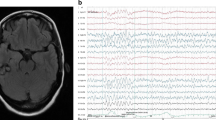
Summary
The clinical and pathological data of a 48 year old patient who survived 40 days are reported. Her disturbance of consciousness corresponded to an apallic syndrome, which 12 days later became akinetic mutism. Symmetrical softening involving the medial thalamic nuclei from the plane of the corpora mamillaria to the red nuclei was found. The ischemic lesion might be explained by transient circulatory collapse combined with hypoplasia of the vertebrobasilar arteries. On the EEG slight irregular alpha activity was recorded (alpha coma) and external stimuli elicited theta-delta waves (paradox activation). A survey of the literature of akinetic mutism is included and the correlation between non-hypnoid unconsciousness and EEG is discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Es wird ein Fall mit apallischem Syndrom mitgeteilt, der 12 Tage später in einem akinetischen Mutismus überging und 40 Tage überlebte. Die histopathologische Untersuchung ergab eine gut abgegrenzte Thalamuserweichung von den Corpora mamillaria bis zum Nucleus ruber, die durch eine allgemeinvaskuläre Insuffizienz, hervorgerufen durch ein kombiniertes Vitium und Hypoplasie des Vertebro-Basilaris-System, entstanden sein dürfte. Der EEG-Befund ergab eine fast regelmäßige Alpha-Tätigkeit („Alpha-Koma“) mit paradoxer Aktivation auf alle Außenreize. Anhand dieses Falles wird die Literatur über den akinetischen Mutismus kritisch gesichtet und der Zusammenhang zwischen EEG-Tätigkeit und nichthypnoiden Bewußtseinsstörungen behandelt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alajouanine, T.: Les altérations des états de conscience á partir de faits anatomo-cliniques. I. Congr. Int. Sci. Neurol. Acta Med. Belg., Bruxelles, pp. 42–48 (1957)
Brage, D., Morea, R., Coppello, A. R.: Syndrome nécrotique tegmento-thalamique avec mutisme akinetique. Rev. neurol. 104, 126–137 (1961)
Cairns, H.: Disturbance of consciousness with lesions of the brain-stem and diencephalon. Brain 75, 109–145 (1952)
Chatrian, G. E., White, L. E., Shaw Cheng-Mei: EEG pattern resembling wakefulness in unresponsive decerebrate state following traumatic brain stem infarct. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 16, 285–289 (1964)
Dolce, G., Fromm, H., Ionescu, A.: Reaktionspotentiale beim Apallischen Syndrom. Z. EEG-EMG 2, 95–100 (1972)
Facon, E., Steriade, M., Wertheim, N.: Hypersomnie prolongée engendrée par les lésions bilatérales du systéme activateur medial le syndrome thrombotique de la bifurcation du tronc basilaire. Rev. neurol. 98, 117–133 (1958)
Feldman, M. H.: Physiological observations in a chronic case of “locked in” syndrome. Neurology 21, 459–478 (1971)
Fischgold, H., Torrubio, H., Matis, P., Arfel-Capdevielle, G.: Reaction EEG d'éveil (arousal) dans le coma. Corrélation cortico-cardio-respiratoires. Presse med. 63, 1231 (1955)
French, J. D.: Brain lesion associatied with prolonged unconsciousness. Arch. Neur. Psychiat. 68, 727–740 (1952)
French, J. D., Magoun, H. W.: Effect of chronic lesions in central cephalic brain stem of monkeys. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 68, 591–604 (1951)
Gerstenbrandt, F.: Das traumatische apallische Syndrom. Wien-New York: Springer 1967
Hassler, R.: Funktionelle Neuroanatomie und Psychiatrie. In: Psychiatrie der Gegenwart. Vol. I/1A, pp. 152–285. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1967
Hawkes, C. H., Brian-Smith, L.: The electroencephalogram in the “locked-in” syndrome. Neurology 24, 1015–1018 (1974)
Ingvar, D. H., Braun, A.: Das komplette apallische Syndrom. Arch. Psychiat. Nervenkr. 215, 219–239 (1972)
Jellinger, K.: Neuropathologie anhaltender Bewußtseinstörungen. Ideggyógy. Szle. 29, 51–68 (1976)
Jellinger, K., Gerstenbrand, F., Pateinsky, K.: Die protrahierte Form der posttraumatischen Encephalopathie. Nervenarzt 34, 145–159 (1963)
Karp, J. S., Kurtig, H. I.: Locked-in state with bilateral midbrain infarcts. Arch. Neurol. 30, 176–178 (1974)
Ketz, E.: Die vertebro-basilaris-Thrombose im konventionellen EEG. Z. EEG-EMG 2, 36–43 (1971)
Klee, A.: Akinetic mutism: review of the literature and report of a case. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 133, 537–553 (1961)
Környey, St.: Histopathologie und klinische Symptomatologie der anoxisch-vasalen Hirnschädigungen, 2. Aufl. Budapest: Akad. Kiadó 1955
Kretschmer, E.: Das apallische Syndrom. Z. Neurol. 169, 575–579 (1940)
Kubiczki, St., Rieger, H., Busse, G., Barckow, D.: EEG-Befunde bei schweren Schlafmittelvergiftungen. Z. EEG-EMG 1, 80–93 (1970)
Lechi, A., Pilleri, G., Carreras, M.: Akinetic mutism due to glioma of the midline. Arch. Psychiat. Nervenkr. 220, 1–7 (1975)
Lhermitte, F., Gautier, J. C., Mateau, R., Chain, F.: Troubles de la conscience et mutisme akinetique. Rev. neurol. 109, 115–131 (1963)
Loeb, C.: Electroencephalographic changes during the state of coma. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 10, 589–606 (1958)
Marquardsen, J., Harwald, B.: The electroencephalogram in acute vascular lesions of the brain stem and the cerebellum. Acta neur. scand. 40, 58–78 (1964)
Messimy, R., DaLage, C., David, M., Harispe, L.: Mutisme akinétique avec rigidité cérébré par thrombose vertebro-basilaire. Rev. neurol. 115, 1015–1028 (1966)
Obrador, S., et al.: Comatose state maintained during eight years following a vascular pontomesencephalic lesion. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 38, 21–26 (1975)
Plum, F., Posner, J. B.: Fhd diagnosis of stupor and coma. Philadelphia: Davis 1972
Skultety, F. M.: Clinical and experimental aspects of akinetic mutism. Arch. Neurol. 19, 1–14 (1968)
Tucker, J. S.: The electroencephalogram in brainstem vascular disease. J. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 10, 405–416 (1958)
Westmoreland, B. F., Klass, D. W., Sharbrough, F. W., Reagan, T. J.: Alpha coma. Arch. Neurol. 32, 713–718 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Professor Dr. St. Környey zum 75. Geburtstag gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szirmai, I., Guseo, A. & Molnár, M. Bilateral symmetrical softening of the thalamus. J. Neurol. 217, 57–65 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316317
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316317