Summary
The effects of dexmedetomidine (DXM), a novel α2-adrenoceptor agonist, on human performance and mood were studied in a double-blind randomized crossover study in 12 healthy student volunteers. Single IM doses of dexmedetomidine, 0.6 μg/kg (DXM1) and 1.2 μg/kg (DXM2), 80 μg/kg midazolam (MID) and saline placebo, were given at one-week intervals. Performance was measured objectively and mood was assessed subjectively with visual analogue scales (VAS) at baseline and 40 min, 2 h, 4 h and 6 h after each injection. Blood pressure and heart rate in the sitting position were measured and venous blood was sampled during each testing round.
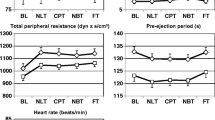
DXM1 did not significantly impair cognitive (digit symbol substitution), coordinative (tracking) or reactive skills, and at 6 h it shortened reaction time and reduced errors in complex tracking. It produced exophoria, increased body sway with the eyes open and impaired subjective performance on VAS. The higher dose dexmedetomidine also caused impaired cognitive, coordinative and reactive skills (although a trend towards improved coordination was found at 6 h), reduced attention, produced exophoria, increased body sway with the eyes open and caused drowsiness, clumsiness, passiveness and mental slowness on the appropriate VAS scales. MID resembled DXM2 in impaired objective and subjective measures of skilled performance, although the objective effects of MID were of speedier onset and shorter duration. In contrast to MID, DXM caused a significant and dose-dependent decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure still detectable 6 h after injection.
It is concluded that IM DXM produces dose related impairment of skilled performance and produces subjective sedation, the effects of 1.2 μg/kg being comparable to those produced by 80 μg/kg MID, although the latter lasted for a shorter period and were not associated with haemodynamic changes. Since the effect of DXM on performance waned earlier than its haemodynamic actions, DXM may constitute a suitable preanaesthetic medication, particularly in hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aantaa R, Kanto J, Scheinin M, Kallio A, Scheinin H (1990) Dexmedetomidine, an α2-adrenoceptor agonist, reduced anesthetic requirements for patients undergoing minor gynecologic surgery. Anesthesiol 73: 230–235
Aho M, Lehtinen A-M, Erkkola O, Kallio A, Korttila K (1991) The effect of intravenously administered dexmedetomidine on perioperative hemodynamics and isoflurane requirements in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Anesthesiol (in press)
Bond A, Lader MH (1974) The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47: 211–218
Brogden RN, Goa KL (1988) Flumazenil. A preliminary review of its benzodiazepine antagonist properties, intrinsic activity and therapeutic use. Drugs 35: 448–467
Charney DS, Heninger GR, Redmond DE (1983) Yohimbine induced anxiety and increased noradrenergic function in humans: effects of diazepam and clonidine. Life Sci 33: 19–29
Flacke JW, Bloor BC, Flacke WE, Wong D, Dazza S, Stead SW, Laks H (1987) Reduced requirement by clonidine with improvement hemodynamic and adrenergic stability in patients undercoing coronary bypass surgery. Anesthesiol 67: 909–917
Frith CD, Dowdy J, Ferrier IN, Crow TJ (1985) Selective impairment of paired associate learning after administration of a centrally-acting adrenergic agonist (clonidine). Psychopharmacol 87: 490–493
Firth CD, McGinty MA, Gergel I, Crow TJ (1989) The effects of scopolamine and clonidine upon the performance and learning of a motor skill. Psychopharmacol 98: 120–125
Garratt JC, Marsden CA (1980) Effect of chronic idazoxan on dorsal raphe nucleus 5-HT neuronal firing. Eur J Pharmacol 183/5: 1911–1912
Ghignone M, Calvillo O, Quintin L (1987) Anesthesia and hypertension: the effect of clonidine on perioperative hemodynamics and isoflurane requirements. Anesthesiol 67: 3–10
Hannington-Kiff JG (1970) Measurements of recovery from outpatient general anaesthesia with simple ocular test. Br Med J 3: 132–135
Heizman P, Ziegler WH (1981) Excretion and metabolism of 14C-midazolam in humans following oral dosing. Arzneim-Forsch (Drug Res) 31 (II): 2200–2223
Hindmarch I (1982) Critical flicker fusion frequency (CFF): the effects of psychotropic compounds. Pharmacopsychiat 15 [Suppl 1]: 44–48
Kallio A, Scheinin M, Koulu M, Ponkilainen R, Ruskoaho H, Viinamäki O, Scheinin H (1989) Effects of dexmedetomidine, a selective α2-adrenoceptor agonist, on hemodynamic control mechanism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46: 33–42
Karhuvaara S, Kallio A, Scheinin M, Anttila M, Salonen JS, Scheinin H (1990) Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics of atipamezole, a novel α2-adrenoceptor antagonist — a randomized, double-blind crossover study in healthy male volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 30: 97–106
Karlsson JOG (1988) Alpha2-adrenoceptors controlling fish pigment cells. Linköping University Medical Dissertations No. 266, Linköping, Sweden
Lammintausta R, Uyeno E, Hollister LE, Csernansky JG (1986) A selective alpha-2-agonist, medetomidine, shows anxiolytic effects in the rat approach/avoidance conflict test. Abstracts ACNB meeting, Washington DC, p 205
Linnavuo M, Ylilääkkölä P, Mattila MJ, Mäki M, Seppälä T (1987) A new device to measure drug-induced changes of reactive and coordinative skills related to driving. Pharmacol Toxicol 61: 142–147
Linnoila M, Guthrie S, Lister R (1986) Mechanism of drug-induced impairment of driving. In: O'Hanlon JF, deGier JJ (eds) Drugs and driving. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 29–49
MacDonald E, Scheinin H, Scheinin M (1988) Behavioural and neurochemical effects of medetomidine, a novel veterinary sedative. Eur J Pharmacol 158: 119–127
Mattila M (1989) Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies on actions and interactions of benzodiazepines on human psychomotor performance. Academic Dissertation, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
Mattila MJ, Saarialho-Kere U, Mattila M (1988) Acute effect of sertraline, amitriptyline, and placebo on the psychomotor performance of healthy subjects over 50 years of age. J Clin Psychiat 49 [Suppl 8]: 52–58
Richelson E (1984) Neuroleptic affinities for human brain receptors and their use in predicting adverse effects. J Clin Psychiat 45: 331–336
Savolainen K, Linnavuo M (1979) Effects of m-xylene on human equilibrium measured with a quantitative method. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 44: 315–318
Scheinin M, Kallio A, Koulu M, Viikari J, Scheinin H (1987) Sedative and cardiovascular effects of medetomidine, a novel selective alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 24: 443–451
Scheinin H, Virtanen R, MacDonald E, Lammintausta R, Scheinin M (1989) Medetomidine — a novel α2-adrenoceptor agonist: a review of its pharmacodynamic effects. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 13 (no 5). Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 635–651
Stein L (1980) Behavioural neurochemistry of benzodiazepines. Arzneim Forsch (Drug Res) 30, Nr 5a: 868–873
Stone BI (1974) Pencil and paper tests — sensitivity to psychotropic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 18: 15S-20S
Subhan Z, Hindmarch I (1983) The effects of midazolam in conjunction with alcohol on ikonic memory and free-recall. Neuropsychobiol 9: 230–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattila, M.J., Mattila, M.E., Olkkola, K.T. et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on human performance and mood. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41, 217–223 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315433
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315433