Summary
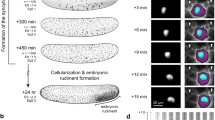
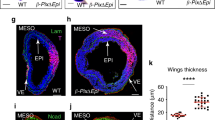
Connecting cords are elongated telophase bridges persisting between separating daughter cells. We have studied them with Scanning Electron Microscopy in the upper cell layer of the quail blastoderm where a high mitotic activity accompanied by interkinetic nuclear migration coincides with morphogenetic movements. The predominant orientation of the connecting cords is parallel to the direction of the morphogenetic movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allenspach AL, Roth LE (1967) Structural variations during mitosis in the chick embryo. J Cell Biol 33:179–196
Andries L, Vakaet L, Vanroelen C (1983) The dorsal surface of the animal pole of the just laid quail egg, studied with SEM. Anat Embryol 166:135–147
Bancroft M, Bellairs R (1974) The onset of differentiation in the epiblast of the chick blastoderm (SEM and TEM). Cell Tissue Res 155:399–418
Bancroft M, Bellairs R (1977) Placodes of the chick embryo studied by SEM. Anat Embryol 154:97–108
Bellairs R, Bancroft M (1975) Midbodies and beaded threads. Am J Anat 143:393–398
Bellairs R, Breathnach AS, Gross M (1975) Freeze-fracture replication of junctional complexes in unincubated and incubated chick embryos. Cell Tissue Res 162:235–252
Buck RC, Ohara PT, Daniels WH (1976) Intercellular bridges of chick blastoderm studied by Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy. Experientia 32:505–506
Buck RC, Tisdale JM (1962) The fine structure of the mid-body of the rat erythroblast. J Cell Biol 13:109–115
Derrick GE (1937) An analysis of the early development of the chick embryo by means of mitotic index. J Morph 61:257–284
Flemming W (1891) Neue Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Zelle. Arch Microsc Anat 37:685
Fujita S (1962) Kinetics of cellular proliferation. Exp Cell Res 28:52–60
Jacob HJ, Christ B, Jacob M, Bijvank GJ (1974) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) studies on the epiblast of young chick embryos. Z Anat Entwickl Gesch 143:205–214
Langman J, Guerrant RL, Freeman BG (1966) Behaviour of neuroepithelial cells during closure of the neural tube. J Comp Neurol 127:399–412
Meier S (1979) Development of the embryonic chick otic placode. II: Electron microscopic analysis. Anat Rec 191:459–478
Nägele RG, Lee HY (1979) Ultrastructural changes in cells associated with interkinetic nuclear migration in the developing chick neuroepithelium. J Exp Zool 210:89–106
Nägele RG, Lee HY (1980) A transmission and scanning electron microscopic study of cytoplasmic threads of dividing neuroepithelial cells in early chick embryos. Experientia 36:338–340
Sauer F (1935) Mitosis in the neural tube. J Comp Neurol 62:377–405
Sauer F (1936) The interkinetic migration of embryonic epithelial nuclei. J Morphol 60:1–11
Schoenwolf G (1982) On the morphogenesis of the early rudiments of the developing central nervous system. Scanning electron microscopy I:289–308
Schoenwolf G (1983) The chick epiblast: a model for examining epithelial morphogenesis. Scanning electron microscopy III:1371–1385
Spratt NT Jr (1952) Localization of the prospective neural plate in the early chick blastoderm. J Exp Zool 120:109–130
Vakaet L (1970) Cinemicrographic investigations of gastrulation in the chick blastoderm. Arch Biol 81:387–426
Vakaet L (1984) Early development in birds. In: Le Douarin N, McLaren A (eds) Chimeras in developmental biology. Academic Press, London, pp 71–88
Vanroelen C, Vakaet L (1981) The effect of the osmolality of the buffer solution of the fixative on the visualization of microfilament bundles in the chick blastoderm. J Submicrosc Cytol 13:89–93
Waterman RE (1976) Topographical changes along the neural fold associated with neurulation in the hamster and mouse. Am J Anat 146:151–172
Watterson RL (1965) Structure and mitotic behavior of the early neural tube. In: De Haan, Ursprung (eds) Organogenesis, Holt, Rinehart & Winston, New York, pp 129–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by Grant no. 3.9001.81 of the Belgian Fund for Medical Scientific Research (F.G.W.O.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Everaert, S., Espeel, M., Bortier, H. et al. Connecting cords and morphogenetic movements in the quail blastoderm. Anat Embryol 177, 311–316 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315838
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315838