Summary
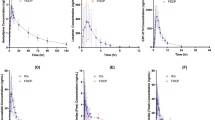
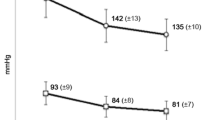
This study investigated potential therapeutic differences between Amlodipine 5 mg and Felodipine ER 10 mg in 12 normotensive/borderline hypertensive subjects by comparison of the plasma drug concentration-time profiles and the blood pressure and heart rate responses.
There was significantly less trough-to-peak variability in plasma drug concentrations with amlodipine with a ratio of 67%, compared to 37% for felodipine. Correspondingly there was less variability with amlodipine in the blood pressure reductions across the dosage interval. Overall, amlodipine displayed a more consistent hypotensive effect across 24 hours and lower blood pressure values at trough, i. e. 24 hours post-dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernethy DR, Schwartz JB (1988) Pharmacokinetics of calcium antagonists under development. Clin Pharmacokinet 15: 1–4
Landmark K (1985) Antihypertensive and metabolic effects of longterm therapy with nifedipine slow-release tablets. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 7: 12–17
Abrahamsson B, Alpsten M, Hugosson M, Töll J, Åberg J (1989) A combined gastro-intestinal transit and absorption study on felodipine extended release tablets. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36 [Suppl]: A.95
Blychert E (1992) Felodipine pharmacokinetics and plasma concentration v effect relationships. Blood Pressure [Suppl]2: 1–30
Meredith PA, Elliott HL (1992) Clinical pharmacokinetics of amlodipine. Clin Pharmacokinet 22: 22–31
Faulkner JK, McGibney D, Chasseaud LF, Perry JL, Taylor IW (1986) The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine in healthy volunteers after single intravenous and oral doses and after 14 repeated oral doses given once daily. Br J Clin Pharmacol 22: 21–25
Beresford AP, Macrae PV, Stopher DA, Wood BA (1987) Analysis of amlodipine in human plasma by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr Biomed App 420: 178–183
Ahnoff M (1984) Determination of felodipine in plasma by capillary gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J Pharmaceut Biomed Analysis 2: 519–526
Rose M, McMahon FG (1990) Some problems with antihypertensive drug studies in the context of the new guidelines. Am J Hyper 3: 151–155
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, Danhof M, Urquart J, Breimer DD (1987) Rate of increase in the plasma concentration of nifedipine as a major determinant of its haemodynamic effect in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 41: 26–30
Donnelly R, Elliott HL, Meredith PA, Reid JL (1988) Nifedipine: individual responses and concentration-effect relationships. Hypertension 12: 443–449
Blychert E, Edgar B, Elmfeldt D, Hedner T (1992) Plasma concentration-effect relationships for felodipine: a meta analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 52: 80–89
Donnelly R, Meredith PA, Howie CA, Elliott HL (1993) Pharmacodynamic modelling of the antihypertensive response to amlodipine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 54: 303–310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bainbridge, A.D., Herlihy, O., Meredith, P.A. et al. A comparative assessment of amlodipine and felodipine ER: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic indices. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45, 425–430 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315513
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315513