Summary
The effect of an analogue of atrial natriuretic peptide (P-ANP) on glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), urinary flow rate, urinary sodium excretion, tubular function estimated by the lithium clearance technique, and plasma levels of sodium and water homeostatic hormones, has been studied in 40 healthy males. Placebo or P-ANP 0.3, 1.5, or 3.0 μg·kg−1 bwt were given as an intravenous bolus injection to different groups.
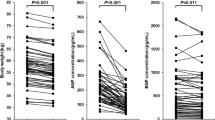
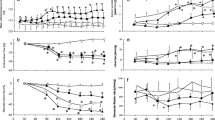
P-ANP did not cause any immediate change in GFR or RPF, but significant dose-dependent increases in filtration fraction, urinary flow rate and urinary excretion rate of sodium were detected during the first 30 min after administration. Proximal absolute and fractional tubular reabsorption and distal absolute tubular reabsorption of sodium did not change after injection of P-ANP, while the distal fractional reabsorption of sodium was reduced in a dose dependent manner during the first 30 min.
Plasma angiotensin II and aldosterone were significantly increased 30 and 150 min after dosage, whereas plasma atrial natriuretic peptide, plasma arginine vasopressin, and urinary excretion of prostaglandin E2 were unchanged. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate both in plasma and urine were increased in a dose-dependent manner.
P-ANP cause a significant reduction in diastolic blood pressure and an increase in pulse rate. Two subjects had vasovagal syncope 30–60 min after injection of P-ANP.
It is concluded that P-ANP has natriuretic, diuretic and hypotensive properties in healthy man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biollaz J, Bidiville J, Diezi J, Waeber B, Nussberger J, Brunner-Ferber F, Gomez HJ, Brunner HR (1987) Site of the action of a synthetic atrial natriuretic peptide evaluated in humans. Kidney Int 32: 537–546
Bolli P, Müller FB, Linder L, Raine AEG, Resink TJ, Erne P, Kiowski W, Ritz R, Bühler FR (1987) The vasodilator potency of atrial natriuretic peptide in man. Circulation 75: 221–228
Christensen P, Leyssac PP (1976) A specific radioimmunoassay for u-PGE2, using an antibody with high specificity and a sephadex LH-20 microcolumn for separation of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins 11: 399–420
Cody RJ, Atlas SA, Laragh JH, Kubo SH, Covit AB, Ryman KS, Shaknovich A, Pondolfino K, Clark M, Camargo MJF, Scarborough RM, Lewicki JA (1986) Atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and heart failure patients. Plasma levels and renal, hormonal, and hemodynamic responses to peptide infusion. J Clin Invest 78: 1362–1374
Cuneo RC, Espiner EA, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG, Livesey JH (1987) Effect of physiological levels of atrial natriuretic peptide on hormone secretion: inhibition of angiotensin-induced aldosterone secretion and renin release in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65: 765–772
Ferrier C, Beretta-Piccoli C, Weidmann P, Gnädinger MP, Shaw S, Suchecka-Rachon K, Saxenhofer H (1989) Hypotension and renal impairment during infusion of atrial natriuretic factor in liver cirrhosis with ascites. Am J Nephrol 9: 291–299
Jespersen B, Eiskjær H, Pedersen EB (1990) Effect of atrial natriuretic peptide on blood pressure, guanosine 3′:5′-cyclic monophosphate release and blood volume in uraemic patients. Clin Sci 78: 67–73
Kappelgaard AM, Nielsen MD, Giese J (1976) Measurement of angiotensin II in human plasma: technical modification and practical experience. Clin Chim Acta 67: 299–306
Koepke JP, DiBona GF (1987) Blunted natriuresis to atrial natriuretic peptide in chronic sodium-retaining disorders. Am J Physiol 252: F865-F871
Mogensen CE (1971) Glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow in short-term and long-term juvenile diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 28: 91–100
Pedersen EB, Danielsen H, Spencer ES (1984) Effect of indapamid on renal plasma flow, glomerular filtration rate, and arginine-vasopressin in plasma in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26: 543–547
Rask-Madsen J, Bruunsgaard A, Munck O, Nielsen MD, Worming H (1974) The significance of bile acids and aldosterone for the electrical hyperpolarization of human rectum in obese patients treated with intestinal by-pass operation. J Gastroenterol 9: 417–426
Schiffrin EL (1988) Decreased density of binding sites for atrial natriuretic peptide on platelets of patients with severe congestive heart failure. Clin Sci 74: 213–218
Schultz HD, Gardner DG, Deschepper CF, Coleridge HM, Coleridge JCG (1988) Vagal C-fiber blockade abolishes sympathetic inhibition by atrial natriuretic factor. Am J Physiol 255: R6-R13
Shionoiri H, Kaneko Y (1985) Intranasal administration of alpha-human natriuretic peptide produces a prolonged diuresis in healthy man. Life Sci 38: 773–778
Solomon LR, Atherton JC, Bobinski H, Hillier V, Green R (1988) Effect of low dose infusion of atrial natriuretic peptide on renal function in man. Clin Sci 75: 403–410
Thomassen AR, Bagger JP, Nielsen TT, Pedersen EB (1987) Atrial natriuretic peptide during pacing in controls and patients with coronary arterial disease. Int J Cardiol 17: 267–276
Thomsen K (1984) Lithium clearance: a new method for determining proximal and distal tubular reabsorption of sodium and water. Nephron 37: 217–223
Veldkamp PJ, Carmines PK, Inscho EW, Navar LG (1988) Direct evaluation of the microvascular actions of ANP in juxtamedullary nephrons. Am J Physiol 254: F440-F444
Volpe M, Mele AF, Indolfi C, Deluca N, Lembo G, Focaccio A, Condorelli M, Trimarco B (1987) Hemodynamic and hormonal effects of atrial natriuretic factor in patients with essential hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 10: 787–793
Weidmann P, Hasler L, Gnädinger MP, Lang RE, Uehlinger DE, Shaw S, Rascher W, Reubi FC (1986) Blood levels and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal man. J Clin Invest 77: 734–742
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eiskjær, H., Schmiegelow, M., Jespersen, B. et al. Renal and hormonal effects and tolerance of an ANP analogue in healthy man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41, 547–554 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314983
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314983