Summary
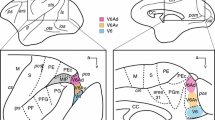
The nucleus ventralis lateralis (VL) and ventralis anterior (VA) thalami have been studied with the electron microscope following lesions of the cerebral cortex and of the nucleus entopeduncularis which represents the homologue of the medial pallidal segment in primates.
It has been confirmed that VL receives a substantial number of afferents from the motor cortex, while cortical fibers to VA originate mainly rostral to the precruciate gyrus. Corticofugal fibers terminate in VL/VA as type SR boutons (Rinvik and Grofová, 1974a) and establish synapses with relay cell dendrites and with vesicle-containing dendrites.
Four to five days following large lesions of the entopeduncular nucleus an electron-lucent form of degeneration occurs in one type of boutons in VL. These boutons are greatly swollen and vesicle-depleted, and contain altered mitochondria, an increased number of glycogen particles, irregular membrane structures and vacuoles. Some of the electron-lucent boutons progress into electron-dense forms at later survival times. Boutons showing these degenerative changes establish symmetrical synapses with relay cell dendrites and/or cell bodies. They do not synapse upon vesicle-containing dendrites and they are never engaged in the VL glomeruli. It is concluded that they belong to the type F1 boutons (Rinvik and Grofová, 1974a).
Similar initial electron-lucent changes are seen in boutons in the nucleus centrum medianum (CM) ipsilateral to the entopeduncular lesions. No evidence was found for a projection from the entopeduncular nucleus to VA.
The findings are discussed with regard to relevant morphological and physiological data in the literature. Particular attention is paid to the interaction at the cellular level in VL between afferents from the intracerebellar nuclei, motor cortex and globus pallidus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alksne, J. F., Blackstad, Th. W., Walberg, F., White Jr., L. E.: Electron microscopy of axon degeneration: A valuable tool in experimental neuroanatomy. Ergebn. Anat. 39, 32 pp. (1966)
Andersen, P., Eccles, J. C., Sears, T. A.: The ventro-basal complex of the thalamus: Types of cells, their responses and their functional organization. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 174, 370–399 (1964)
Anderson, C. A., Westrum, L. E.: An electron microscopic study of the normal synaptic relationship and early degenerative changes in the rat olfactory tubercle. Z. Zellforsch. 127, 462–482 (1972)
Angaut, P.: Etude anatomique expérimentale des efférences cérébelleuses ascendantes. Analyse électro-anatomique des projections cérébelleuses sur le noyau ventral latéral du thalamus. 186 pp. Thesis, Paris 1969
Carpenter, M. B.: Comparisons of the efferent projections of the globus pallidus and substantia nigra in the monkey. In: Efferent organization and the integration of behavior (Maser, J. D., ed.), p. 137–174. New York and London: Academic Press 1973
Carpenter, M. B., Strominger, N. L.: Efferent fiber projections of the subthalamic nucleus in the rhesus monkey. A comparison of the efferent projections of the subthalamic nucleus, substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Amer. J. Anat. 121, 41–72 (1967)
Desiraju, T., Purpura, D. P.: Synaptic convergence of cerebellar and lenticular projections to thalamus. Brain Res. 15, 544–547 (1969)
Dormont, J. F., Ohye, C.: Entopeduncular projection to the thalamic ventrolateral nucleus of the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 12, 254–264 (1971)
Fox, C. A., Hillman, D. E., Siegesmund, K. A., Sether, L. A.: The primate globus pallidus and its feline and avian homologues: A Golgi and electron microscopic study. In: Evolution of the forebrain (R. Hassler and H. Stephen, eds.), p. 237–248. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme 1966
Frigyesi, T. L., Machek, J.: Basal ganglia-diencephalon synaptic relations in the cat. I. An intracellular study of dorsal thalamic neurons during capsular and basal ganglia stimulation. Brain Res. 20, 201–217 (1970)
Frigyesi, T. L., Rabin, A.: Basal ganglia-diencephalon synaptic relations in the cat. III. An intracellular study of ansa lenticularis, lenticular fasciculus and pallidosubthalamic projection activities. Brain Res. 35, 67–87 (1971)
Frigyesi, T. L., Schwartz, R.: Cortical control of thalamic sensorimotor relay activities in the cat and the squirrel monkey. In: Corticothalamic projections and sensorimotor activities (T. Frigyesi, E. Rinvik and M. D. Yahr, eds.), p. 161–191. New York: Raven Press 1972
Gentschev, T., Sotelo, C.: Degenerative patterns in the ventral cochlear nucleus of the rat. Brain Res. 62, 37–60 (1973)
Gray, E. G., Guillery, R. W.: Synaptic morphology in the normal and degenerating nervous system. Int. Rev. Cytol. 19, 111–182 (1966)
Grofová, I.: Ansa and fasciculus lenticularis of Carnivora. J. comp. Neurol. 138, 195–208 (1970)
Harding, B. N.: An ultrastructural study of the centre median and ventrolateral thalamic nuclei of the monkey. Brain Res. 54, 335–340 (1973a)
Harding, B. N.: An ultrastructural study of the termination of afferent fibres within the ventrolateral and centre median nuclei of the monkey thalamus. Brain Res. 54, 341–346 (1973b)
