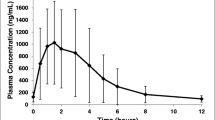
Summary
7 patients with end-stage renal disease on regular haemodialysis were treated orally with a loading dose of 200 mg ofloxacin and multiple maintenance doses of 100 mg per 24 h for 10 days. The pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin and its metabolites were studied at the end of the treatment period. Plasma and dialysate concentrations of ofloxacin and ofloxacin metabolites were measured by HPLC.
Peak (3.1 mg·1−1) and trough levels (1.6 mg·1−1) and the AUC of ofloxacin were comparable to the values in healthy volunteers given 300 to 400 mg ofloxacin p.o. The mean half-life, determined in the dialysis-free interval (t1/2β) and during the haemodialysis session (t1/2HD), was 38.5 h and 9.9 h, respectively. Extrarenal clearance (32.7 ml·min−1) was unchanged as compared to that reported in healthy volunteers after a single dose of ofloxacin. The fractional removal by haemodialysis amounted to 21.5%. Two metabolites, ofloxacin-N-oxide and demethyl-ofloxacin, were detected in plasma. Despite prolonged t1/2β of both metabolites (66.1 and 50.9 h) and multiple doses of ofloxacin the peak concentrations of the metabolites reached only 14% and 5% of that of the parent drug, respectively.
It is concluded that in patients on regular haemodialysis treatment the dosage adjustment employed resulted in safe and therapeutically favourable plasma concentrations. The observed accumulation of ofloxacin metabolites does not appear to have any toxic or therapeutic significance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monk JP, Campoli-Richards DM (1987) Ofloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 33: 346–391
Lode H, Höffken G, Olschewski P, Sievers B, Kirch A, Borner K, Koeppe P (1987) Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin after parenteral and oral administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31: 1338–1342
Borner K, Lode H (1986) Biotransformation von ausgewählten Gyrasehemmern. Infection 14 [Suppl 1]: S54-S59
Fillastre JP (1988) Quinolones and renal failure. Quinol Bull 4: 1–8
Gutzler F (1987) Vergleichende Untersuchungen zu den unterschiedlichen chromatographischen Nachweismethoden der Gyrase-Hemmer und ihrer Metaboliten in Körperflüssigkeiten und Geweben. Fortschr antimikr antineoplast Chemother 6–10: 1897–1906
Lee ChC, Marbury TC (1984) Drug therapy in patients undergoing haemodialysis. Clinical pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet 9: 42–66
Fillastre JP, Leroy A, Humbert G (1987) Ofloxacin pharmacokinetics in renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31: 156–160
Höffler D, Koeppe P (1987) Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin in healthy subjects and patients with impaired renal function. Drugs 34 [Suppl 1]: 51–55
Dagrosa EE, Verho M, Malercyk V, de Looze S, Hajdu P (1986) Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin, a new broad spectrum antimicrobial agent. Clin Ther 8: 632–645
Maher JF (1987) Influence of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis on elimination of drugs. Perit Dial Bull 7: 159–167
Dagrosa EE, Verho M, Malercyk V (1986) Pharmakokinetik von Ofloxacin. In: Adam D, Knothe H, Lode H, Stille W (eds) Ofloxacin. FAC 5-5. Futuramed, München
White LO, MacGowan AP, Lovering AM, Reeves DS, Mackay IG (1987) A preliminary report on the pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin, desmethyl ofloxacin and ofloxacin N-oxide in patients with chronic renal failure. Drugs 34 [Suppl 1]: 56–61
Verho M, Dagrosa EE, Malercyk V (1986) Klinische Pharmakologie von Ofloxacin: Ein neues Chemotherapeutikum aus der Reihe der Gyrasehemmer. Infection 14 [Suppl 1]: S47-S53
Phillips I, King A, Shannon K (1988) In vitro properties of the quinolones. In: Andriole VT (ed) The Quinolones. Academic Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kampf, D., Borner, K. & Pustelnik, A. Multiple dose kinetics of ofloxacin and ofloxacin metabolites in haemodialysis patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42, 95–99 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314927
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314927