Summary
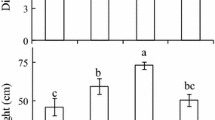
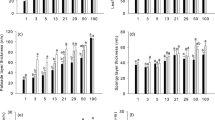
The photosynthetic response to sunflecks was investigated in the fern Polypodium virginianum growing on cliff edges of the Niagara Escarpment, in southern Ontario, Canada. Ferns were exposed to natural precipitation, continuous watering, or continuous drought prior to exposure to artificial sunflecks. The results were analyzed using temperature, humidity and previous exposure to light as covariates. The response to sunflecks was extremely rapid and showed no measurable induction period in the field. Controlled experiments completed in the laboratory showed exceptionally short induction periods. Previous exposure to sunflecks, and desiccation did not influence the time constants of response to sunflecks although drying did reduce maximum rates of CO2 exchange. Polypodium virginianum shows an extremely rapid response to fluctuations in the supply of light, and this is interpreted to be advantageous to this species because of the array of extremely hostile conditions that occur at cliff edges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett RM, Matthes-Sears U, Larson DW (1990) Organization of the Niagara Escarpment cliff community. II Characterization of the physical environment. Can J Bot 68:1931–1941
Björkman O, Powles SB (1984) Inhibition of photosynthetic reactions under waterstress: interaction with light level. Planta 161:490–504
Chazdon RL (1988) Sunflecks and their importance to forest understory plants. Advan Ecol Res 18:1–63
Chazdon RL, Fletcher N (1984) Photosynthetic light environments in a lowl and tropical rain forest in Costa Rica. J Ecol 72:553–564
Chazdon RL, Pearcy RW (1986a) Photosynthetic responses to light variation in rainforest species. I. Induction under constant and fluctuating light conditions. Oecologia 69:517–523
Chazdon RL, Pearcy RW (1986b) Photosynthetic responses to light variation in rainforest species. II. Carbon gain and photosynthetic efficiency during lightflecks. Oecologia 69:524–531
Dromgoole FI (1987) Photosynthesis of marine algae in fluctuating light. I. Adjustment of rate in constant and fluctuating light conditions. Func Ecol 1:377–386
Eickmeier WG (1983) Photosynthetic recovery of the resurrection plant Selaginella lepidophylla (Hook. and Grev.) Spring: effects of prior desiccation rate and mechanisms of desiccation damage. Oecologia 58:115–120
Elias P (1983) Water relations pattern of understory species influenced by sunflecks. Biol Plant 25:68–74
Grime JP (1979) Plant Strategies and Vegetation Processes. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Gross LJ (1982) Photosynthetic dynamics in varying light environments: a model and its application to whole leaf carbon gain. Ecology 63:84–93
Hicks DJ, Chabot BF (1985) Deciduous forest. In: Chabot BF, Mooney HA (ed) Physiological Ecology of North American Plant Communities. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 257–277
Kershaw KA (1985) Physiological ecology of lichens. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kirschbaum MUF, Pearcy RW (1988) Concurrent measurements of oxygen- and carbon-dioxide exchange during lightflecks in Alocasia macrorrhiza (L.) G.Don. Planta 174:527–533
Knapp AK, Smith WK (1987) Stomatal and photosynthetic responses during sun/shade transitions in subalpine plants: influence on water efficiency. Oecologia 74:62–67
Knapp AK, Smith WK. (1990) Stomatal and photosynthetic responses to variable sunlight. Physiol Plat 78:160–165
Larson DW, Spring SH, Matthes-Sears U, Bartlett RM (1989) Organization of the Niagara Escarpment cliff community. Can J Bot 67:2731–2742
Lellinger DB (1985) A field manual of the ferns and fern allies of the United States and Canada. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC, p 197
Lloyd RM, Lang FA (1964) The Polypodium vulgare complex in North Amercia. B Fern Gazz 9:168–177
Matthes-Sears U, Larson DW (1990) Environmental controls of carbon uptake in two woody species with contrasting distributions at the edge of cliffs. Can J Bot 68:2371–2380
Masarovicova E, Elias P (1986) Photosynthetic rate and water relations in some forest herbs in spring and summer. Photosynthetica 20:187–195
Pearcy RW (1987) Photosynthetic gas exchange responses of Australian tropical forest trees in canopy, gap and understory micro-environments. Func Ecol 1:169–178
Pearcy RW (1990) Sunflecks and photosynthesis in plant canopies. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 41:421–453
Pfitsch WA, Pearcy RW (1989a) Daily carbon gain by Adencaulon bicolor (Asteraceae), a redwood forest understory herb, in relation to its light environment. Oecologia 80:465–470
Pfitsch WA, Pearcy RW (1989b) Steady-state and dynamic photosynthetic response of Adencaulon bicolor (Asteraceae) in its red-wood forest habitat. Oecologia 80:471–476
Regehr DL, Bazzaz FA (1976) Low temperature photosynthesis in successional winter annuals. Ecology 57:1297–1303
SAS Institute Inc. (1986) SAS system for linear models, 1986 Edition. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC
SAS Institute Inc. (1988) SAS/STAT user's guide, Release 6.03 Edition. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC
Smith WK (1981) Temperature and water relation patterns in subalpine understory plants. Oecologia 48:353–359
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry. Freeman, San Fran
Weber JA, Jurik TW, Tenhunen JD, Gates DM (1985) Analysis of gas exchange in seedlings of Acer saccharum: integration of field and laboratory studies. Oecologia 65:338–347
Young DR, Smith WK (1983) Effect of cloudcover on photosynthesis and transpiration in the subalping understory species Arnica latifolia. Ecology 64:681–687
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gildner, B.S., Larson, D.W. Photosynthetic response to sunflecks in the desiccation-tolerant fern Polypodium virginianum . Oecologia 89, 390–396 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317417
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317417