Abstract
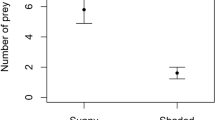
Population parameters of the orb-web spider Nephila clavata were estimated at two sites with different spider densities (for 2 successive years at the high density site and 1 year at the low density site), and the relationship between survival rate and feeding conditions was examined. The rate of decrease of population density was almost constant over time and nearly the same at the two sites. Daily survival rate (sum of the effects of mortality and emigration) was low during August to early September and increased markedly thereafter. Daily immigration rate (number of immigrants/number of residents) was high during August to early September. Since there were strong negative correlations between survival and immigration rates, low survival rate seems to be caused by a high rate of emigration. Strong positive correlations were found between survival rate and feeding frequency (mean percent observed feeding). Analysis of covariance revealed that the parameters of the regression between survival rate and feeding frequency did not differ significantly among three occasions. These results suggest that feeding condition has a significant influence on dispersal activity of populations in this spider.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JF (1974) Responses to starvation in the spiders Lycosa lenta Hentz and Filistata hibernalis (Hentz). Ecology 55:576–585
Edgar WD (1971) Seasonal weight changes, age structure, natality and mortality in the wolf spider Pardosa lugubris Walck in central Scotland. Oikos 22:84–92
Enders F (1974) Vertical stratification in orb-web spiders (Araneidae, Araneae) and a consideration of other methods of coexistence. Ecology 55:317–328
Gillespie RG, Caraco T (1987) Risk-sensitive foraging strategies of two spider populations. Ecology 68:887–899
Humphreys WF (1976) The population dynamics of an Australian wolf spider, Geolycosa godeffroyi (L. Koch 1985) (Arancae: Lycosidae). J Anim Ecol 45:59–80
Iwao S (1971) Dynamics of numbers of a phytophagous ladybeetle, Epilachna vigintioctomaculata, living in patchily distributed habitats. In: den Boer PJ, Gradwell GR (eds) Dynamics of populations. Proceedings of the advanced study institute on dynamics of numbers in populations. Oosterbeek, the Netherlands, pp 129–147
Juliano SA (1986) Food limitation of reproduction and survival for populations of Brachinus (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ecology 67:1036–1045
Kajak A (1967) Productivity of some populations of web spiders. In: Petrusewicz (ed) Secondary productivity of terrestrial ecosystems, Panstwowe Wydawn, Warsawa, pp 807–820
Kessler A (1973) A comparative study of the production of eggs in eight Pardosa species in the field (Araneae: Lycosidae). Tijdschr Entomol 116:23–41
Lawton JH (1971) Maximum and actual field feeding rates in larvae of the damselfly, Pyrrhosoma nymphula (Sulzer) (Odonata: Zygoptera). Freshw Biol 1:99–111
Lenski RE (1984) Food limitation and competition: a field experiment with two Carabus species. J Anim Ecol 53:203–216
Matsura T, Nagai S (1983) Estimation of prey consumption of a mantid, Paratenodera angustipennis (S.) in a natural habitat. Res Popul Ecol 25:298–308
Mcqueen DJ (1978) Field studies of growth, reproduction, and mortality in the burrowing wolf spider Geolycosa domifex (Hancock). Can J Zool 56:2037–2049
Miyashita K (1968) Growth and development of Lycosa T-insignita Boes et. Str. (Araneae: Lycosidae) under different feeding conditions. Appl Entomol Zool 3:81–88
Miyashita T (1990) Decreased reproductive rate of the spider, Nephila clavata, inhabiting small woodlands in urban areas. Ecol Res 5:341–351
Miyashita T (1991) Direct evidence of food limitation for growth rate and body size in the spider Nephila clavata. Acta Arachnol 40:17–21
Miyashita T (1992a) Variability in food consumption rate of natural populations in the spider, Nephila clavata. Res Popul Ecol 34: 15–28
Miyashita T (1992b) Food limitation of population density in the orb-web spider, Nephila clavata. Res Popul Ecol 34:143–153
Olive CW (1982) Behavioral response of a sit-and-wait predator to spatial variation in foraging gain. Ecology 63:912–920
Provencher L, Riechert SE (1991) Short-term effects of hunger conditioning on spider behavior, predation, and gain of weight. Oikos 62:160–166
Tanaka K (1989) Energetic cost of web construction and its effect on web relocation in the web-building spider Agelena limbata. Oecologia 81:459–464
Tanaka K (1991) Food consumption and diet composition of the web-building spider Agelena limbata in two habitats. Oecologia 86:8–15
Turnbull AL (1964) The search for prey by a web building spider, Achaearanea tepidariorum (Araneae: Theridiidae). Can Entomol 96:568–579
Vollrath F (1985) Web spider's dilemma: a risky move or site dependent growth. Oecologia 68:69–72
Wise DH (1975) Food limitation of the spider Linyphia marginata: experimental field studies. Ecology 56:637–646
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyashita, T. Feeding rate may affect dispersal in the orb-web spider Nephila clavata . Oecologia 92, 339–342 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317459
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317459