Hassler, R.: Über die afferenten Bahnen und Thalamuskerne des motorischen Systems des Großhirns. II. Mitt. Weitere Bahnen aus Pallidum, Ruber, vestibulären System zum Thalamus; Übersicht und Besprechung der Ergebnisse. Arch. Psychiat. Nervenkr. 182, 786–818 (1949)
Hassler, R.: Spezifische und unspezifische Systeme des menschlichen Zwischenhirns. In: Progress in brain research, vol. 5, Lectures on the diencephalon (W. Bargmann and J. P. Schadé, eds.), p. 1–32. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1964
Hassler, R.: Hexapartition of inputs as a primary role of the thalamus. In: Corticothalamic projections and sensorimotor activities (T. Frigyesi, E. Rinvik and M. D. Yahr, eds.), p. 551–578. New York, Raven Press 1972
Holländer, H., Line Vaaland, J.: A reliable staining method for semithin sections in experimental neuroanatomy. Brain Res. 10, 120–126 (1968)
Jasper, H., Ajmone-Marsan, C.: A stereotaxic atlas of the diencephalon of the cat. University of Toronto Press, published by The National Research Council of Canada 1954
Jones, E. G., Rockel, A. J.: Observations on complex vesicles, neurofilamentous hyperplasia and increased electron density during terminal degeneration in the inferior colliculus. J. comp. Neurol. 147, 93–118 (1973)
Kievit, J., Kuypers, H. G. J. M.: Fastigial cerebellar projections to the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus and the organization of the descending pathways. In: Corticothalamic projections and sensorimotor activities (T. Frigyesi, E. Rinvik and M. D. Yahr, eds.), p. 91–124. New York: Raven Press 1972
Kuo, J.-S., Carpenter, M. B.: Organization of pallidothalamic projections in the Rhesus Monkey. J. comp. Neurol. 151, 201–236 (1973)
Marshall, K. C., McLennan, H.: The synaptic activation of neurones of the feline ventrolateral thalamic nucleus: possible cholinergic mechanisms. Exp. Brain Res. 15, 472–483 (1972)
Mehler, W. R.: Connections of the basal ganglia and of the cerebellum. Confin. neurol. (Basel), in press (1974)
Nauta, W. J. H., Mehler, W. R.: Projections of the lentiform nucleus in the monkey. Brain Res. 1, 3–42 (1966)
Olszewski, J.: The thalamus of the Macaca Mulatta. An Atlas for use with the stereotaxic instrument, p. 93. Basel-New York: S. Karger 1952
O'Neal, J. T., Westrum, L. E.: The fine structural synaptic organization of the cat lateral cuneate nucleus. A study of sequential alterations in degeneration. Brain Res. 51, 97–124 (1973)
Purpura, D. P.: Synaptic mechanisms in coordination of activity in thalamic internuncial common paths. In: Corticothalamic projections and sensorimotor activities (T. Frigyesi, E. Rinvik and M. D. Yahr, eds.), p. 21–51. New York: Raven Press 1972
Purpura, D. P., Frigyesi, T. L., McMurtry, J. G., Scarff, T.: Synaptic mechanisms in thalamic regulation of cerebello-cortical projection activity. In: The thalamus (D. P. Purpura and M. D. Yahr, eds.), p. 153–170. New York: Columbia University Press 1966
Purpura, D. P., Scarff, T., McMurtry, J. G.: Intracellular study of internuclear inhibition in ventrolateral thalamic neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 487–496 (1965)
Rinvik, E.: Organization of thalamic connections from motor and somatosensory cortical areas in the cat. In: Corticothalamic projections and sensorimotor activities (T. Frigyesi, E. Rinvik and M. D. Yahr, eds.), p. 57–88. New York: Raven Press 1972
Rinvik, E., Grofová, I.: Light and electron microscopical studies of the normal nuclei ventralis lateralis and ventralis anterior thalami in the cat. (1974a, in press)
Rinvik, E., Grofová, I.: Cerebellar projections to the nuclei ventralis lateralis and ventralis anterior thalami. Experimental electron microscopical and light microscopical studies in the cat. (1974b, in press)
Sakata, H., Ishijima, T., Toyoda, Y.: Single unit studies on ventro-lateral nucleus of thalamus in cats: its relation to the cerebellum, motor cortex and basal ganglia. Jap. J. Physiol. 16, 42–60 (1966)
Scheibel, M. E., Scheibel, A. B.: The organization of the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus. A Golgi study. Brain Res. 1, 250–268 (1966)
Strick, P. L.: Light microscopic analysis of the cortical projection of the thalamic ventrolateral nucleus in the cat. Brain Res. 55, 1–24 (1973)
Uchizono, K.: Characteristics of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central nervous system of the cat. Nature 207, 642–643 (1965)
Westrum, L. E.: Early forms of terminal degeneration in the spinal trigeminal nucleus following rhizotomy. J. Neurocytol. 2, 189–215 (1973)
Westrum, L. E., Black, R. G.: Changes in the synapses of the spinal trigeminal nucleus after ipsilateral rhizotomy. Brain Res. 11, 706–709 (1968)
Westrum, L. E., Black, R. G.: Fine structural aspects of the synaptic organization of the spinal trigeminal nucleus (pars interpolaris) of the cat. Brain Res. 25, 265–287 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grofová, I., Rinvik, E. Cortical and pallidal projections to the nucleus ventralis lateralis thalami. Anat Embryol 146, 113–132 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315589
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315589