson, C.-G., Eide, S., Hellerström, C.: Glucose in the mouse secretion as one important blastocyst nutrient at initiation of implantation. In press. Cell Tiss. Res.
Psychoyos, A.: Hormonal control of ovoimplantation. Vitam. Horm. 31, 201 (1973)
Psychoyos, A., Bitton-Casimir, V., Brun, J.L.: Repression and activation of the mammalian blastocyst. In: Regulation of growth and differentiated function in eukaryte cells, p. 509. New York: Raven Press 1975
Schlafke, S., Enders, A.C.: Protein uptake by rat preimplantation stage. Anat. Rec. 175, 539 (1973)
Surani, M.A.H.: Hormonal regulation of proteins in the uterine secretion of ovariectomized rats and the implications for implantation and embryonic diapause. J. Reprod. Fert. 43, 411 (1975)
Surani, M.A.H.: Uterine luminal proteins at the time of implantation in rats. J. Reprod. Fert. 48, 141 (1976)
Tice, L.W., Barrnett, R.J.: The fine structural localisation of glucose-6-phosphatase in rat liver. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 754 (1962)
Vordbrodt, A., Konwinksi, M., Solter, D., Koprowski, H.: Ultrastructural cytochemistry of membrane-bound phosphatases in preimplantation mouse embryos. Devl Biol. 55, 117 (1977)
Wachstein, M., Meisel, E.: On the histochemical demonstration of glucose-6-phosphatase. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 4, 592 (1956)
Webb, F.T.G., Surani, M.A.H.: Influence of environment on blastocyst proliferation, differentiation, and implantation. In: Regulation of growth and differentiated function in eukaryote cells. (G.P. Talwar, ed.), p. 60. New York: Raven Press 1975
Weitlauf, H.M.: Metabolic changes in blastocysts of mice and rats during delayed implantation. J. Reprod. Fert. 39, 213 (1974)
Weitlauf, H.M.: Factors in mouse uterine fluid that inhibit the incorporation of 3H-uridine by blastocysts in vitro. J. Reprod. Fert. 52, 321 (1978)
Weitlauf, H.M., Greenwald, G.S.: A comparison of 35S-methionine incorporation by the blastocysts of normal and delayed implanting mice. J. Reprod. Fert. 10, 203 (1965)
Yoshinaga, K., Adams, C.E.: Delayed implantation in the spayed, progesterone treated adult mouse. J. Reprod. Fert. 12, 593 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nilsson, B.O., Lundkvist, Ö. Ultrastructural and histochemical changes of the mouse uterine epithelium on blastocyst activation for implantation. Anat Embryol 155, 311–321 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317644
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317644